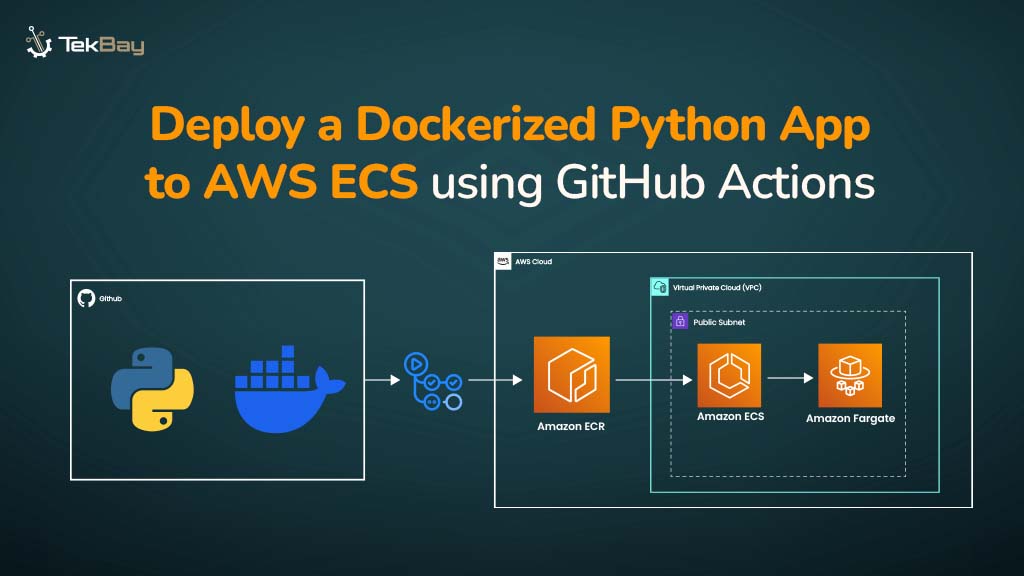
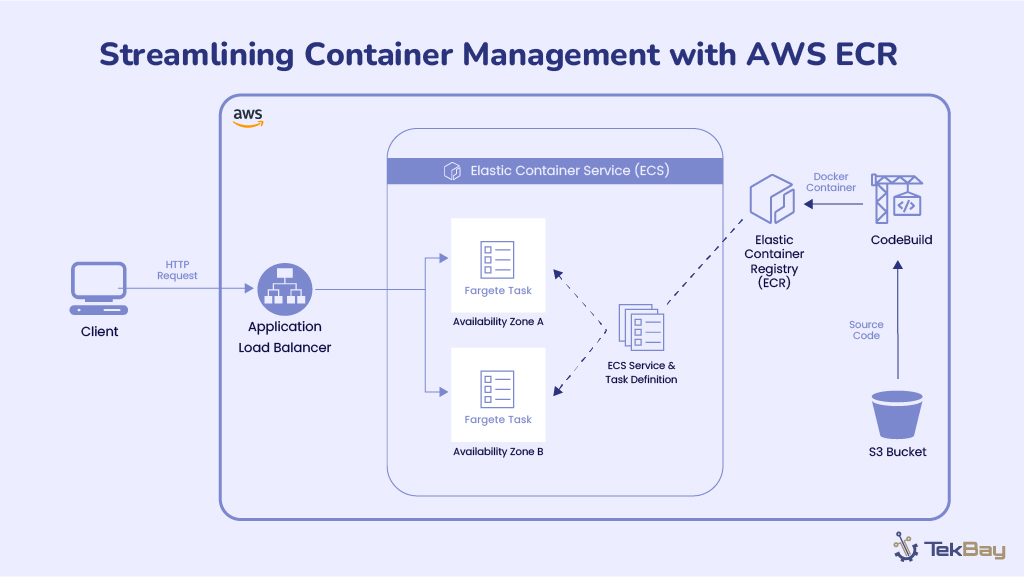
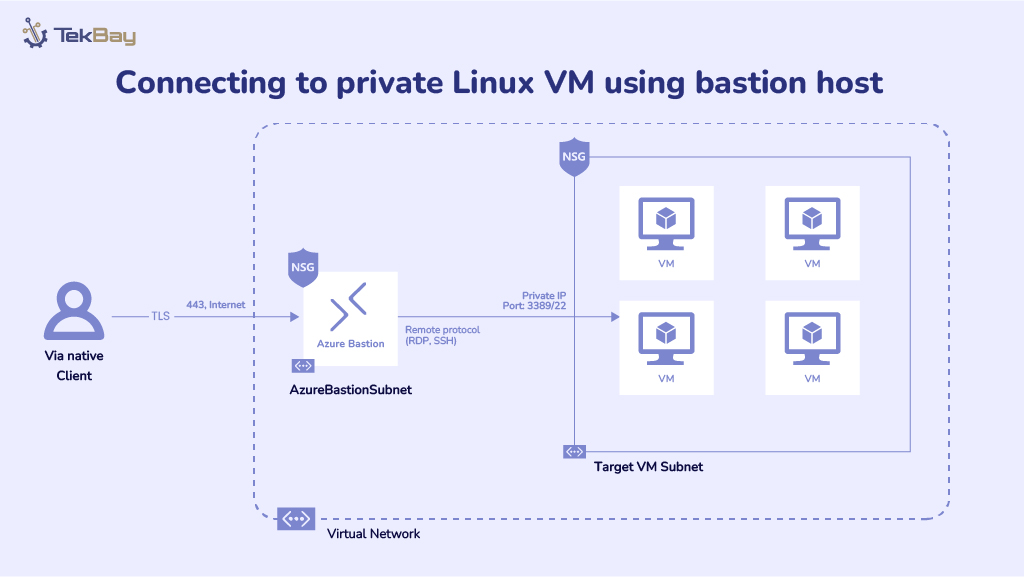
Amazon Web Services (AWS) powers millions of businesses worldwide with flexible, scalable cloud infrastructure. However, as AWS adoption grows, so do the challenges of managing and optimizing cloud spending.
According to Flexera’s State of Cloud Report 2025, the estimated wasted cloud spend on IaaS and PaaS was 27% and the wasted software spend in public cloud was 24%. For AWS users, wasted spend isn’t just a budgeting concern; it’s lost potential for innovation and growth. Thankfully, AWS offers built-in tools to track usage, rightsize resources, and reduce costs automatically.
This guide explores practical strategies and AWS-native tools to help you control costs and maximize cloud value.
Why AWS Cost Optimization Matters?
AWS cost optimization focuses on aligning cloud strategy with business outcomes, maximizing resource efficiency, and reducing unnecessary expenses. Selecting appropriate instances, rightsizing workloads, and utilizing AWS tools can lower bills and ensure predictable costs. For example, Spot Instances can save up to 90%, while Savings Plans can reduce costs by up to 72% compared to On-Demand pricing.
Its key benefits include:
- Operational Efficiency: Eliminate waste from idle or over-provisioned resources.
- Predictable Budgeting: Avoid surprises with better cost visibility.
- Scalability: Reinvest savings to scale the business or experiment with new ideas.
Understanding Where Costs Come From
AWS costs typically fall into three main buckets:
1. Compute Costs
