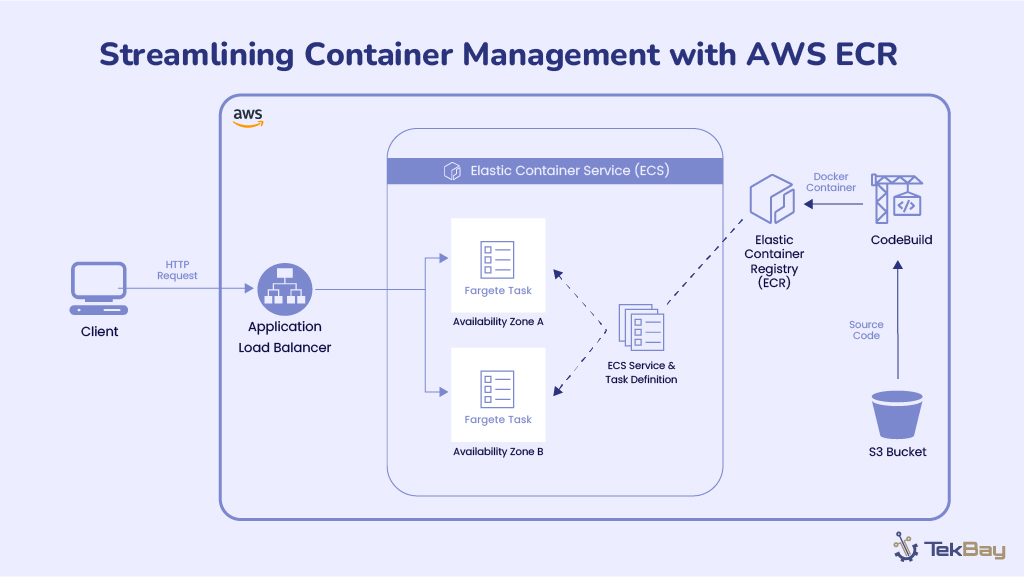
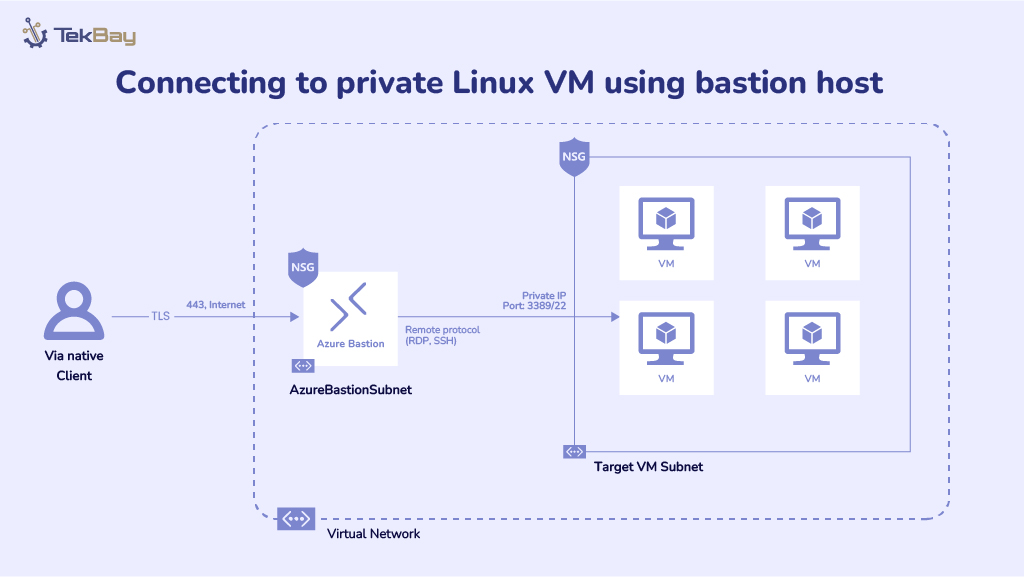
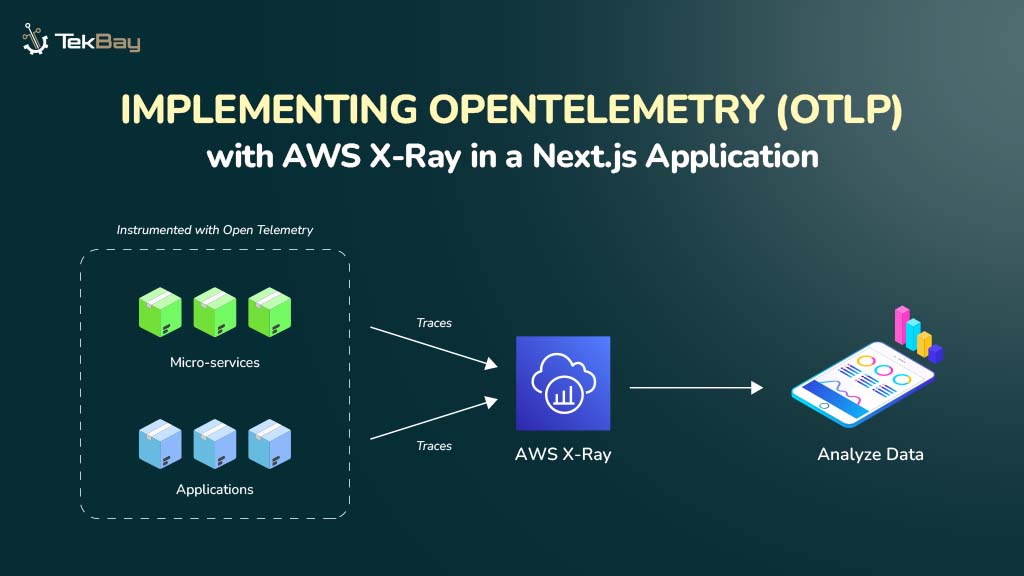
Resilience is the capability of any system to bounce back from unexpected problems like hardware failures or natural disasters. Obtaining resiliency is all about minimizing downtime, protecting your data, and ensuring your services keep running smoothly, no matter what type of problems happen.
Backing up your resources, using auto-scaling mechanisms, setting up required alarms, and using multi-availability zones and multi-regions are some methods to boost your application’s resiliency. But how do you know which alarms to create and which to back up?
Wouldn’t it be nice if there were a system from which we could check how resilient our system is?
They understand how vital resilience is at AWS, so they created the AWS Resilience Hub. It’s a control center that shows how resilient your applications are. It helps you spot potential weak spots, follow best practices, and continuously improve your applications to tackle any disaster that can come your way.
Benefits of Using Resilience Hub:
- Central Hub: Resilience Hub is a central place for you to go to for seeing how you can improve the resiliency of your system.
- Guidance: It not only shows you the resilience score of your system. It also recommends some improvements to obtain higher resiliency. It’s like having a resilience coach.
- Continuous improvement: Resilience Hub keeps an eye on your resilience and alerts you if anything needs attention, helping you stay resilient over time. You can also schedule assessment checks to perform daily.
- Fault Templates: Resilience Hub also provides some fault templates/scenarios that can be used to test
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the amount of time you’re willing to wait for a system to get back up and running after an outage.
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is how much data you can lose during an outage.
By understanding your system’s RTO and RPO, you can design resilience strategies that work for you.
Setting up a resilience hub application and policy in the AWS Resilience Hub is straightforward. First, you define your application’s architecture and dependencies, then select the relevant AWS services and resources.
The Resilience Hub will assess your application’s resilience and give customized recommendations based on best practices. You can then create and implement resilience policies to enforce the resilience configurations you want and monitor your application’s resilience status.
Along the way, you’ll come across some key terms:
- Resilience Policies: These are pre-defined rules that help make sure your application follows resilience best practices.
- Resilience Scores: Numerical values that show how resilient your application is, so you can track and improve over time.
- Resilience Recommendations: Practical advice and suggestions from the Resilience Hub to boost your application’s resilience.
- Resilience Tooling: A set of tools and services within the Resilience Hub that help you implement and monitor resilience.
Resilience isn’t just a technical thing—it’s a mindset that should be woven into every part of your cloud journey. By using the AWS Resilience Hub, you can stay ahead of potential issues, minimize downtime, and ensure that your applications are always available, reliable, and ready to ride out any waves that come their way.
Let us understand how we can create and use AWS Resilience Hub.
Prerequisites:
- AWS account with admin privileges
- A resource group containing applications provisioned in AWS
Resiliency Policy
A resiliency policy contains information and objectives that you use to assess whether your application can recover from a type of disruption, such as software, hardware, Availability Zone, or AWS Region. These policies do not change or affect an actual application.
Multiple applications can have the same resiliency policy. When you create a resiliency policy, you define the recovery time objective (RTO) and recovery point objective (RPO) targets. When you run an assessment, AWS Resilience Hub determines whether the application is estimated to meet the objectives that are defined in the resiliency policy.
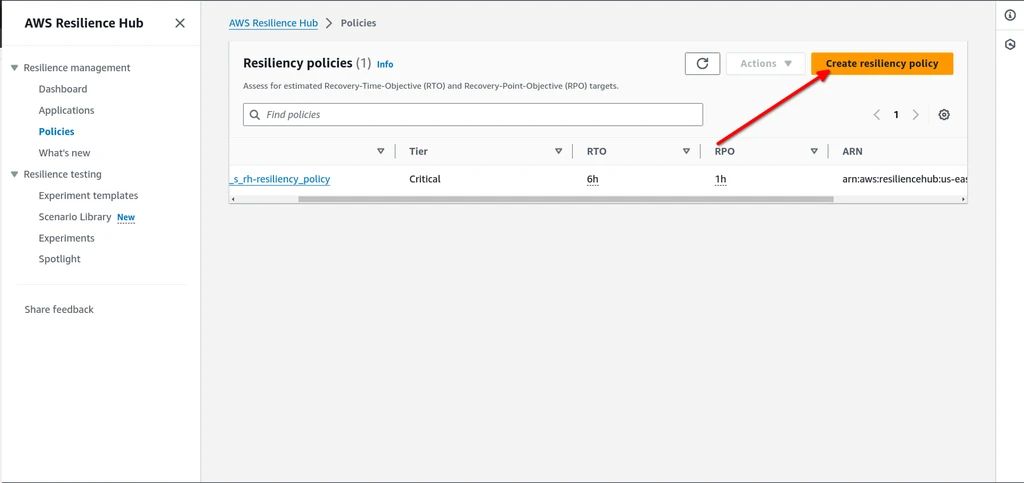
Let’s create a Resiliency policy. First, go to the AWS console and search for AWS Resilience Hub.
