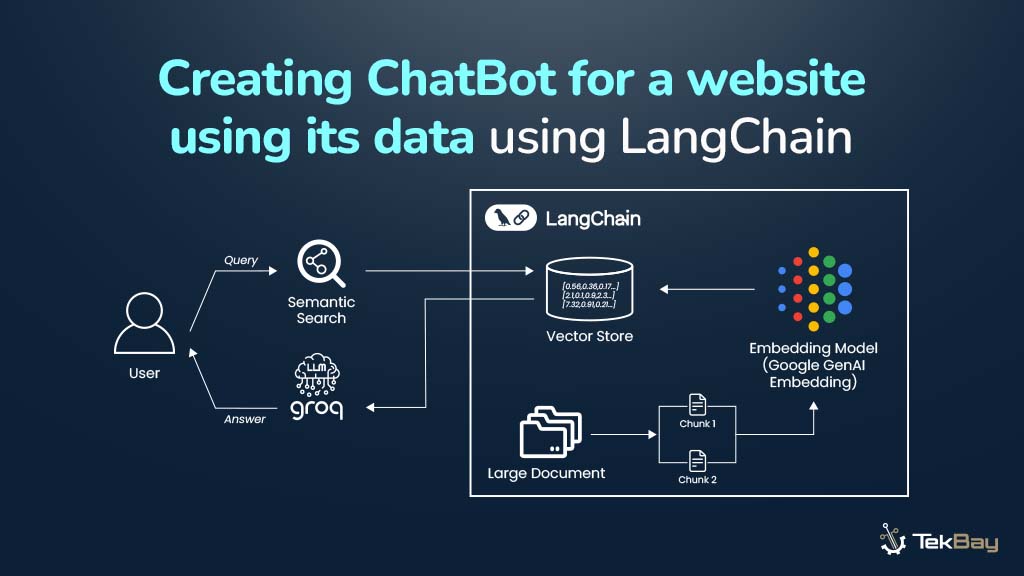
Chatbots are transforming the way users interact with websites and services, helping them navigate content and find answers quickly. Yet, traditional chatbots often fall short due to generic responses, slow replies, and a limited understanding of the site’s content.
To overcome these limitations, a chatbot needs efficient content retrieval, workflow orchestration, and intelligent inference, which is exactly what LangChain and Groq provide. LangChain manages LLM workflows, handles document processing, and structures data retrieval, while Groq provides low-latency inference, generating fast and accurate answers.
This guide explains how to build a Website Q&A Chatbot that understands a site and delivers real-time answers, guiding the process from content preparation to deployment.
Prerequisites
The following are required to build the Website Q&A Chatbot:
- Python 3.10+
- Familiarity with FastAPI and Streamlit
- API keys for Google Generative AI and Groq
- Access to the website content for scraping
- Python libraries:
pip install pymupdf langchain langchain-core langchain-community langchain-text-splitters langchain-google-genai langchain-groq python-dotenv faiss-cpu fastapi uvicorn streamlit httpxProject Setup
A clear project structure helps maintain organization and simplifies development. Here is the recommended layout:
chatbot-project/ ├── app/ │ ├── faiss_index/ # FAISS vector index files │ ├── vectorstore_loader.py # Script to load vector store │ ├── chatbot_api.py # FastAPI backend │ ├── chatbot_ui.py # Streamlit frontend (optional) ├── data/ │ └── website_content.pdf # Cleaned website content ├── .env # API keys ├── website_content.html # Raw HTML content ├── requirements.txt # All dependencies ├── vectorstore_builder.py # Script to build FAISS vector store
The .env file should contain the API keys:
GOOGLE_API_KEY=your_google_api_key
GROQ_API_KEY=your_groq_api_keySteps to Create the Website Q&A Chatbot
Step 1: Creating the Vector Store
The first step is to convert website content into a searchable vector store that the chatbot can query. This involves scraping content, cleaning it, splitting it into chunks, generating embeddings, and storing them in FAISS.
1.1. Scrape Website Content
Download the website content as HTML:
curl <https://www.website.com/> > website_content.htmlClean the content to remove headers, footers, scripts, or unnecessary elements. Convert the cleaned content into Markdown or PDF for processing. The final result is exported as a PDF and saved in the data/ folder.
1.2. Load Content into LangChain Documents
Parse the cleaned PDFs into LangChain Document objects, storing both text and metadata such as page number and file source, creating a structured format ready for splitting and embedding.