Compute costs arise from services like EC2, Lambda, ECS, and Fargate, which power applications, serverless functions, and containerized workloads. These costs escalate when instances are oversized for their workloads, left running during low-demand periods, or misconfigured in autoscaling groups, leading to unnecessary expenses.
For example, an EC2 instance running 24/7 at low CPU utilization can cost hundreds of dollars monthly, while proper autoscaling could cut this significantly. Running too many instances unnecessarily further inflates bills. Common issues include:
- Oversized or underutilized instances
- Always-on instances with low usage
- Poorly tuned autoscaling
- Running excessive instances
2. Storage Costs
Storage costs stem from services like Amazon S3 for object storage, EBS for block storage, Glacier for archival, and EFS for file systems. These can accumulate rapidly when data is stored in expensive tiers (e.g., S3 Standard instead of Glacier), or when unused snapshots, unattached EBS volumes, or forgotten AMIs linger. For instance, retaining old snapshots can add thousands annually to bills. Proper lifecycle policies and tier management are critical to control costs. Common issues include:
- Unused snapshots
- Misconfigured storage classes
- Forgotten AMIs and unattached volumes
- Inefficient S3 storage management
3. Data Transfer Costs
Data transfer costs are incurred when moving data between AWS services, across regions, or to the internet, often referred to as bandwidth or egress fees. These costs can spike with frequent inter-region data replication, heavy internet-facing traffic (e.g., serving large files globally), or underutilized CDNs like Amazon CloudFront, which could reduce egress by caching data closer to users.