In the left navigation menu, choose Policies and click on Create Resiliency policy.
Select a creation method and give it a proper name and description. When choosing a tier, choose according to your system’s resiliency requirement. For this demo, I am selecting Non-critical.
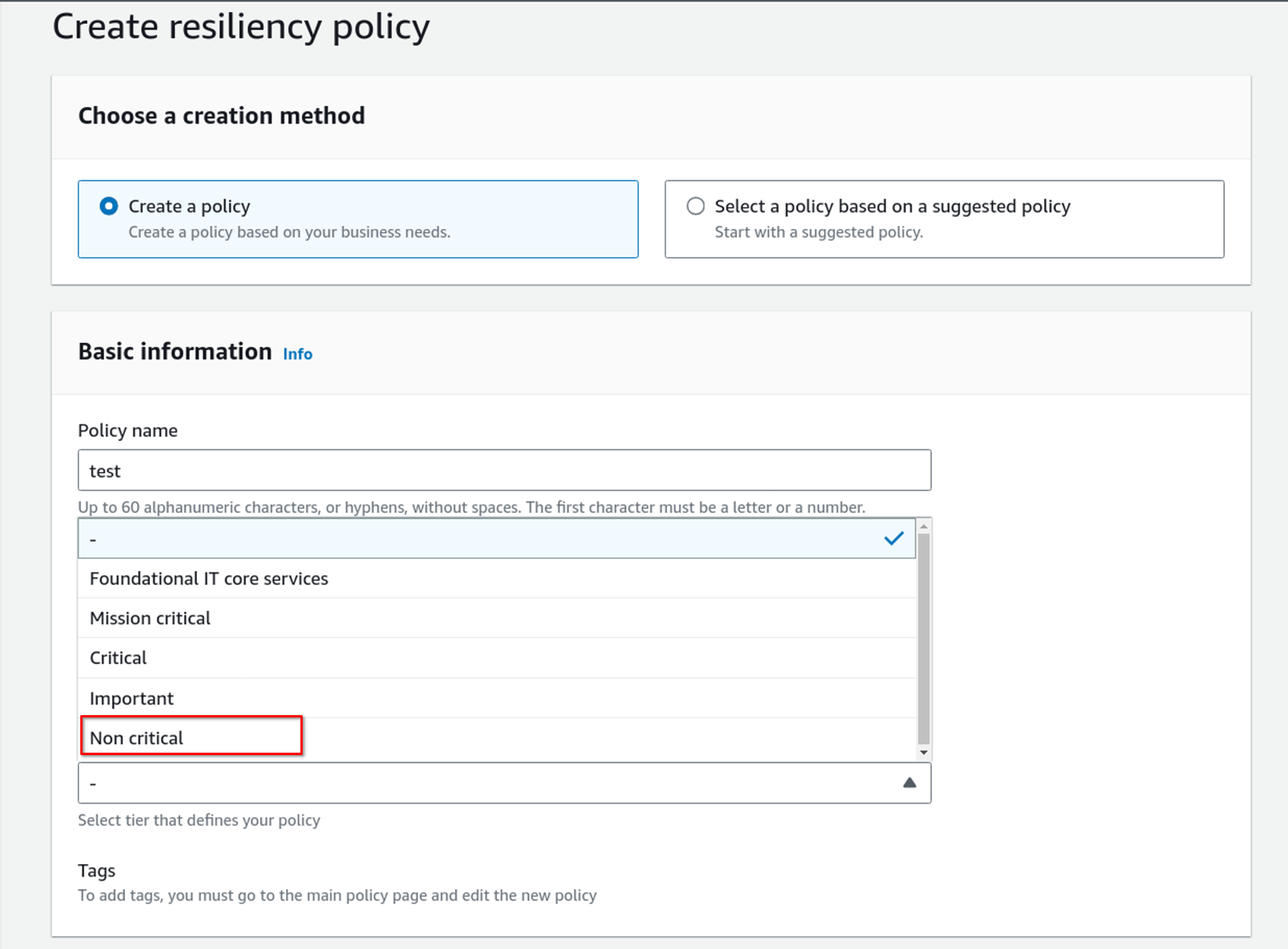
Fill out the RTO and RPO you want for these different categories.
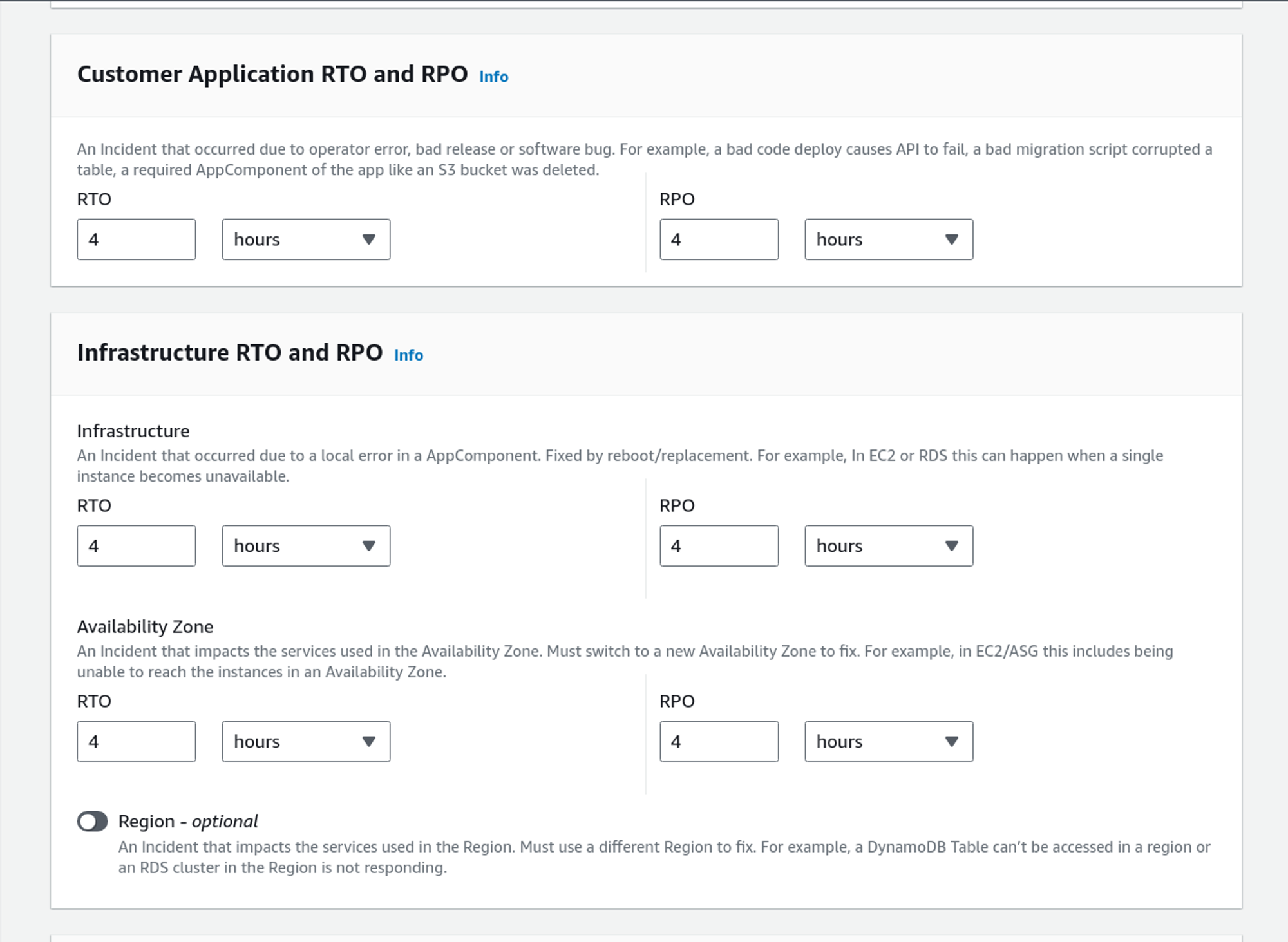
After filling out the RTOs and RPOs, click on Create.
This is the Resiliency Policy that we have just created.
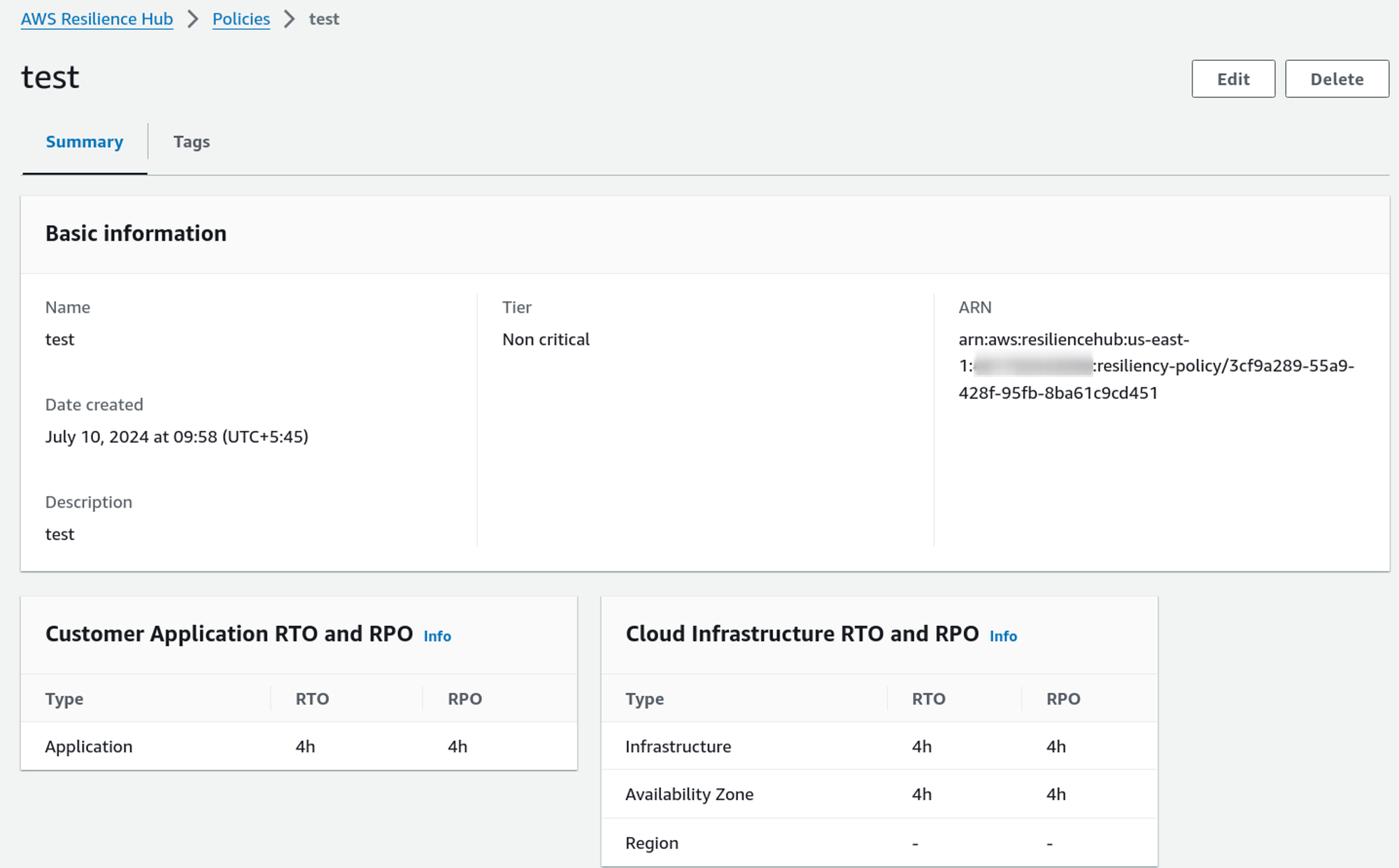
Resilience Hub App
Now, let’s move towards creating a Resilience Hub Application.