This functionality is implemented in vectorstore_builder.py using PyMuPDF (fitz), which efficiently extracts text from each PDF page.
import fitz # PyMuPDF
from langchain_core.documents import Document
import os
def load_pdf_bytes(pdf_path: str) -> list[Document]:
with open(pdf_path, "rb") as f:
content = f.read()
pdf_doc = fitz.open(stream=content, filetype="pdf")
docs = []
for i in range(pdf_doc.page_count):
text = pdf_doc[i].get_text()
if text.strip():
docs.append(Document(
page_content=text,
metadata={"source": os.path.basename(pdf_path), "page": i + 1}
))
pdf_doc.close()
return docs1.3. Split Text for Better Processing
Break each document into smaller, overlapping chunks to improve retrieval accuracy and maintain context across long documents. LangChain’s RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter can be used to break down the text into chunks of a specified size.
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1000, # Maximum number of characters per chunk
chunk_overlap=200 # Number of overlapping characters between chunks
)
chunks = splitter.split_documents(all_docs)1.4. Generate Embeddings
After splitting the text into manageable chunks, convert each chunk into vector embeddings using Google Generative AI. These embeddings capture the semantic meaning of the text, enabling AI models to understand and retrieve relevant information efficiently.
from langchain_google_genai import GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
embeddings = GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings(
model="models/embedding-001",
google_api_key=os.getenv("GOOGLE_API_KEY")1.5 Store Embeddings in a Vector Database
After generating embeddings, store them in a vector database for efficient retrieval. FAISS (Facebook AI Similarity Search) is used to store and query embeddings, enabling fast semantic search across large documents.
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
import os
vectorstore = FAISS.from_documents(chunks, embeddings)
index_path = "app/faiss_index"
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(index_path), exist_ok=True)
vectorstore.save_local(index_path) # Save the vector store locally
print(f"Vectorstore saved to '{index_path}/'")1.6 Automating the Workflow
To make the entire process efficient, automate parsing multiple PDFs, splitting text, generating embeddings, and building the FAISS vector store. This ensures consistency and saves time when working with large document collections.
The process_folder function handles all these steps for a folder of PDFs:
def process_folder(folder_path: str, index_path="app/faiss_index"):
"""Automate the process of parsing PDFs, splitting, embedding, and saving the vector store."""
all_docs = []
for filename in os.listdir(folder_path):
if filename.lower().endswith(".pdf"): # Process only PDF files
full_path = os.path.join(folder_path, filename)
docs = load_pdf_bytes(full_path)
all_docs.extend(docs)
if not all_docs:
raise ValueError(f"No PDF files found in '{folder_path}' or all PDFs are empty.")
chunks = splitter.split_documents(all_docs) # Split documents into chunks
embeddings = generate_embeddings() # Generate embeddings