For example, transferring 1TB across regions monthly can cost $90-$200. Strategic region selection and CDN usage are key to minimizing these fees. Common issues include:
- Inter-region transfers
- Internet-facing traffic
- Poor CDN implementation
- Unoptimized data transfers
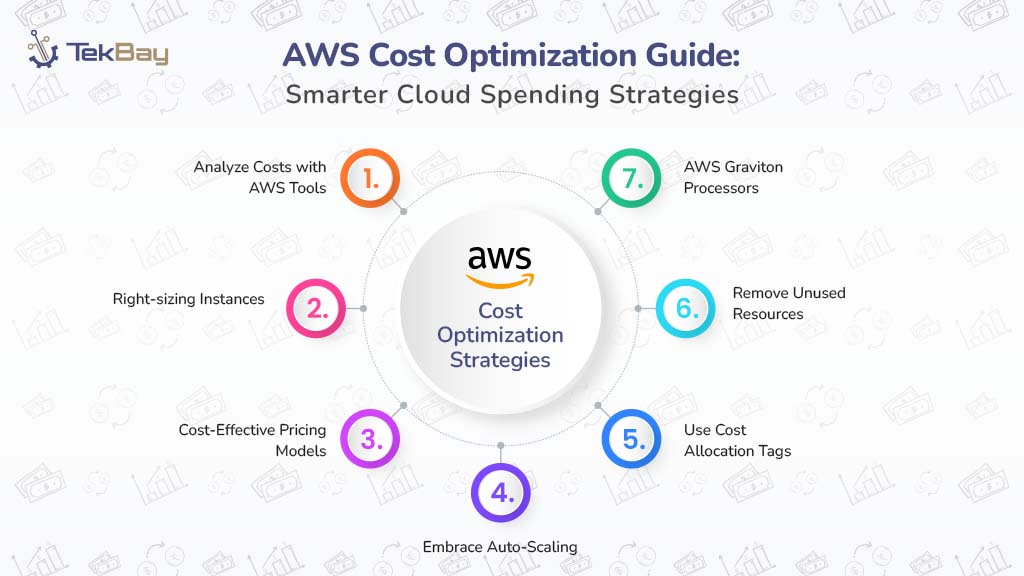
Proven AWS Cost Optimization Strategies
Here are proven strategies to reduce the AWS bill, backed by powerful tools and best practices.
1. Analyze Costs with AWS Tools
To track and analyze usage, AWS provides native tools like:
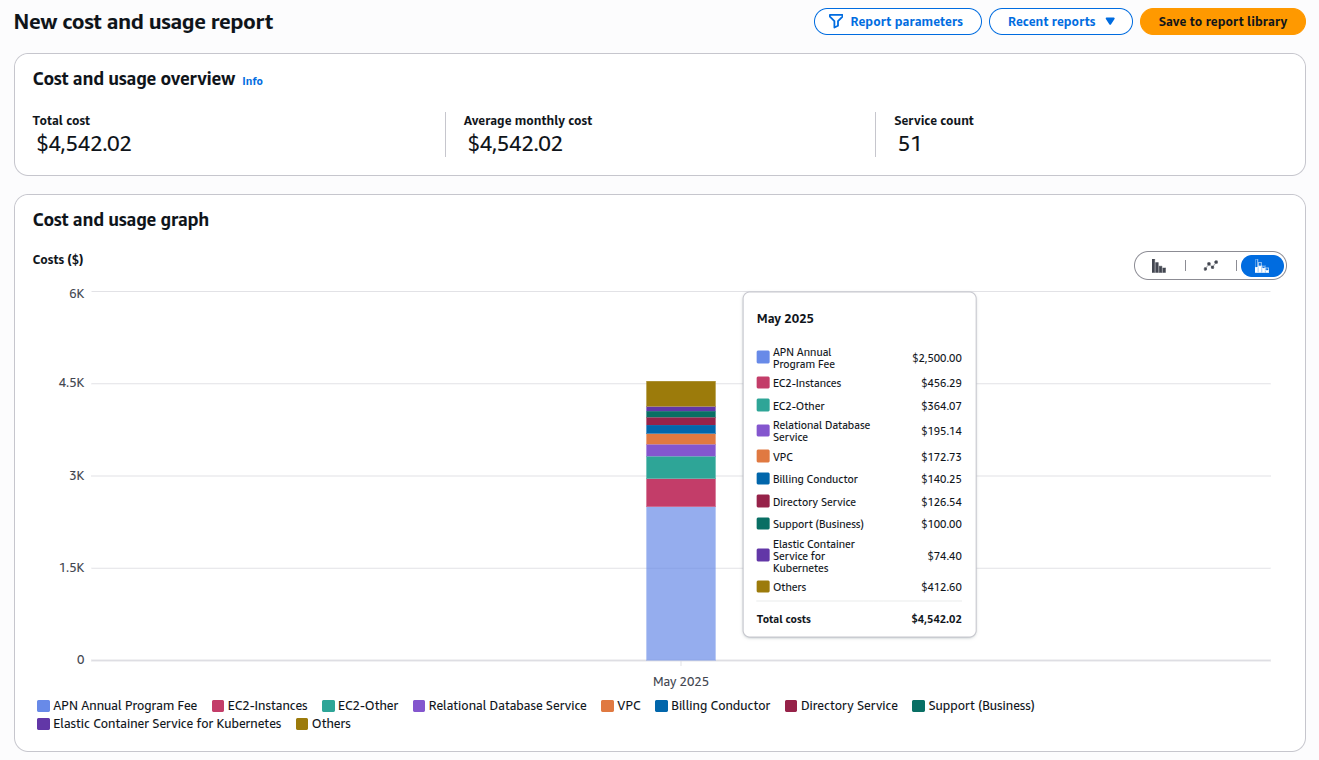
- AWS Cost Explorer: Visualize historical spending, forecast future costs, and identify trends by service, region, or tag. It’s free for basic features like monthly cost trends and Reserved Instance (RI) recommendations.
- AWS Cost and Usage Report (CUR): Offers detailed insights into usage patterns, ideal for in-depth analysis and budgeting.