In the left navigation menu, choose Applications and click on Add Application.
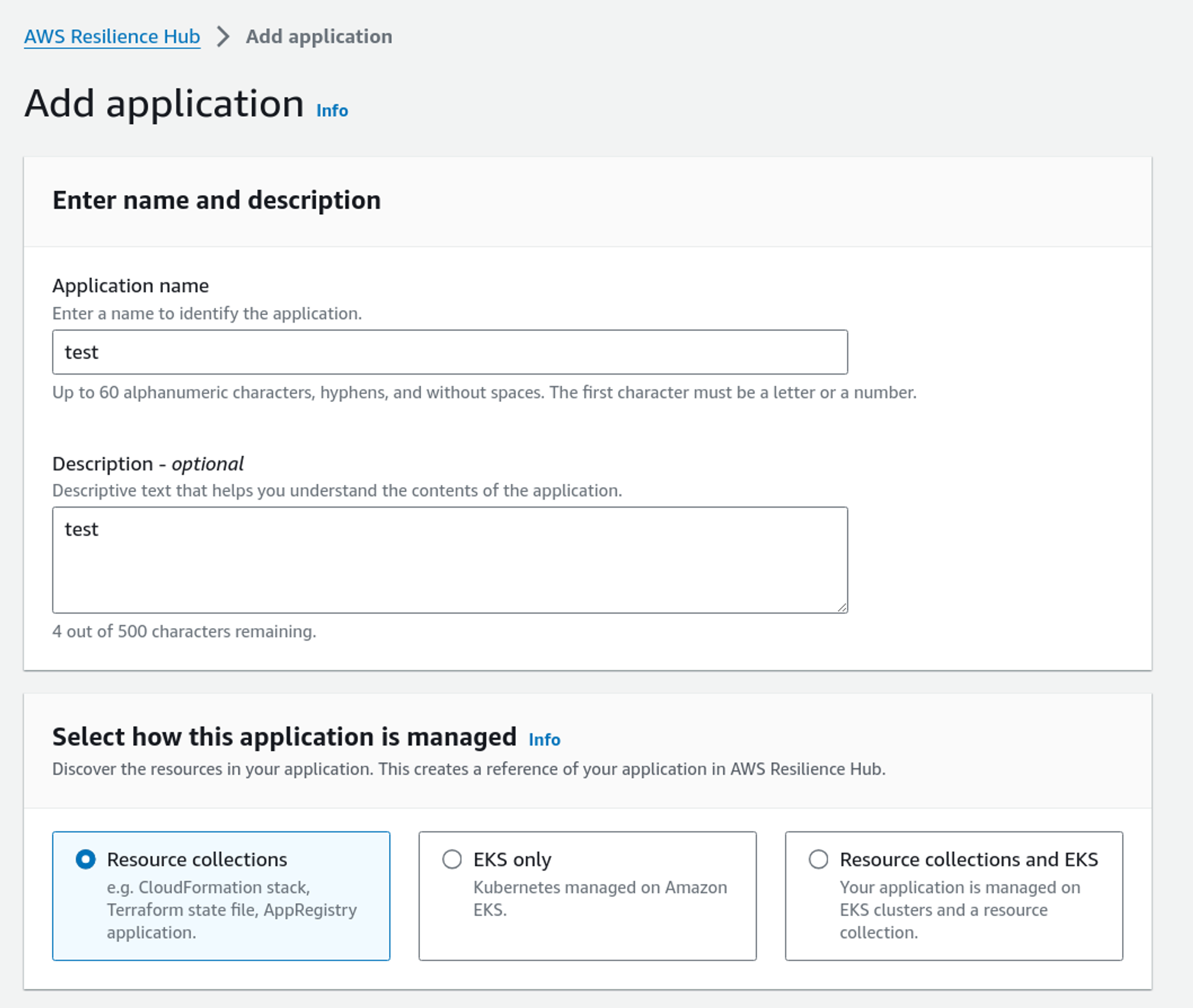
Give a decent application name and description. Select how this application is managed. This means how you use the Resilience Hub to discover the resources. We also have options to use EKS.
We can now use CloudFormation Stack, Resource group, AppRegistry application, and Terraform state files to import groups of resources. For this demo, I am using a resource group that I have already created.
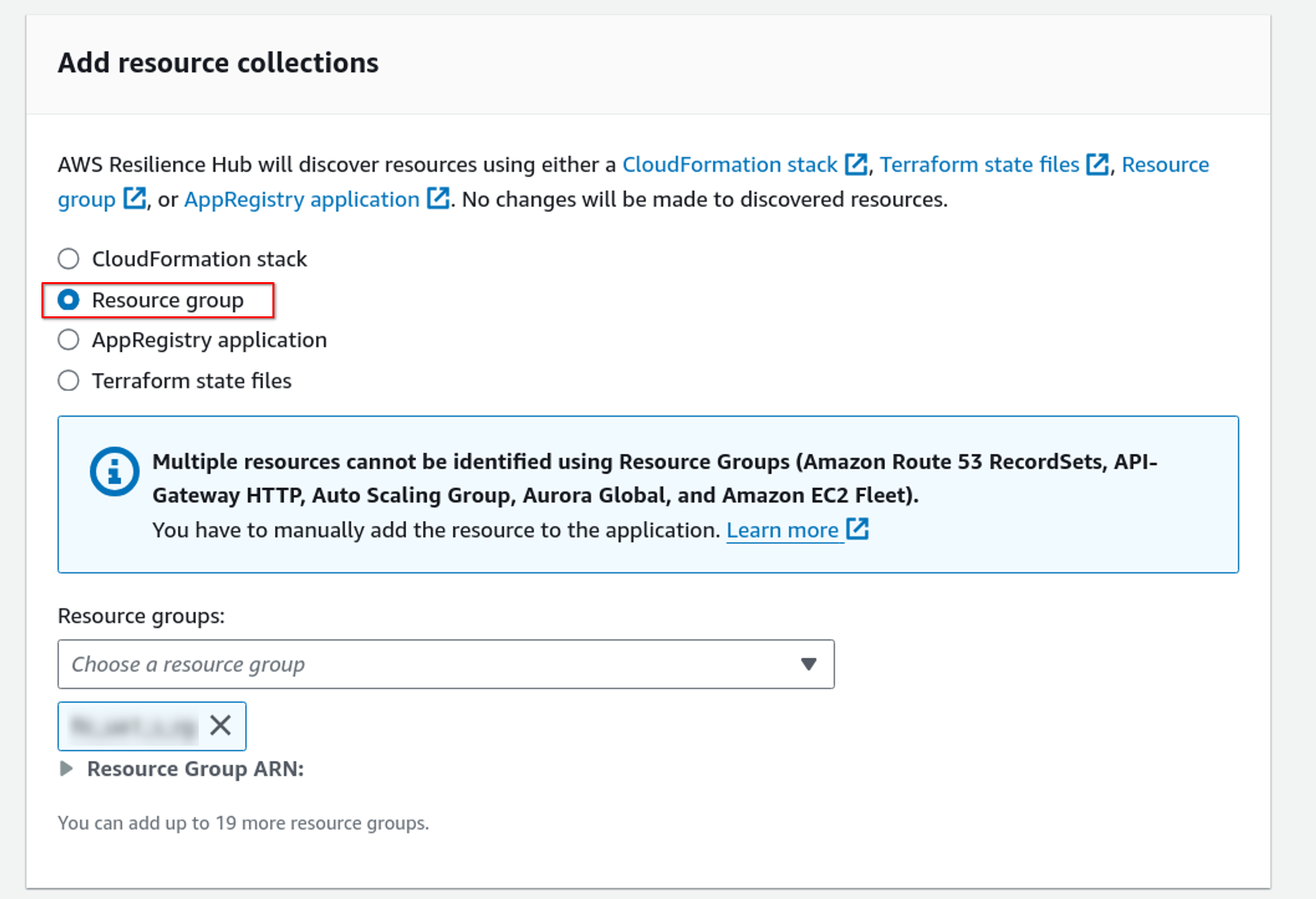
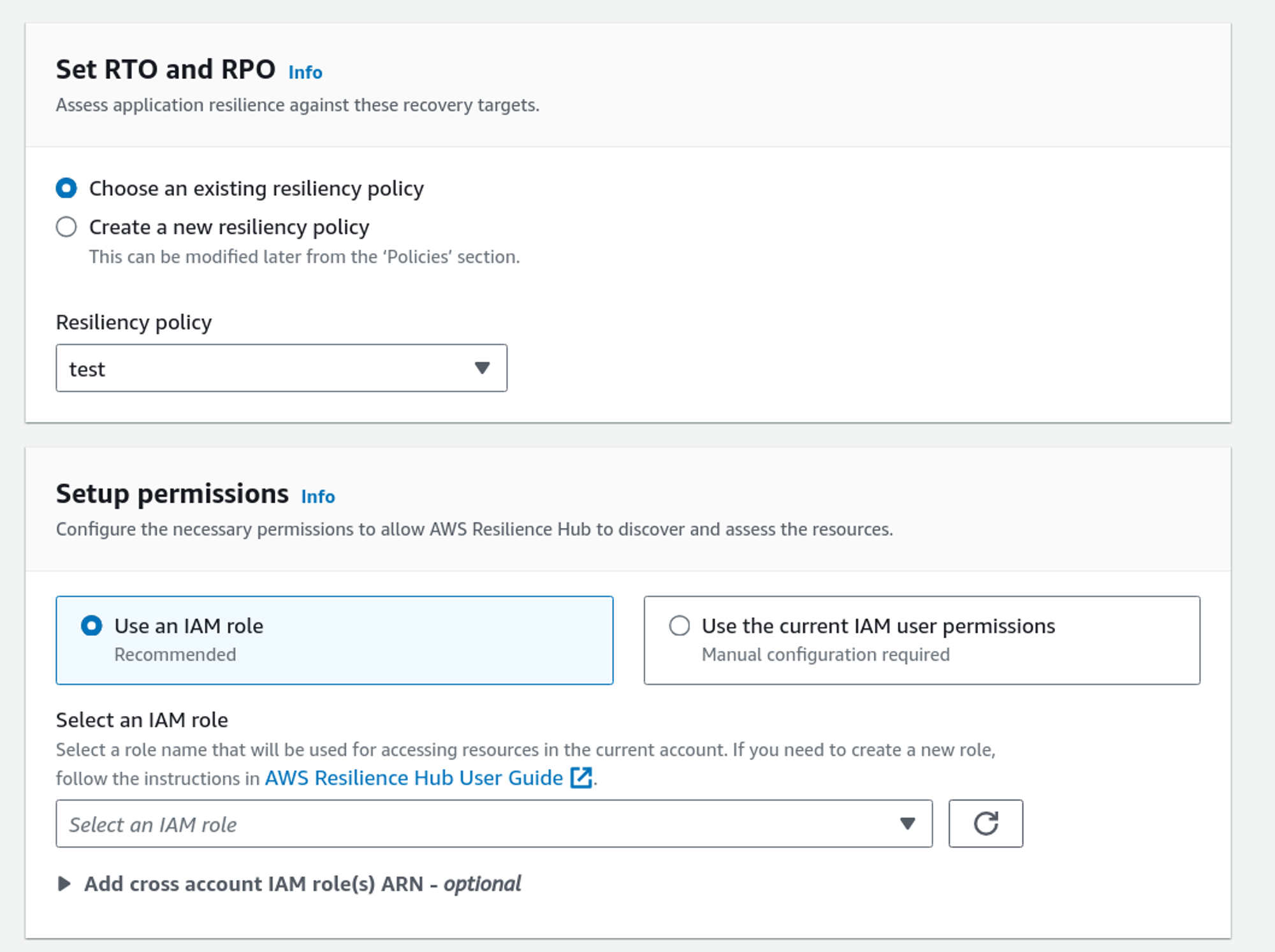
Now select the resiliency policy we created above. Add an IAM role with the required permissions to describe and list it.
A simple role policy can be like this:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"resiliencehub:List*",