vectorstore = build_and_save_vectorstore(chunks, embeddings, index_path) # Build and save the vectorstore
return vectorstore
## Main execution
if __name__ == "__main__":
vectorstore = process_folder("data") # Run the process for the PDFs in the "data" folderStep 2: Creating the Q/A Chatbot
With the vector store ready, let’s build a chatbot by loading the FAISS index, creating a retrieval-based QA chain with Groq’s LLM, and setting up a FastAPI backend.
2.1 Load the Vector Store
Once the FAISS vector store has been built and saved, it can be loaded into memory for querying. This allows the FastAPI backend to access the vector store and perform queries using Groq’s models. The following code is used to load it from vectorstore_loader.py:
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain_google_genai import GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
embeddings = GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings(
model="models/embedding-001",
google_api_key=os.getenv("GOOGLE_API_KEY")
)
def load_vectorstore(path="app/faiss_index"):
return FAISS.load_local(path, embeddings, allow_dangerous_deserialization=True) 2.2 Create a Retrieval-Based QA Chain
Groq provides free access to LLMs with low-latency inference. This guide uses the llama-3.1-8b-instant model to create a retrieval-based QA chain that searches the FAISS vector store and generates answers. The following code is implemented in chatbot_api.py :
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain_groq import ChatGroq
import os
def get_qa_chain(vectorstore):
llm = ChatGroq(
groq_api_key=os.getenv("GROQ_API_KEY"),
model_name="llama-3.1-8b-instant"
)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_type="similarity", search_kwargs={"k": 3})
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
retriever=retriever,
)
return qa_chain2.3 Set Up the FastAPI Backend
A FastAPI backend is created to serve the chatbot. Incoming POST requests with a question are processed by the Groq-powered QA chain, which returns the generated answer. The following code is placed in chatbot_api.py:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain_groq import ChatGroq
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from app.vectorstore_loader import load_vectorstore
import os
load_dotenv()
app = FastAPI()
def get_qa_chain(vectorstore):
llm = ChatGroq(
groq_api_key=os.getenv("GROQ_API_KEY"),
model_name="llama-3.1-8b-instant"
)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_type="similarity", search_kwargs={"k": 3})
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
retriever=retriever,
)
return qa_chain
vectorstore = load_vectorstore()
qa_chain = get_qa_chain(vectorstore)
class Query(BaseModel):
question: str
@app.post("/chat")
async def chat(query: Query):
result = qa_chain(query.question)
return {
"answer": result["result"],
}Run the FastAPI server with
uvicorn app.chatbot_api:app --reloadOnce running:
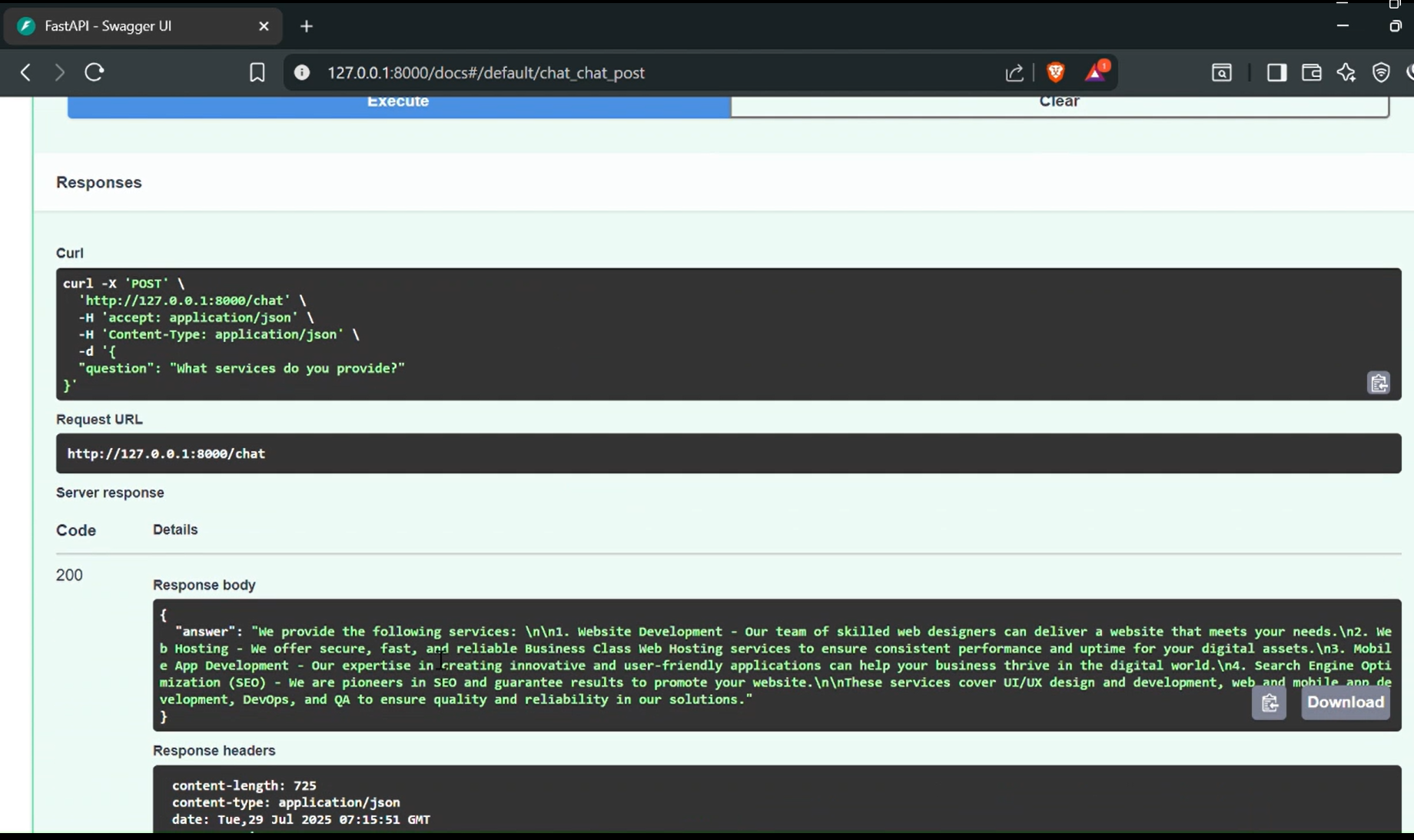
- POST requests can be sent to
http://localhost:8000/chatwith the question in JSON format. - The server responds with an answer generated by Groq’s model based on the indexed content.
