Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming AI development, but running them locally can be challenging without the right tools.
Available in multiple model variants, DeepSeek-R1 delivers powerful performance for various AI applications. Deploying these models on your hardware gives you privacy, control, and the ability to tailor performance to your needs.
Overview
This guide covers the steps for deploying DeepSeek-R1 locally using Ollama and Open WebUI on a CPU or GPU system. The 1.5B and 7B parameter models can be used depending on the hardware’s capabilities.
Ollama acts as the backend to efficiently run the model, while Open WebUI provides an intuitive interface for seamless interaction and management.
For users who want to enhance performance, it also covers optimization of the Ollama server to handle multiple concurrent requests and fine-tune its resource management.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before diving in, make sure you have the following:
Hardware:
- CPU Deployment: A modern multi-core CPU (quad-core or better recommended).
- RAM: 8GB or more is recommended.
- Storage: SSD storage is highly recommended to reduce model load times.
Software:
- Operating System: Linux, macOS, or Windows (with WSL2 for Linux-based tools).
- Git: For cloning repositories.
- Docker (Recommended for containerized deployments).
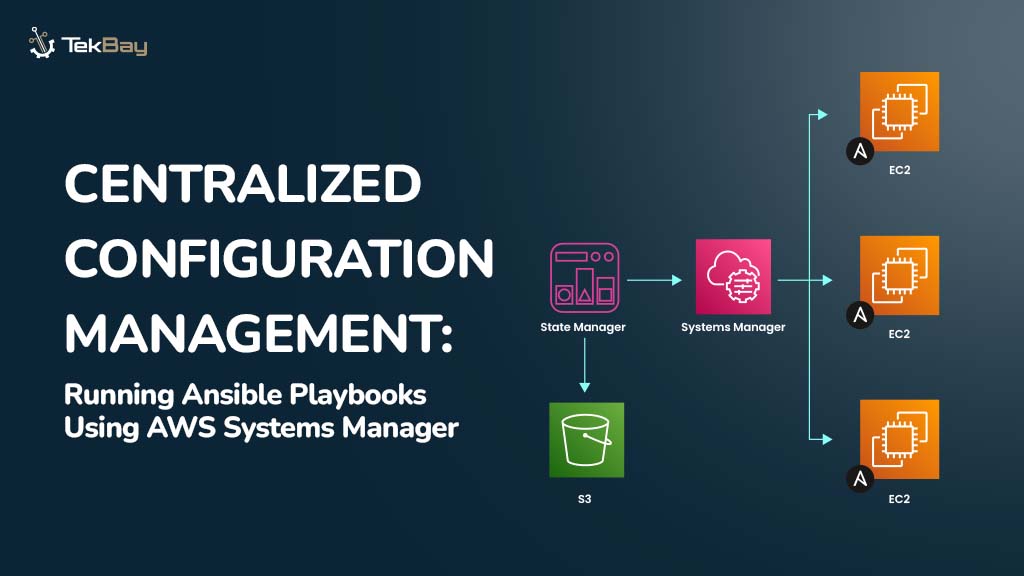
Step-by-Step Guide To Deploy DeepSeek-R1 LLM Locally
Step 1: Install Ollama
Ollama is a framework for running large language models (LLMs) locally. It supports pre-packaged models, is easy to install, and is cross-platform (macOS, Windows, Linux).
To install Ollama, run the following command in your terminal:
curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh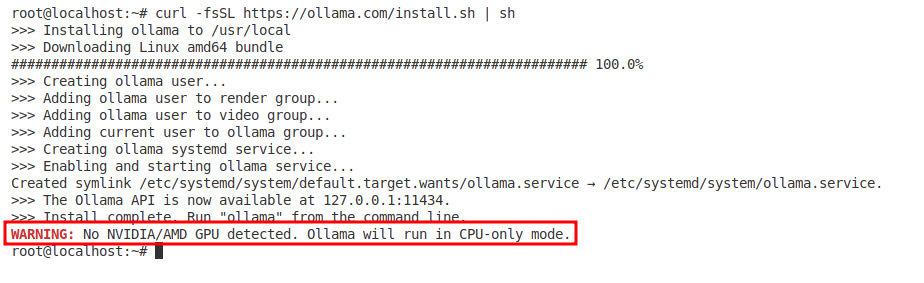
Note: Since we are running the model on a CPU-based system, the above warning may appear, which is normal and can be avoided.
Learn more on Ollama’s official site.