"resiliencehub:Describe*"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
We can also set up notifications for drift detection and perform an assessment. Select the options if you want, and then click on Add application.
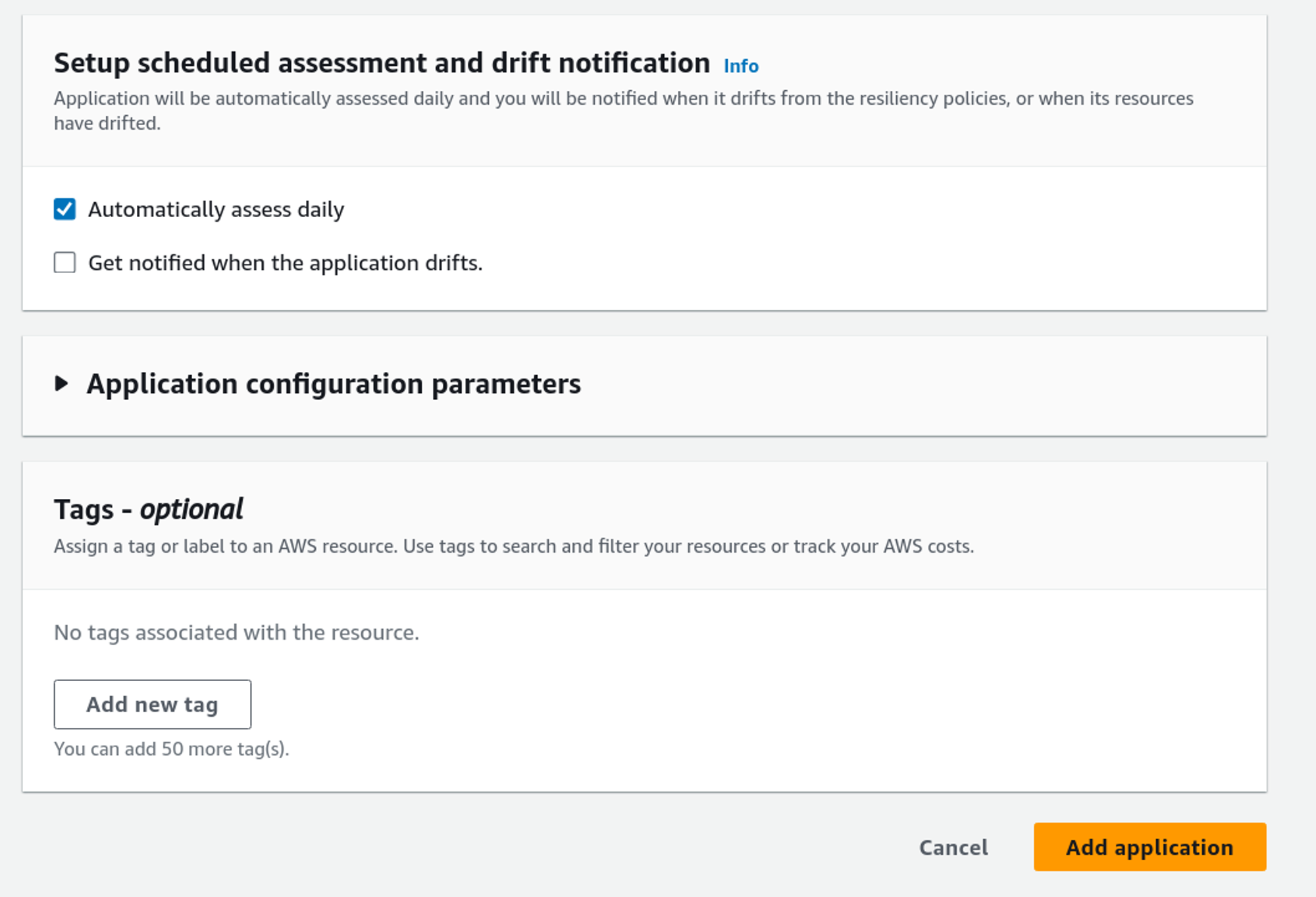
We have successfully created the Resilience Hub App. Now, let’s explore it.
Here is the application’s console. Click the Application Structure tab to check the resources selected for resiliency.
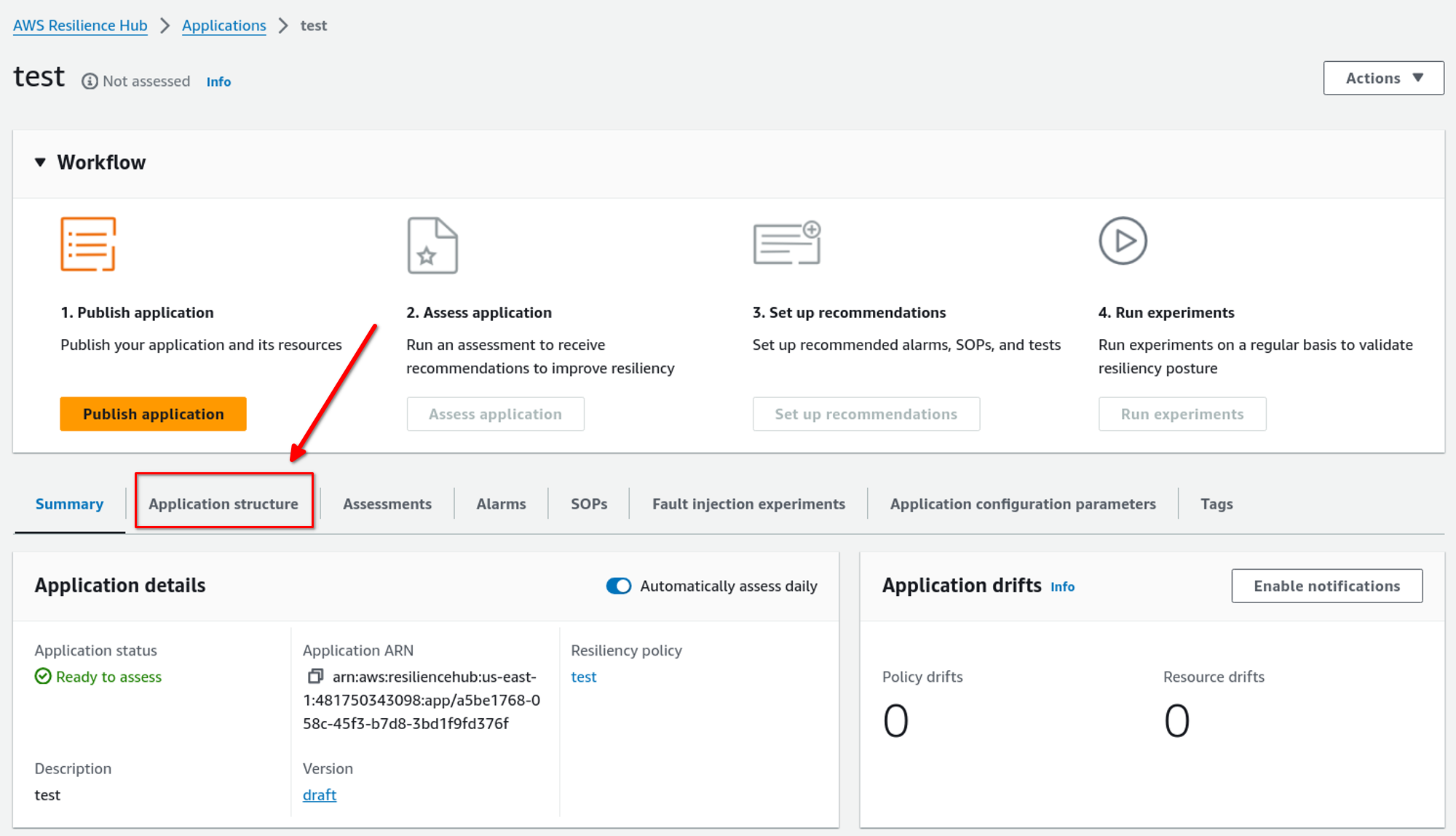
Here, we can see what resources have been imported into the application, app components, and available versions. We can also change the input source from here. After checking the imported resources, we can publish a new version and start an assessment. To do that, just click on Publish and Assess.