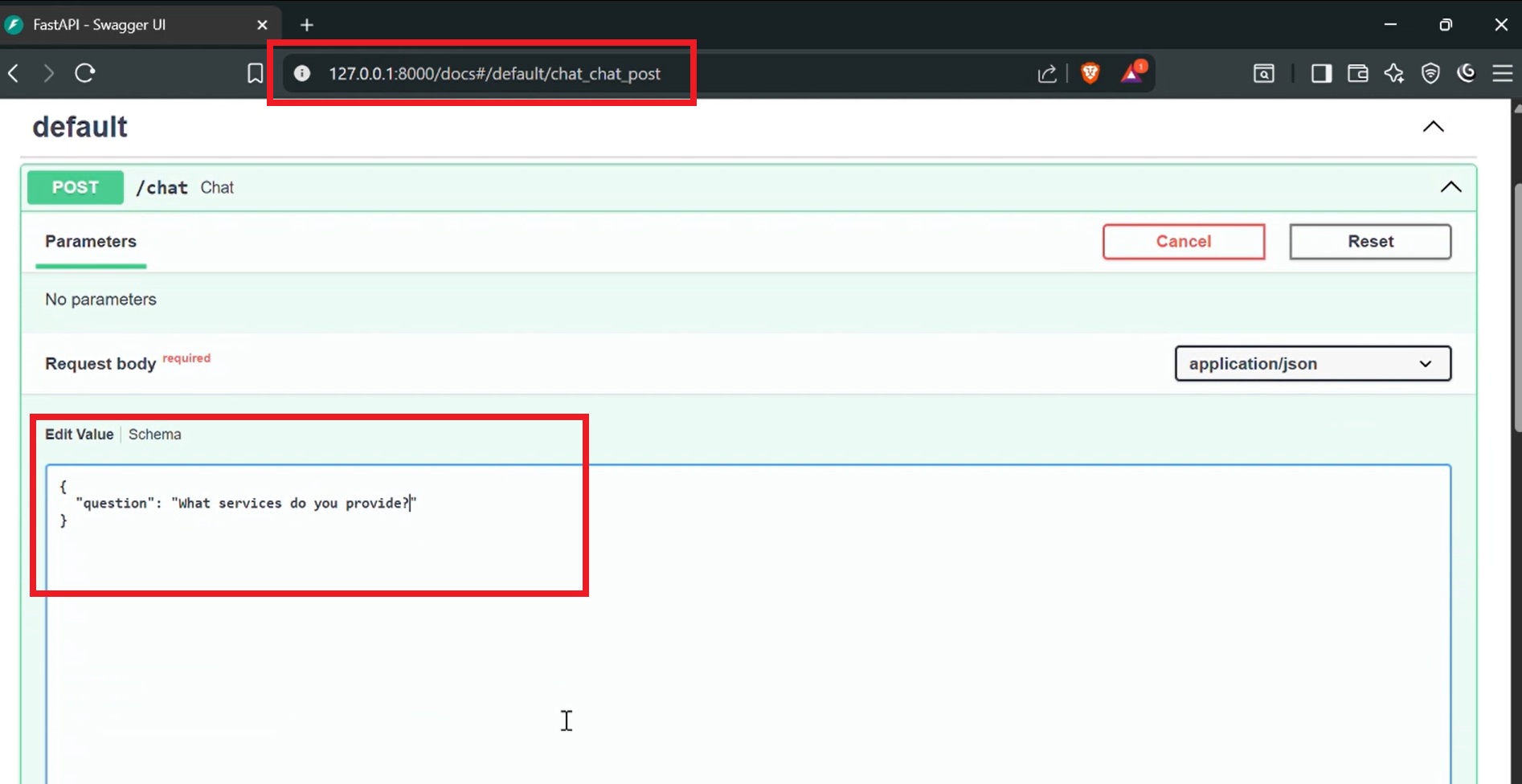
- Swagger UI is available at
http://localhost:8000/docsfor interactive API testing and documentation.