- AWS Budgets: Set custom budget alerts to avoid overspending.
2. Right-Sizing Instances
Rightsizing involves matching instance types and sizes to workload needs, avoiding over-provisioning.
- AWS Compute Optimizer: Uses machine learning to recommend optimal EC2 instance types, potentially reducing costs by up to 25%.
- Optimizing autoscaling thresholds cuts costs by 20% annually for one workload, without affecting performance.
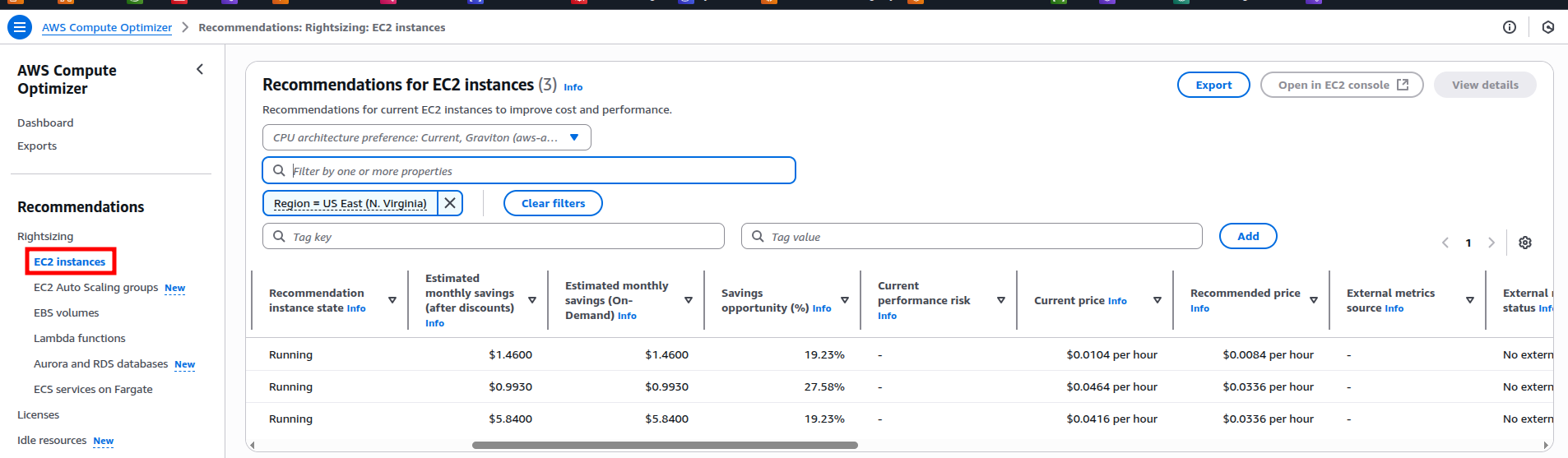
3. Leverage Cost-Effective Pricing Models
Choose the right pricing model for the workload:
| Pricing Model | Best For | Savings Potential |
| On-Demand | Short-term, unpredictable use | Baseline |
| Savings Plans | Steady workloads (1-3 years) | Up to 72% |
| Reserved Instances | Predictable usage | Up to 75% |
| Spot Instances | Fault-tolerant, flexible tasks | Up to 90% |
Review workloads and migrate eligible services to Savings Plans or Spot Instances.