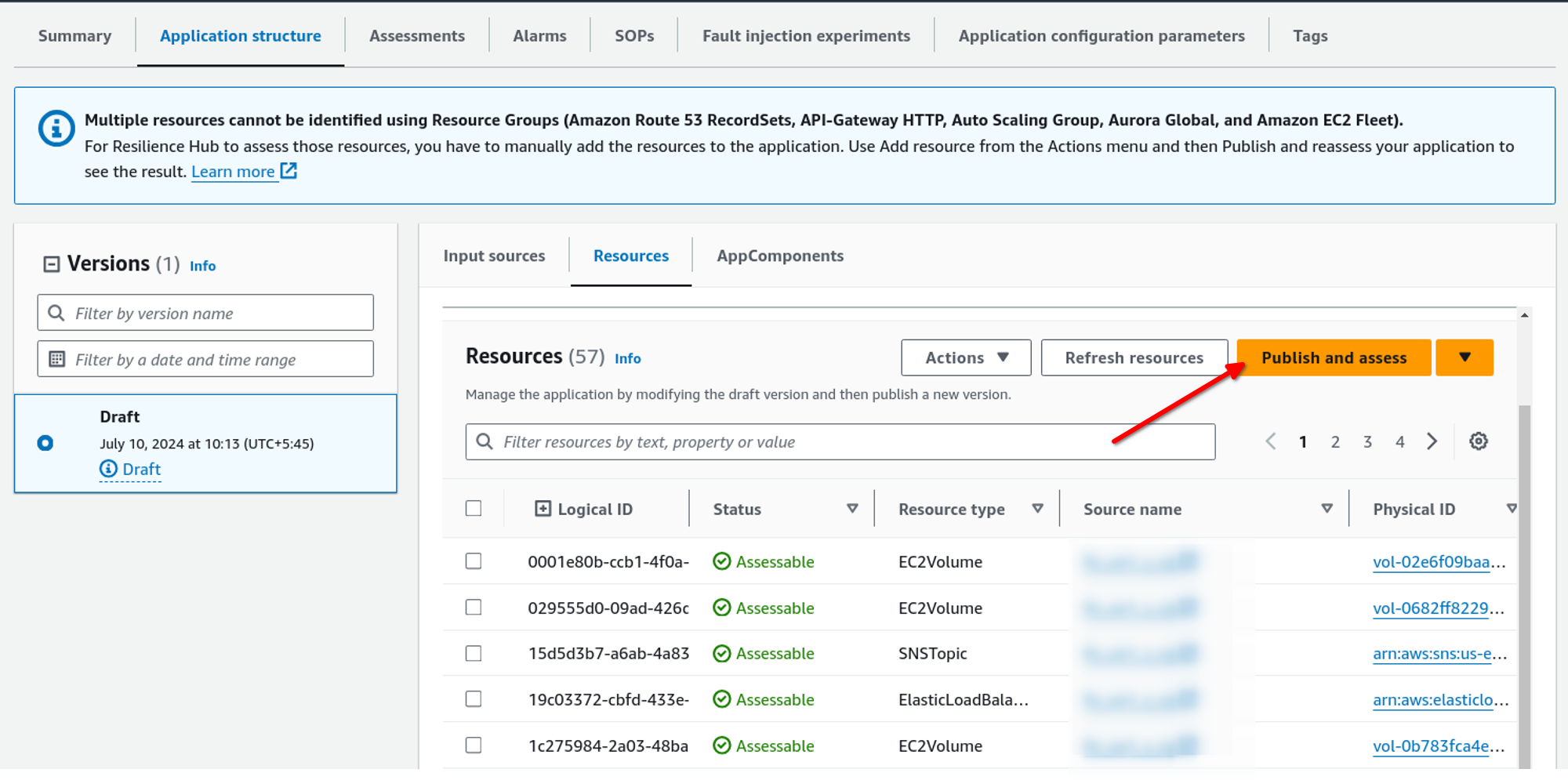
A confirmation box like the one below will appear, give a version name, and click on Publish and assess.
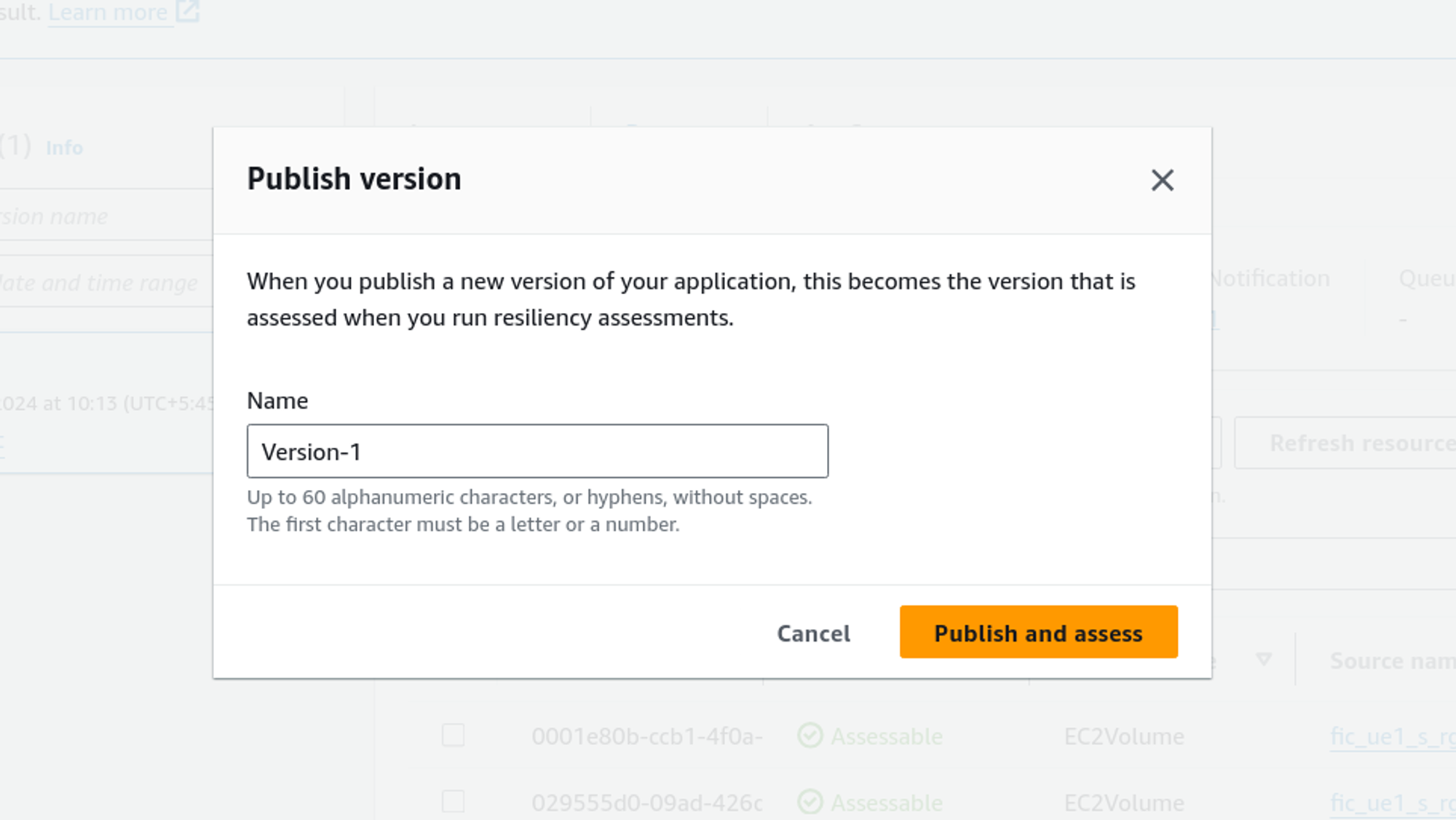
Now we can view the assessment in Assessment tab. We can also run a new assessment by just clicking on Run new assessment. To see assessment report click on the name of the assessment as shown in the picture below.