Step 3: Add a Streamlit Frontend (Optional)
For a user-friendly interface, a Streamlit app can be added on top of the FastAPI backend. This simple UI lets users type questions and instantly see answers generated by the chatbot.
import streamlit as st
import requests
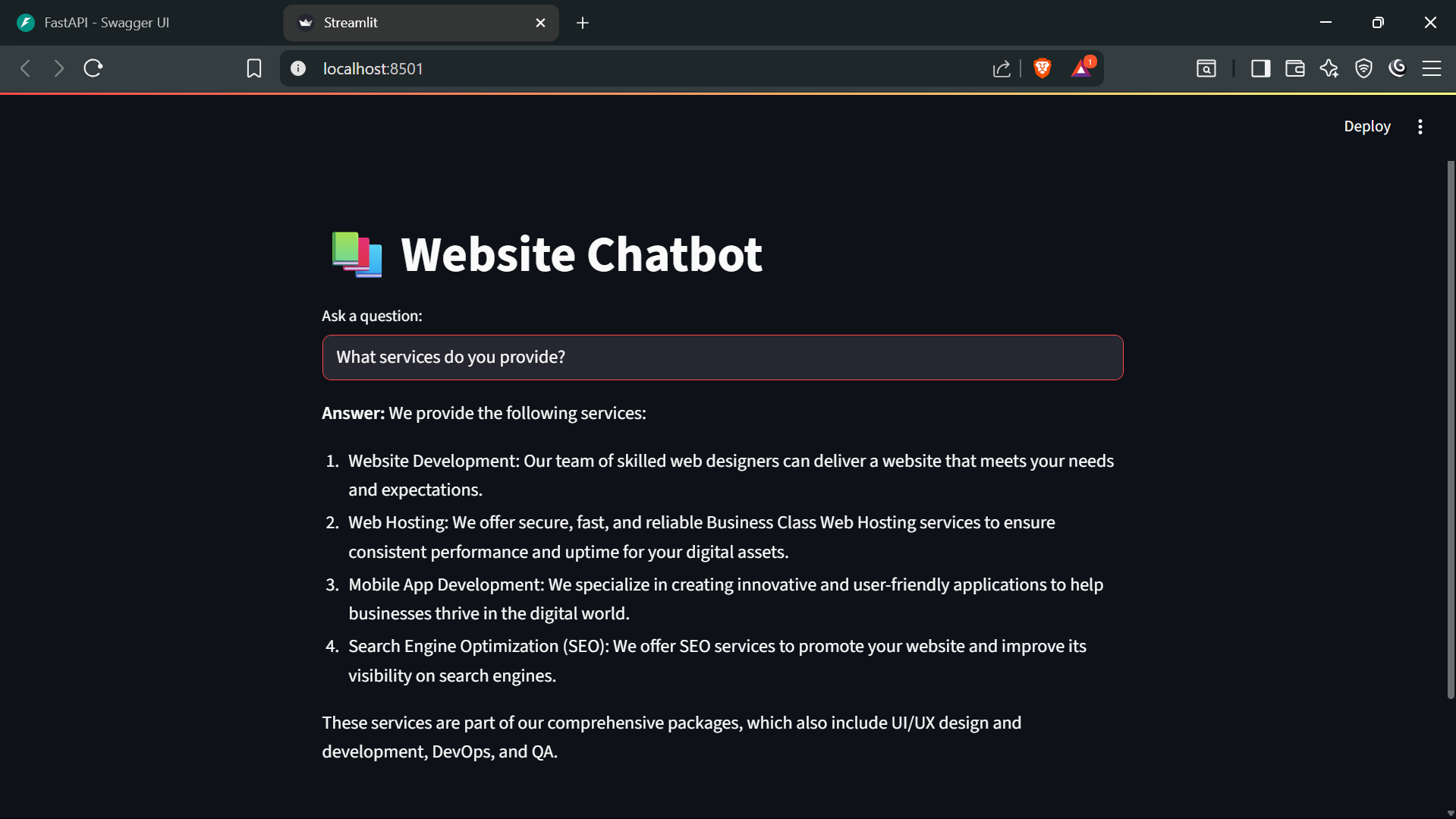
st.title("📚 Website Chatbot")
query = st.text_input("Ask a question:")
if query:
with st.spinner("Thinking..."):
response = requests.post("<http://localhost:8000/chat>", json={"question": query})
data = response.json()
st.write("**Answer:**", data["answer"])Run the backend first:
uvicorn app.chatbot_api:app --reloadThen launch the frontend:
streamlit run app/chatbot_ui.pyOnce the UI is running, questions can be entered, and the system queries the FastAPI backend, which uses the Groq model to generate the responses.
Conclusion
The website’s Q&A chatbot enables users to ask questions and receive answers directly from the site’s content. It combines a vector store, Google Generative AI embeddings, and Groq’s LLM to retrieve relevant information efficiently. With an optional Streamlit frontend, users can interact through a simple interface, showing a practical way to turn website content into an accessible, queryable system.