Verify Installation
Once the installation completes, confirm that Ollama is installed by checking its version:
ollama --version
Step 2: Pull the DeepSeek-R1 Model
Now that Ollama is installed, we need to download the DeepSeek-R1 models. You can download both the 1.5B and 7B versions using the Ollama CLI:
ollama pull deepseek-r1
ollama pull deepseek-r1:7bThis command fetches the model from the official Ollama repository and stores it locally.
Note: DeepSeek-R1 7B version is significantly more powerful but requires more RAM and CPU resources.
Verify Downloaded Models
To confirm that both models were downloaded successfully, run:
ollama list
Step 3: Run DeepSeek-R1 Locally Using CLI
Since the models are downloaded, you can run them locally with Ollama. You can start each model using the following commands:
ollama run deepseek-r1
ollama run deepseek-r1:7bOnce started, the model will run locally, and you can interact with it via the command line.
Observing the Model’s Response:
In the image below, the model is running and begins its internal reasoning to generate a greeting message for anyone reading the blog.
This process is displayed under the <think> tag, showing how the model decides what message to provide.
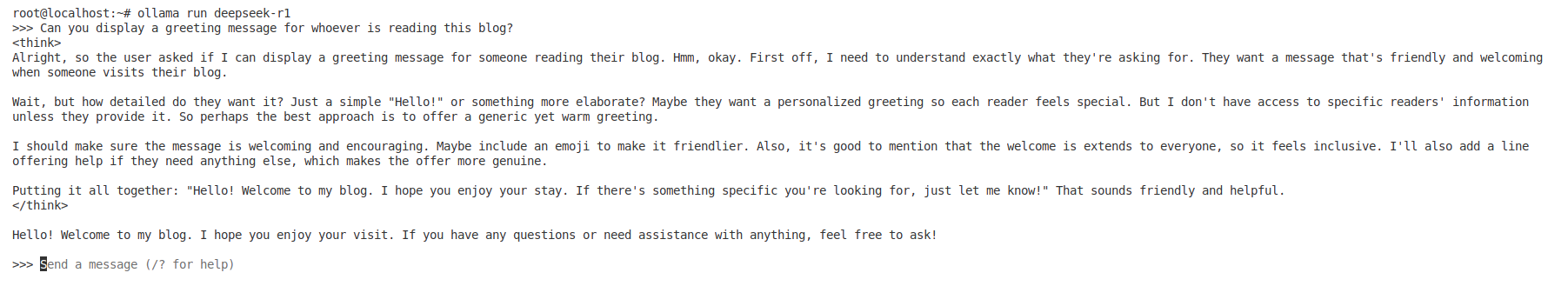
Interacting with DeepSeek-R1
We can also query the model to test if it responds appropriately.
Using the Ollama API, we can interact with DeepSeek-R1 by sending requests to its local endpoint. We used curl to send a prompt (Hello, how are you today?) to DeepSeek-R1 running locally.
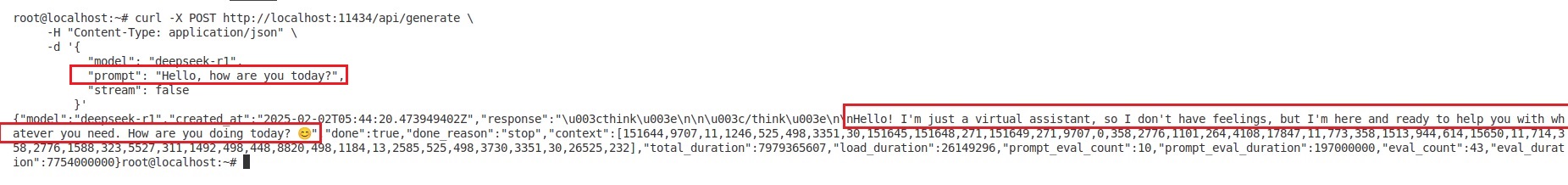
The model processes the prompt and generates a relevant reply, as seen in the response.
Step 4: Prepare for Open WebUI Deployment Using Docker
Instead of interacting via CLI, you can use a web-based interface for a better experience. In this step, you’ll prepare the environment to deploy the Open WebUI by ensuring Docker is installed on your system.
This lets you manage and query your models through a clean, browser-based UI.
First, ensure that Docker is present in your system by running:
docker --version
If you do not have one, read the Docker Installation Guide.
Step 5: Deploy the Open WebUI Using Docker
Once Docker is ready, we’ll deploy Open WebUI (formerly known as Ollama Web UI) for more efficient model interaction.
The following Docker command will map the container port 8080 to the host port 3000 and ensure the container can communicate with the Ollama server running on your host machine.