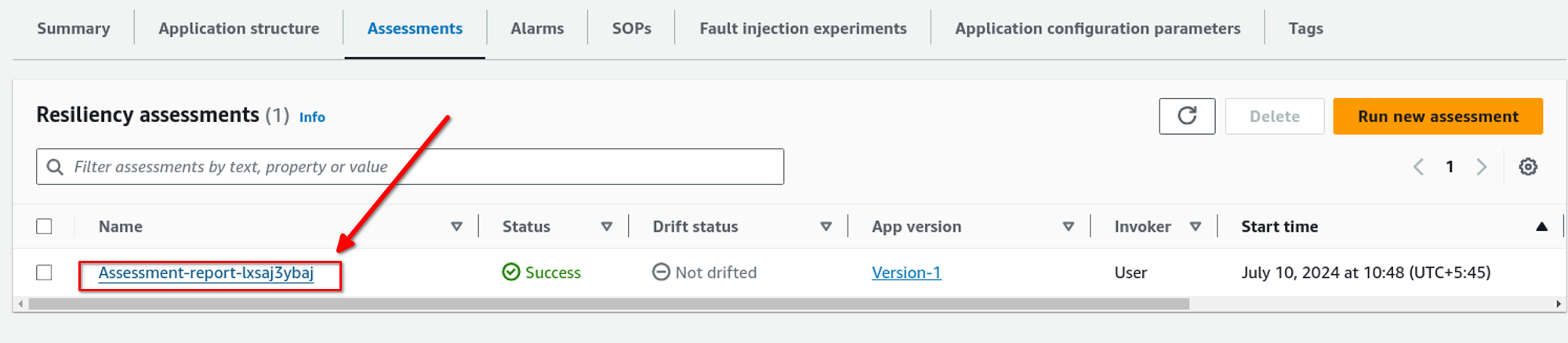
So, here, according to the Resilience Hub, the system does not match the RTO and RPO as we have expected.
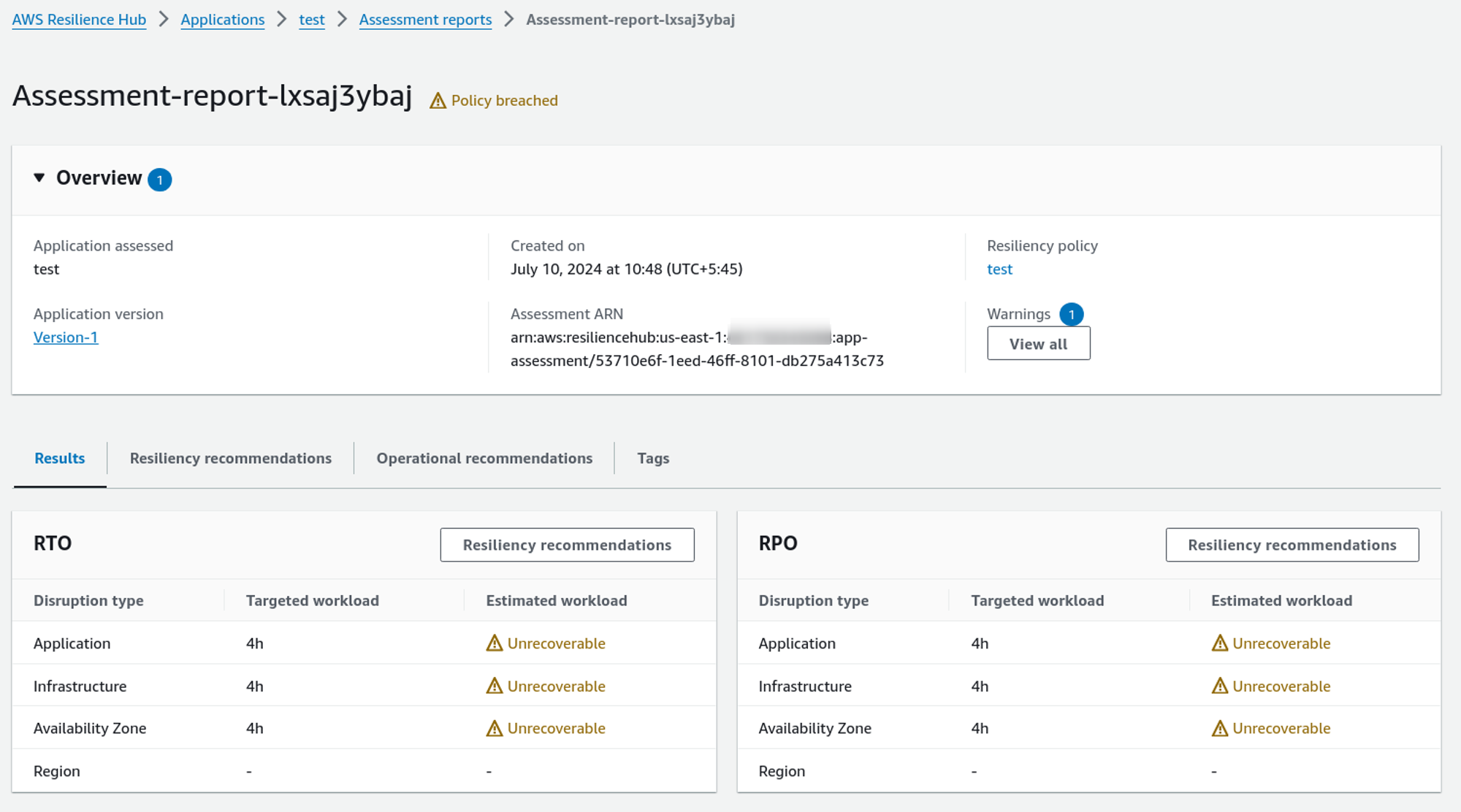
Let’s see what we can do to improve that. By going to the Resiliency recommendation tab, we can see which application does not match our resiliency policy.
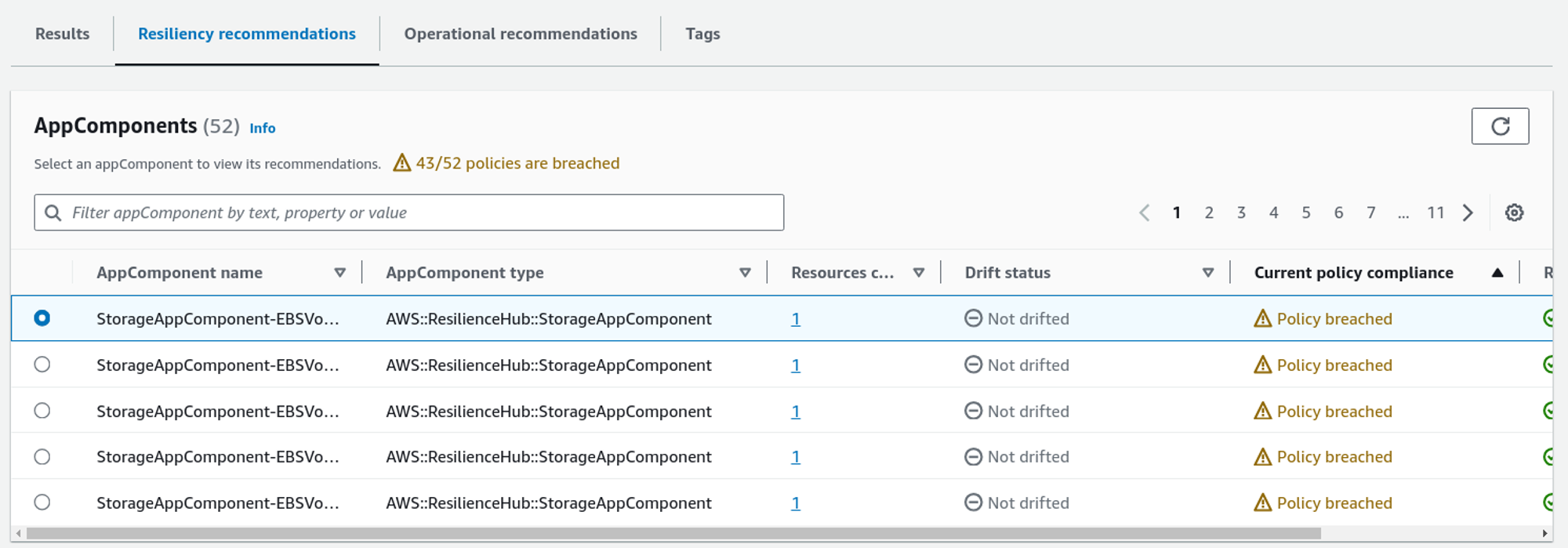
It gives the following suggestions with cost that can increase monthly.
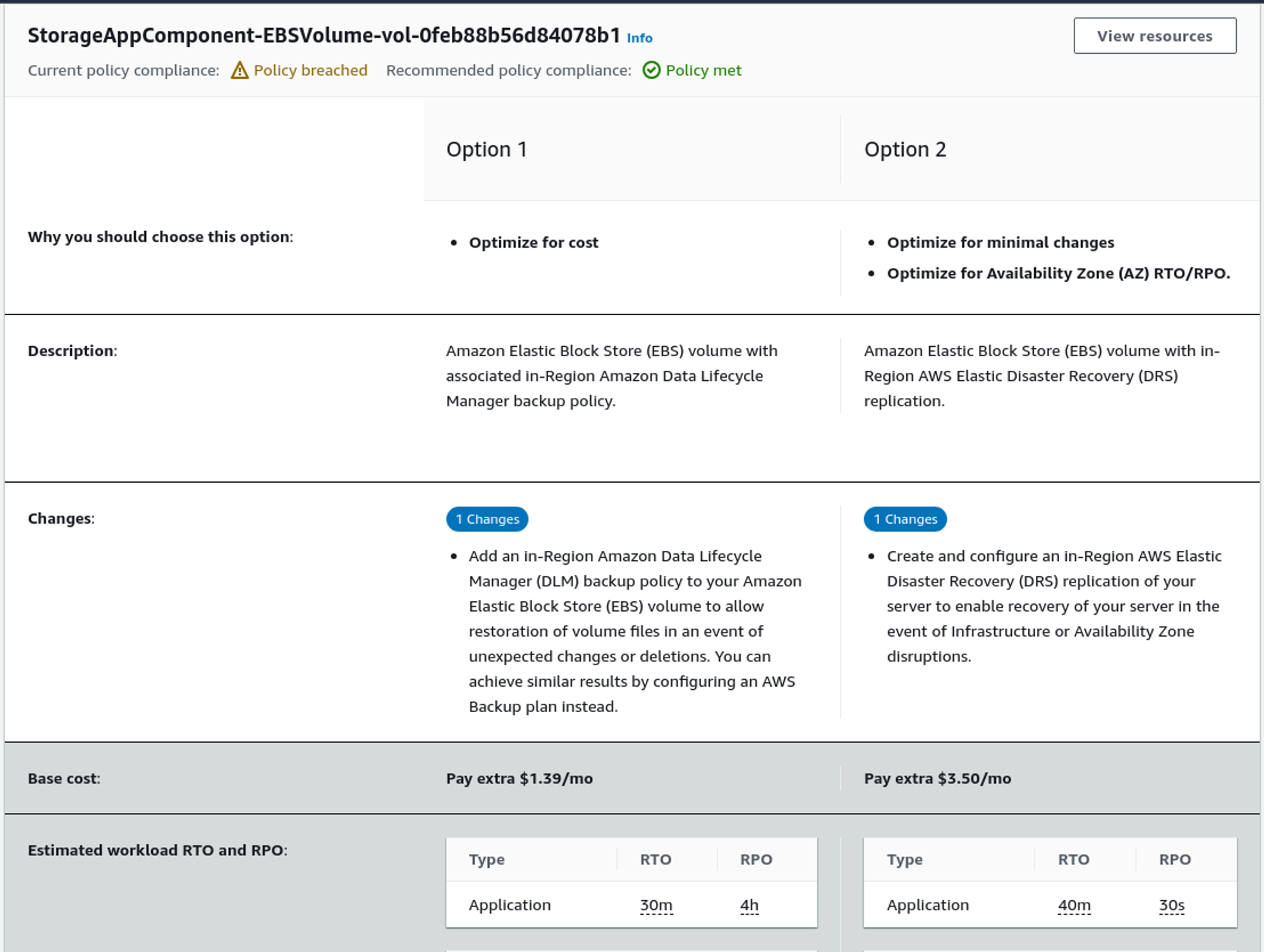
Seeing the recommendations, we can increase the RTO and RPO of the system.