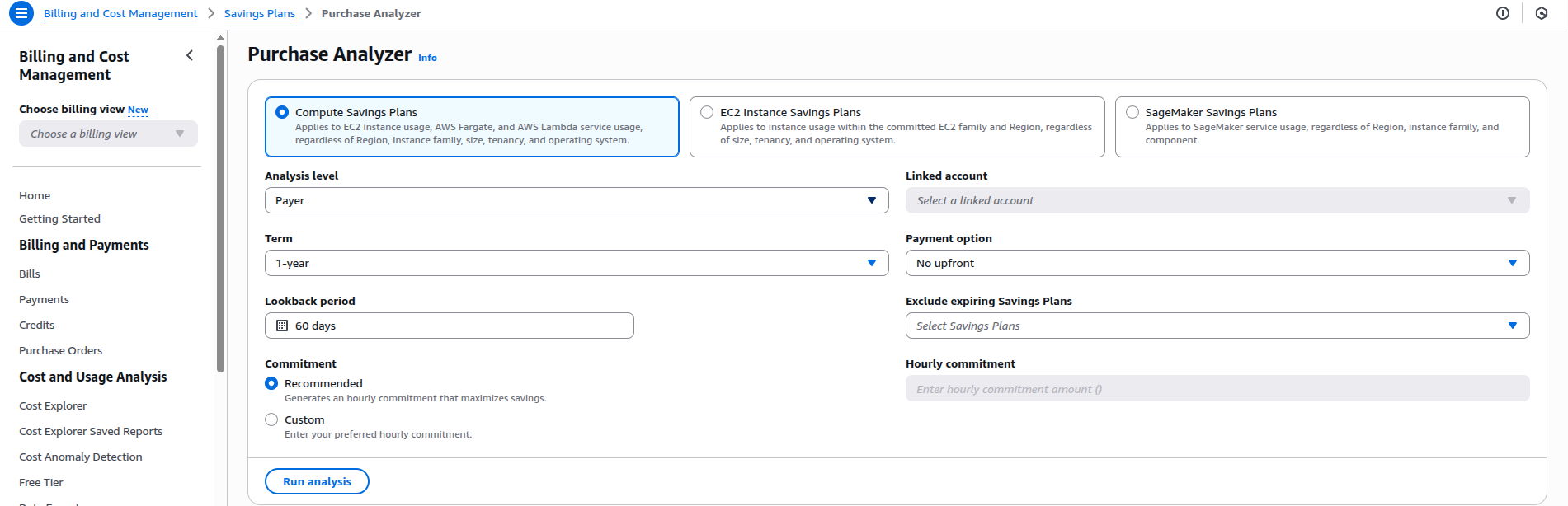
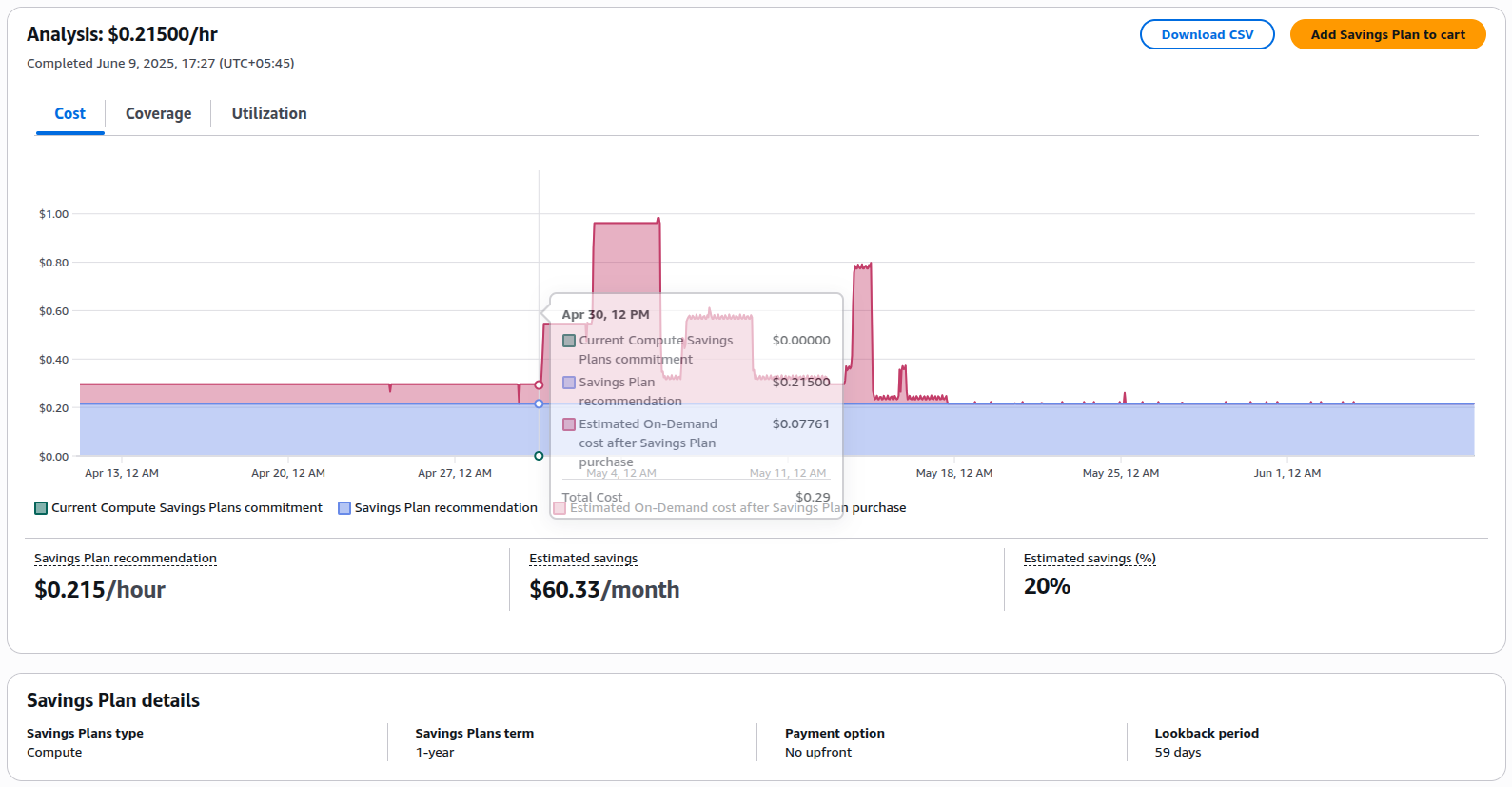
4. Embrace Auto-Scaling
Auto Scaling adjusts resources based on demand, preventing over-provisioning.
- EC2 Auto Scaling: Automatically adds or removes instances based on defined policies, ensuring payment is made only for the required capacity.
- DynamoDB Auto Scaling: Scales database capacity for read/write requests, balancing cost and performance.
5. Optimize Storage
Storage costs can escalate without proper management.
- Amazon S3: Move infrequently accessed data to lower-cost tiers like S3 Infrequent Access or Glacier.
- EBS Volumes: Delete unused volumes or snapshots. Use newer, cost-efficient volume types like gp3 instead of gp2. For example, migrating EBS volumes to GP3 can reduce costs while maintaining performance.
6. Reduce Data Transfer Costs
Minimize data egress by optimizing data flows.
- Use AWS Regions Strategically: Keep data transfers within the same region to avoid inter-region fees.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Use Amazon CloudFront to cache content closer to users, reducing egress costs.
7. Use Cost Allocation Tags
Tagging resources helps track spending by team, project, or environment (e.g., Team=Marketing, Project=MobileApp).
- AWS Cost Allocation Tags: Apply tags to resources for detailed cost tracking. Tag EC2 instances by department to identify high-spending teams.