Run the following Docker command:
docker run -d -p 3000:8080 --add-host=host.docker.internal:host-gateway -v open-webui:/app/backend/data --name open-webui --restart always ghcr.io/open-webui/open-webui:main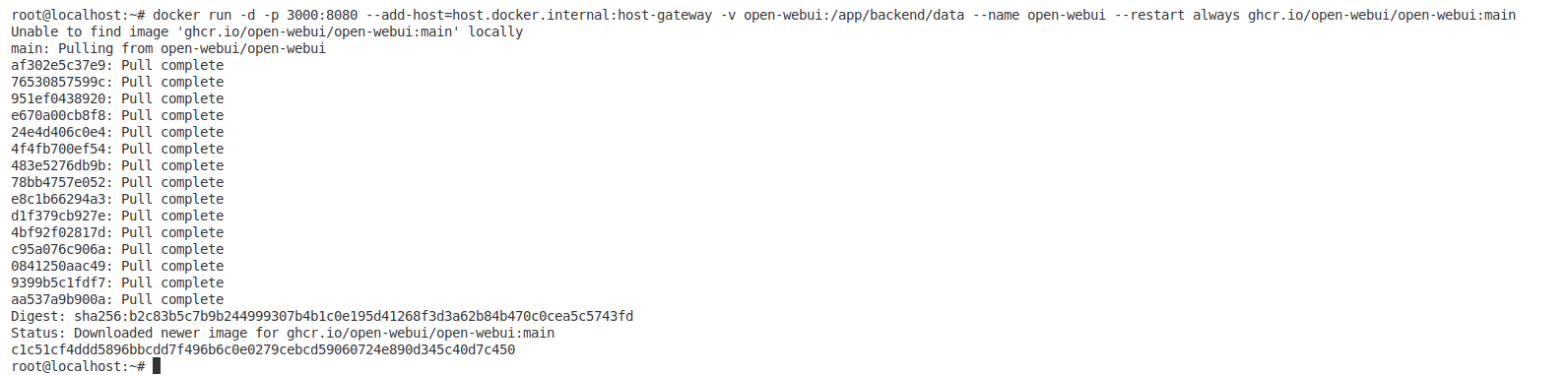
Now, the WebUI has been successfully deployed, which can be accessed at http://localhost:3000.
[Optional] Advanced Ollama Performance Tuning
For users looking to squeeze extra performance and customize how Ollama handles model inference and resource management, you can adjust several environment variables before starting the Ollama server.
export OLLAMA_FLASH_ATTENTION=1
export OLLAMA_KV_CACHE_TYPE=q8_0
export OLLAMA_KEEP_ALIVE="-1"
export OLLAMA_MAX_LOADED_MODELS=3
export OLLAMA_NUM_PARALLEL=8
export OLLAMA_MAX_QUEUE=1024
What Do These Tweaks Do?
- OLLAMA_FLASH_ATTENTION: Enabling this can boost performance by optimizing attention mechanisms within the model.
- OLLAMA_KV_CACHE_TYPE: This setting manages the key-value caching strategy; q8_0 can help reduce memory footprint while maintaining speed.
- OLLAMA_KEEP_ALIVE: This controls connection persistence; setting it to -1 disables the timeout.
- OLLAMA_MAX_LOADED_MODELS: Adjust this based on your system’s memory capacity to control how many models are loaded concurrently.
- OLLAMA_NUM_PARALLEL: Increasing this value can improve throughput on multi-core systems.
- OLLAMA_MAX_QUEUE: This defines the maximum number of queued requests, which is useful for high-concurrency environments.
When to Use These Tweaks?
- If the model loads slowly, increase
OLLAMA_MAX_LOADED_MODELS. - If memory usage is too high, adjust
OLLAMA_KV_CACHE_TYPE. - If performance is slow, enable
OLLAMA_FLASH_ATTENTION.
Security Considerations for Local Hosting
When deploying models like DeepSeek-R1 locally, you must ensure that your environment is secure, considering factors like:
- Access Control: Prevent unauthorized access to the system where the model is hosted.
- Network Security: Ensure that any API endpoints exposed locally are protected, using firewalls or VPNs where necessary.
- Data Protection: If you plan to store sensitive data, make sure it’s encrypted and properly handled.
If you ever plan to scale or move to the cloud, AWS services like EC2 can provide the necessary computing power for running DeepSeek-R1, while AWS WAF can help you maintain high levels of security.
Conclusion
Following this guide, you can successfully set up your local environment to run DeepSeek-R1 with Ollama and Open WebUI. With the 1.5B and 7B parameter models at your disposal, you can explore their capabilities and integrate them into your workflows.
Happy deploying and experimenting with your AI models!