It now only gives resiliency recommendations, but it also gives operational recommendations on the Operational recommendation tab.
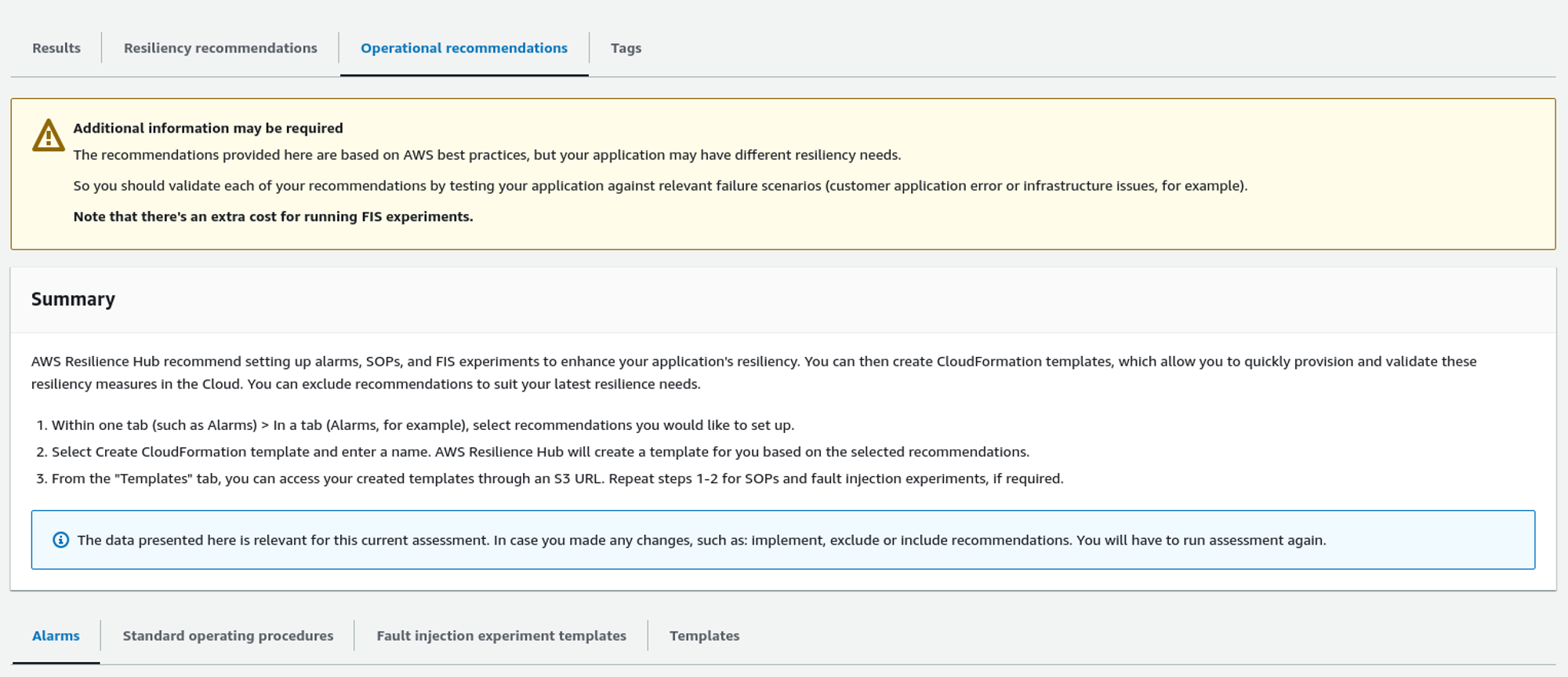
It usually provides alarm recommendations, Standard operating procedures (SOP), and Fault injection experiment templates.
Here is the list of alarms that Resilience Hub recommends installing. We can also create a CloudFormation template by selecting the alarms we want to apply and clicking Create CloudFormation template. We can later use that CloudFormation template to provision those alarms in the system.
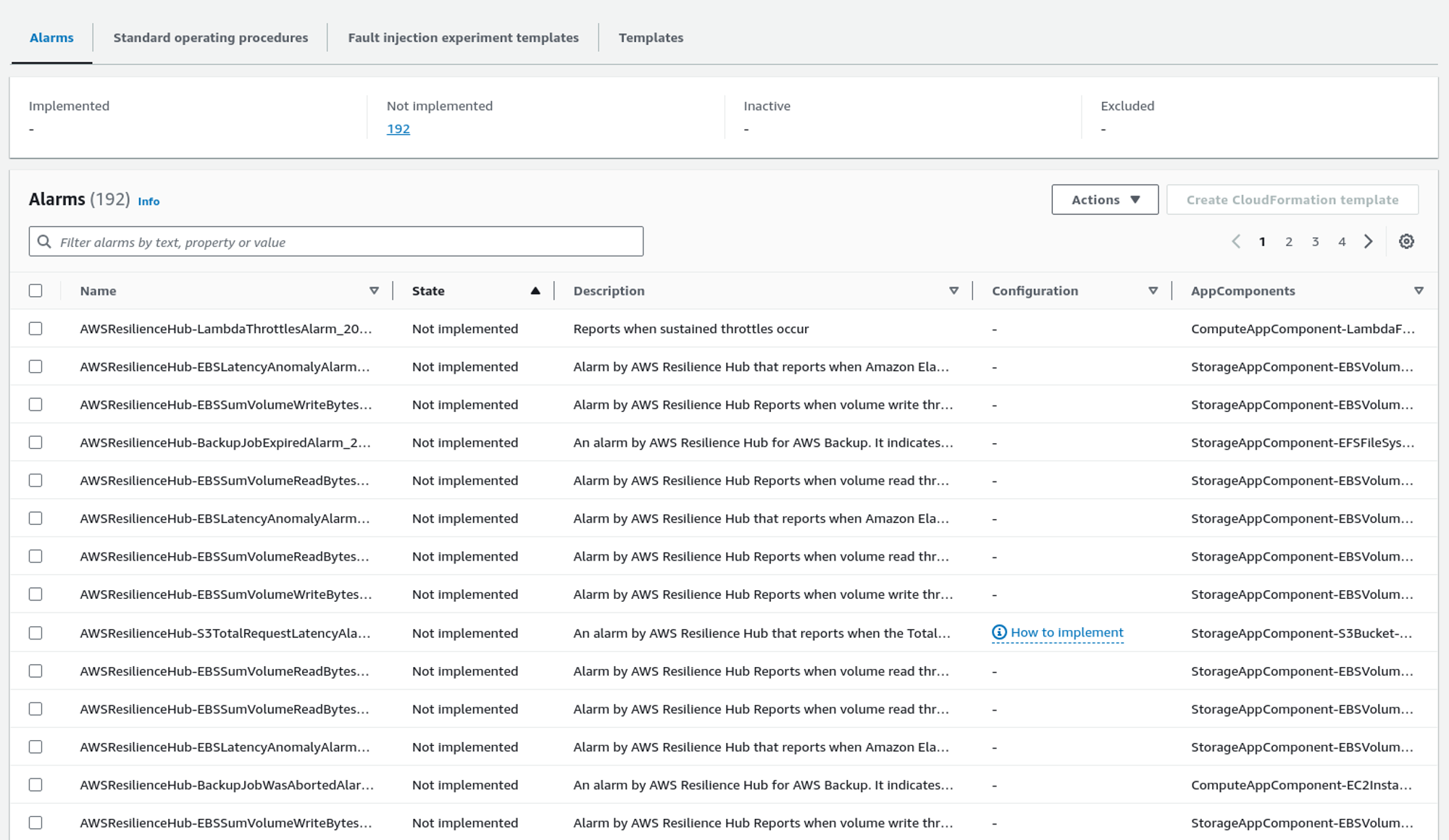
As for alarms, Resilience Hub also recommends standard operating procedures (SOPs). We can also implement the SOPs in the system using the CloudFormation template.