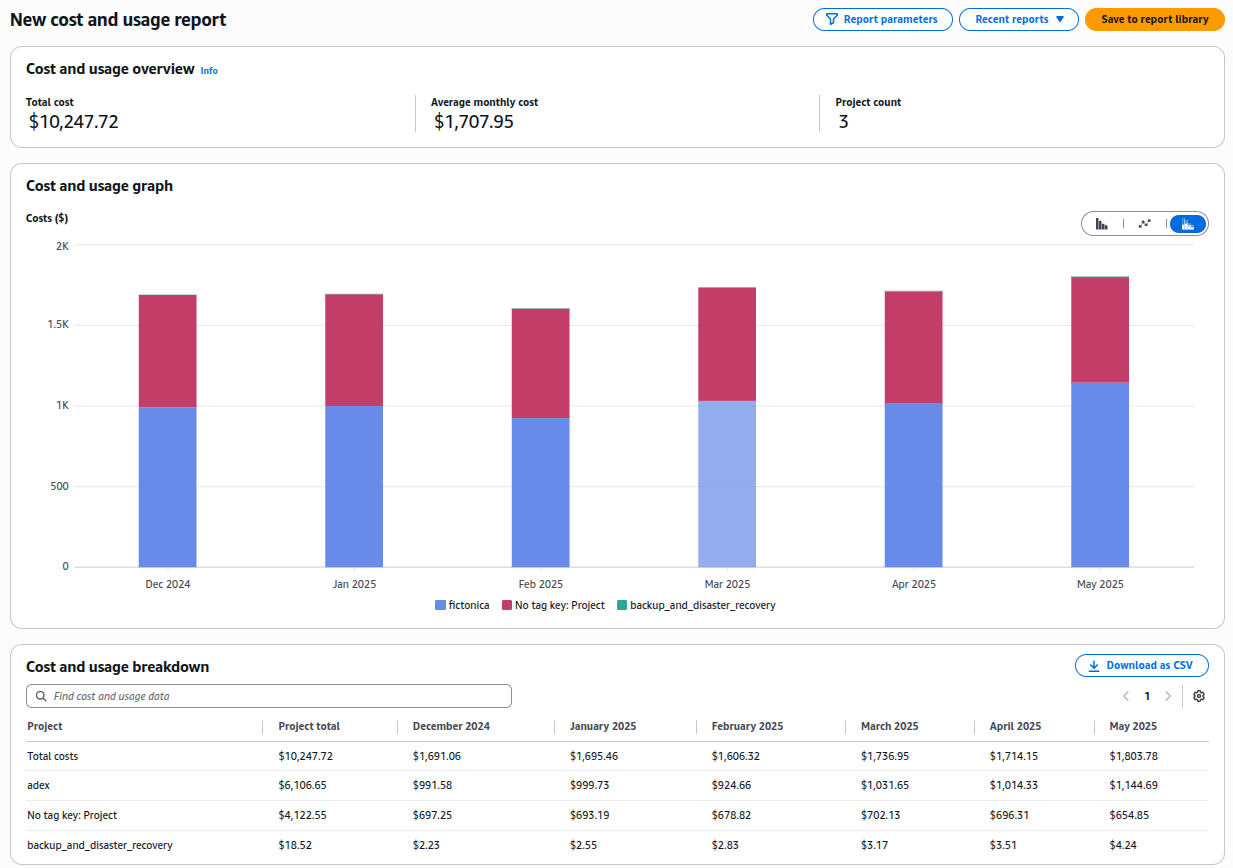
8. Eliminate Unused Resources
Unused resources like idle RDS instances or unattached EBS volumes can rack up costs.
- AWS Trusted Advisor: Identifies underutilized resources, such as EBS volumes with low IOPS or unused RDS instances.
Use Trusted Advisor to find and delete unused resources.
9. Adopt AWS Graviton Processors
Graviton-based EC2 instances offer up to 40% better price-performance than comparable instances.