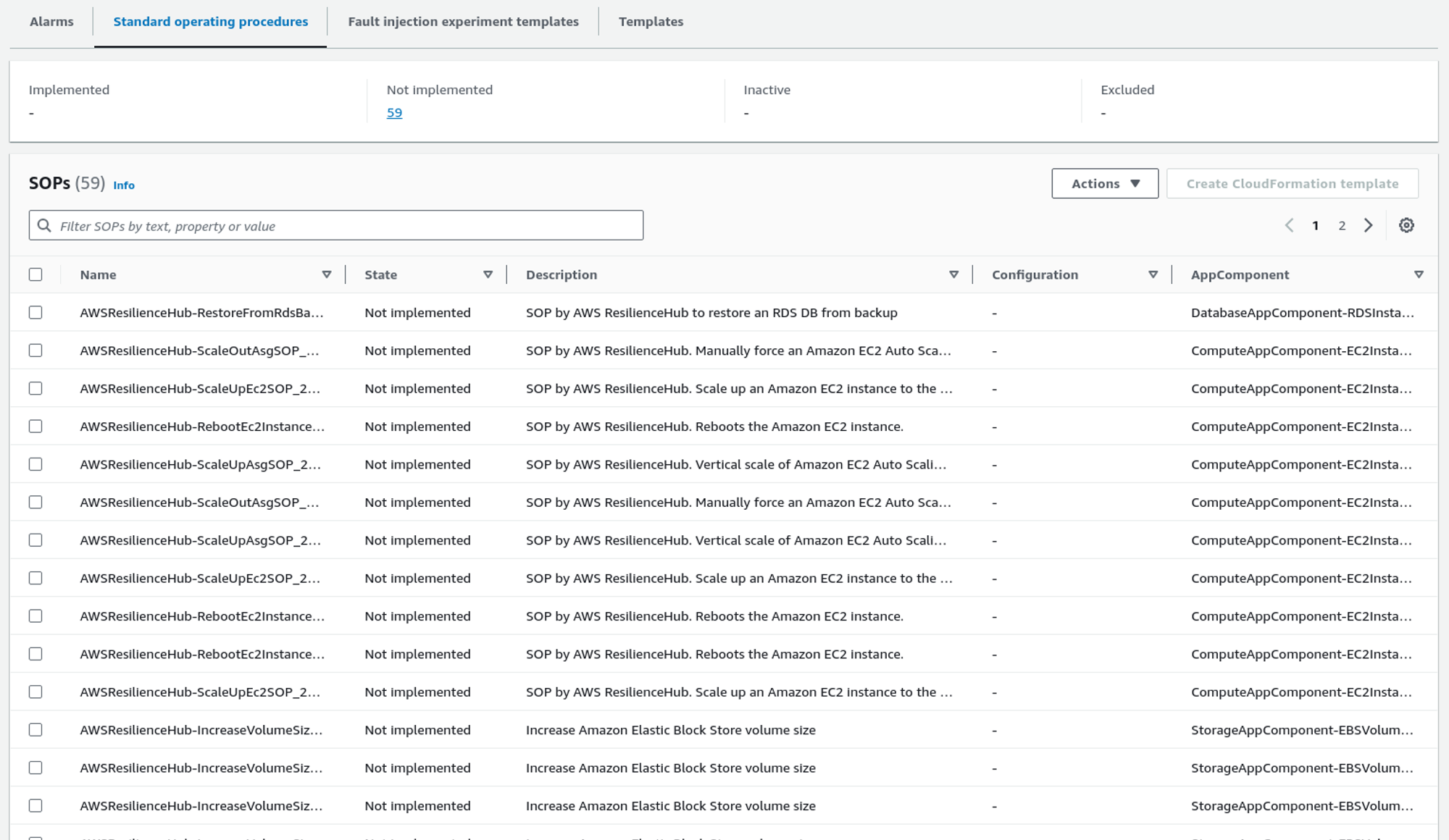
Likewise, it also provides some fault injection experiment templates to test the system in different conditions.
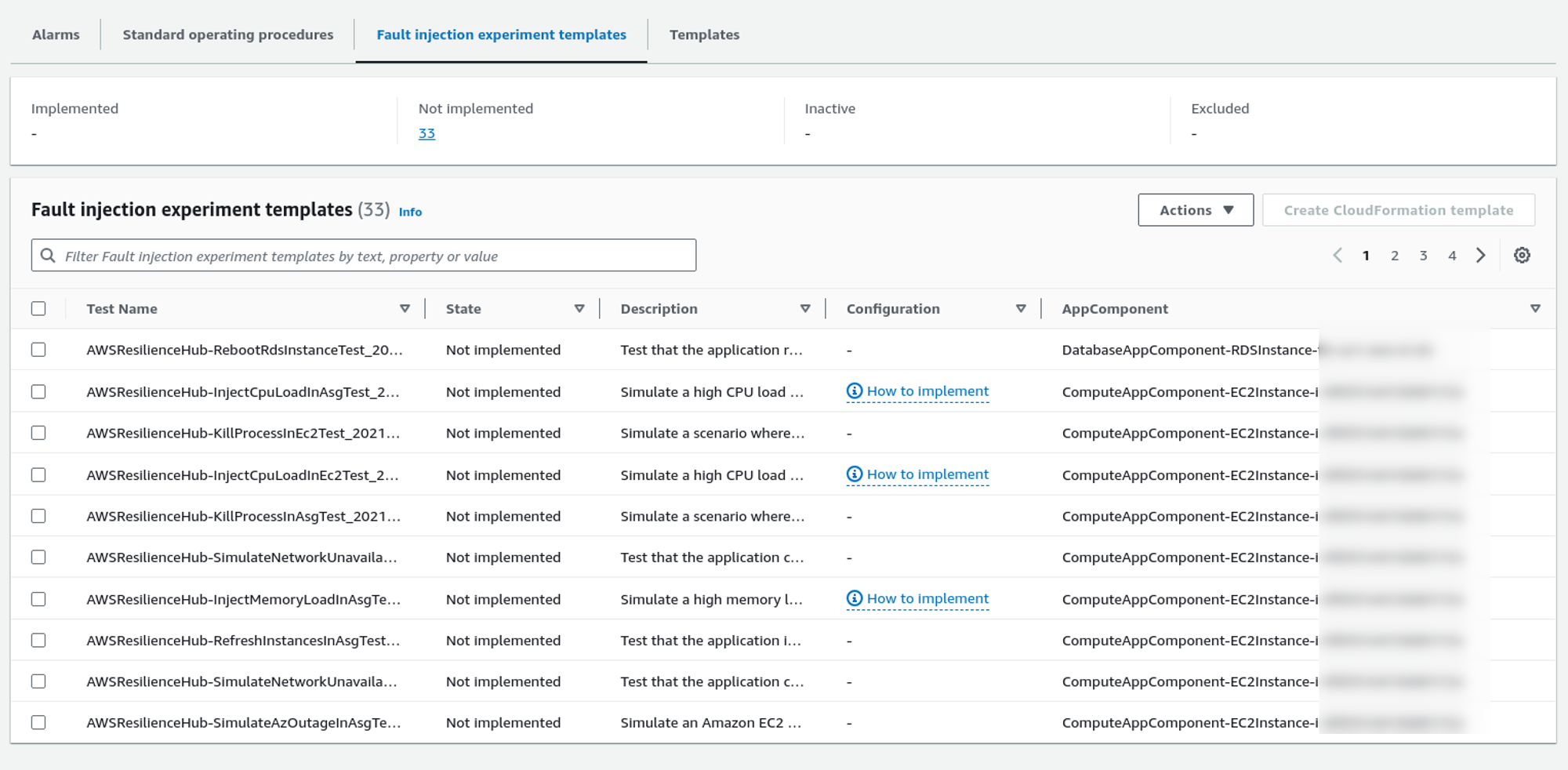
How does the Resiliency Score Work?
The resiliency score tells how resilient your system is based on an analysis made by AWS Resilience Hub. The higher the resiliency score, the higher the system’s resiliency.
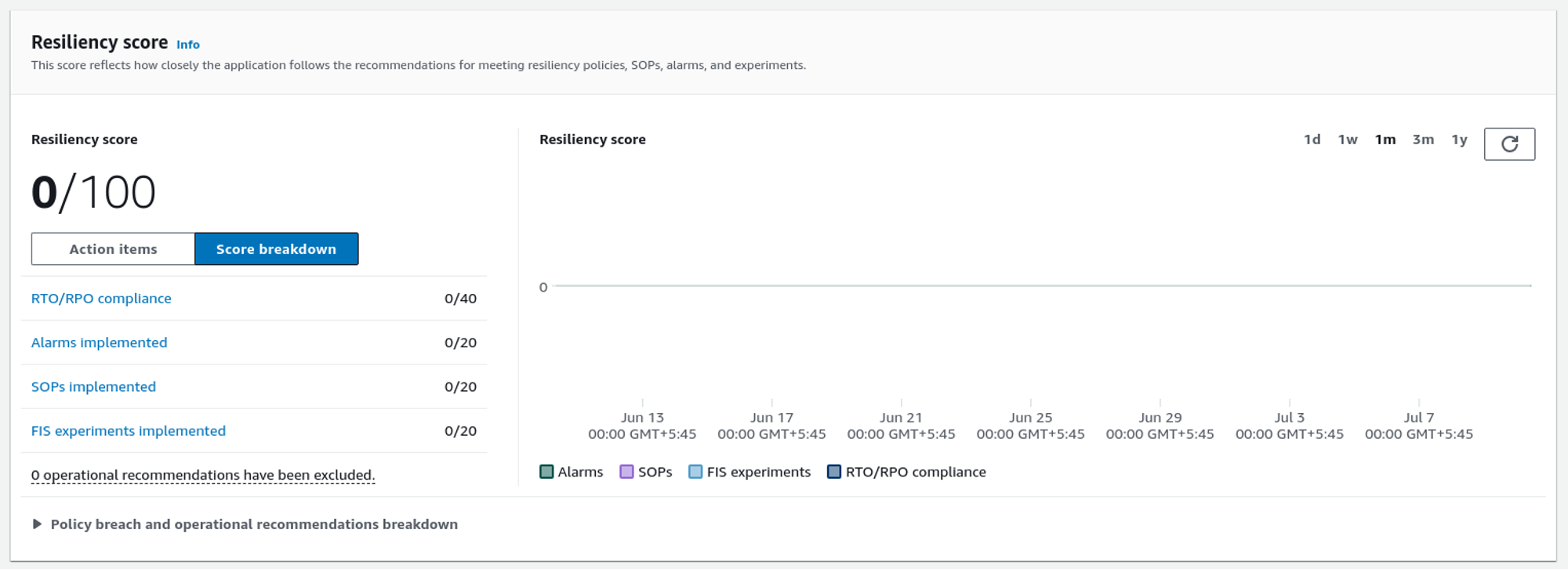
The resiliency score will increase if we implement the recommendation provided by AWS Resilience Hub.
We can also exclude some of the Resilience Hub’s recommendations. To learn how to do so, see this blog.
Conclusion
AWS Resilience Hub helps you build robust applications capable of withstanding various failures and disasters, ensuring business continuity and customer satisfaction. It provides a clear view of your application’s resilience status, identifies potential weak points, and offers actionable recommendations and templates to strengthen your system. It provides detailed assessment reports, along with RTO and RPO objectives.