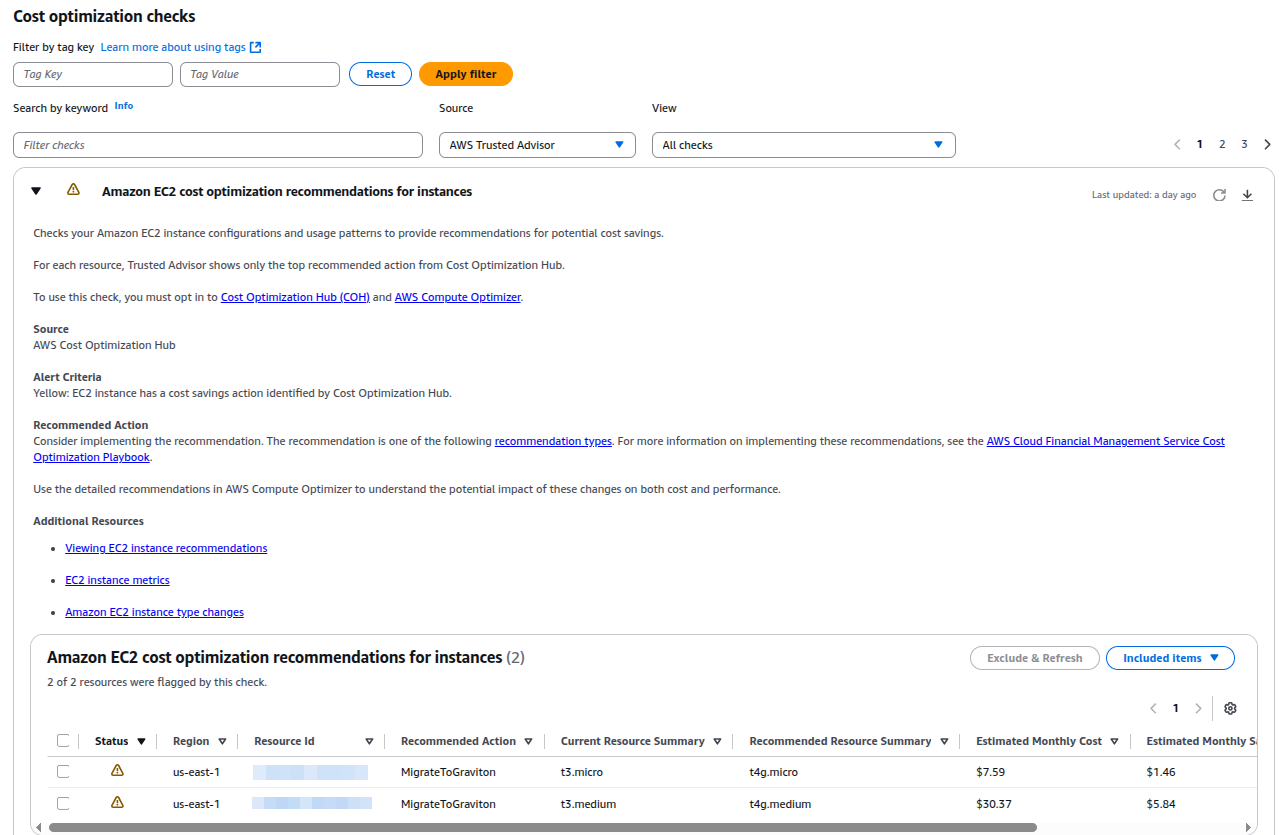
AWS Cost Optimization Tools at a Glance
| Tool | Purpose |
| AWS Cost Explorer | Visual cost and usage analysis |
| Compute Optimizer | Instance rightsizing recommendations |
| Trusted Advisor | Detects underused and idle resources |
| AWS Budgets | Alerts for cost thresholds |
| AWS Pricing Calculator | Forecast and plan for new workloads (AWS Pricing Calculator ) |
| Cost Optimization Hub | Central dashboard for cost-saving tips |
Best Practices for Ongoing Optimization
- Monitor Regularly: Review Cost Explorer and Trusted Advisor weekly to catch inefficiencies early.
- Automate Savings: Use tools like Datadog App Builder to automate resource cleanup.
- Educate Teams: Train developers on cost-aware practices to prevent oversizing.
- Align with Business Goals: Use CloudZero to connect costs to business metrics, ensuring spending drives value.
Challenges and Solutions
| Challenges | Solutions |
| Billing complexity and opaque costs | Use Cost Explorer and CUR for transparency and tag resources for clarity |
| Over-provisioning due to poor architecture | Right-size with Compute Optimizer and adopt auto-scaling |
| Unpredictable workloads | Use Spot Instances or Savings Plans for flexibility |
Conclusion
AWS cost optimization is a continuous process involving strategic planning, appropriate tools, and proactive monitoring. By analyzing costs, rightsizing instances, leveraging pricing models, and optimizing storage and data transfer, it’s possible to significantly reduce the AWS bill while maintaining performance. Starting with tools like AWS Cost Explorer and Trusted Advisor can help identify quick wins.
Adopting advanced strategies, such as using Graviton processors and Savings Plans, is recommended for long-term savings. With these practices, cloud infrastructure can become cost-effective and a source of competitive advantage.
Ready to Save? Log in to the AWS Billing Console, enable Cost Explorer, and start implementing these strategies today.