Patch management is more than just applying security patches and updates; it is about making infrastructure stable and enforcing compliance to prevent vulnerabilities and ensure peak system performance.
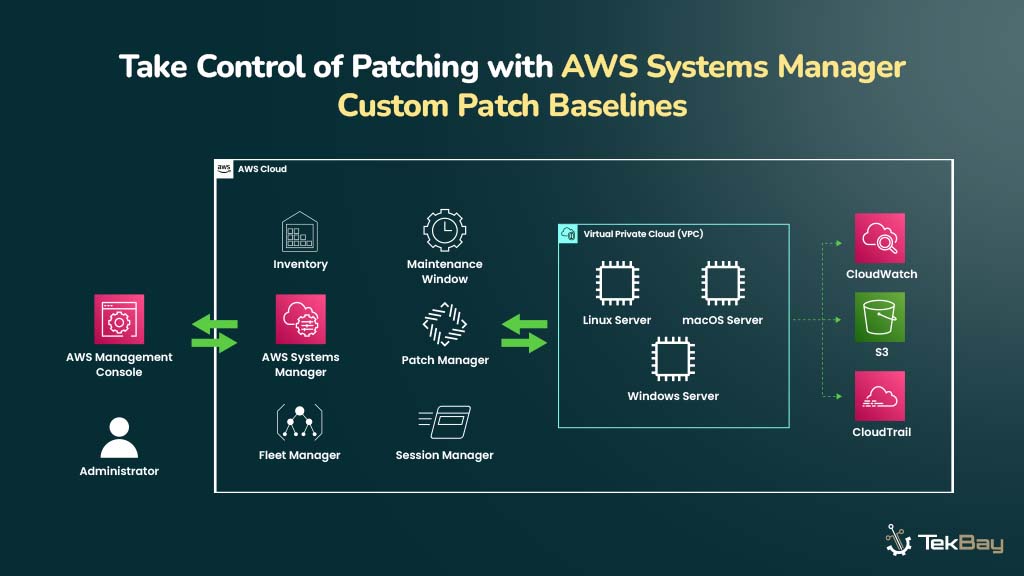
Patch Manager, a feature of AWS Systems Manager, provides default patch baselines. Since these built-in baselines cannot be customized, they may not always meet an organization’s specific needs, such as compliance and operational policies.
In such scenarios, custom patch baselines are preferable because they are tailored to one’s specific requirements, including which patches to apply, when, and under what conditions, across AWS-managed environments.
In this guide, you will learn how to use AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager to create, configure, and apply custom patch baselines to AWS EC2 instances. (The same approach can be used for other AWS-managed instances, such as on-premises servers registered with AWS Systems Manager.)
AWS Systems Manager Patch Baselines: Overview And Benefits
AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager simplifies patch management across AWS services, including Amazon EC2 instances and other AWS-managed resources.
It enables administrators to automate patch deployment using patch baselines, defining which updates to apply, defer, or exclude based on security and compliance policies.
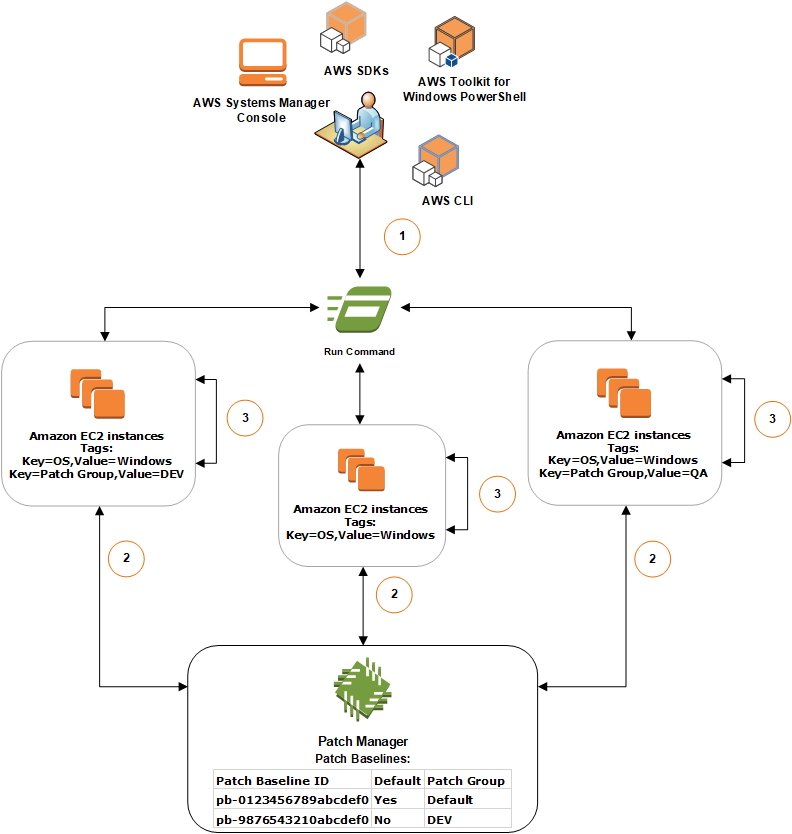
AWS provides default baselines, but custom baselines allow more control over patching policies.
Instances are grouped using tags, allowing different patching rules for environments like Development (DEV), Quality Assurance (QA), and Production (PROD).
Administrators can create, assign, and apply custom patch baselines using the AWS Console, CLI, SDKs, or PowerShell. This ensures that patches are deployed in a controlled and consistent manner.
Read this documentation for more on AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager.
Key Concepts in Patch Management
- Default Patch Baseline: AWS provides default baselines for different OS types, but they might not align with your security policies.
- Custom Patch Baseline: A user-defined baseline that controls which patches are applied and when.
- Patch Groups: A tagging mechanism that ensures specific EC2 instances or managed nodes use the intended custom patch baseline.
Reasons To Use Custom Patch Baselines in AWS Patch Management
- Security-First Approach – Apply only security updates while skipping feature patches.
- Environment-Specific Patching – Different patching strategies for Production, Staging, and Dev.
- Controlled Auto-Approval – Define rules like approval after 7 days or only installation of critical patches.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure you have the following:
- AWS Account with Console and Resource Access
- An EC2 instance running on your account with SSM Agent installed
- Ensure the EC2 instance has an IAM role with the AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore policy attached.
Step-by-Step: Setting Up Custom Patch Baselines for EC2
Step 1: Launch and Configure an EC2 Instance
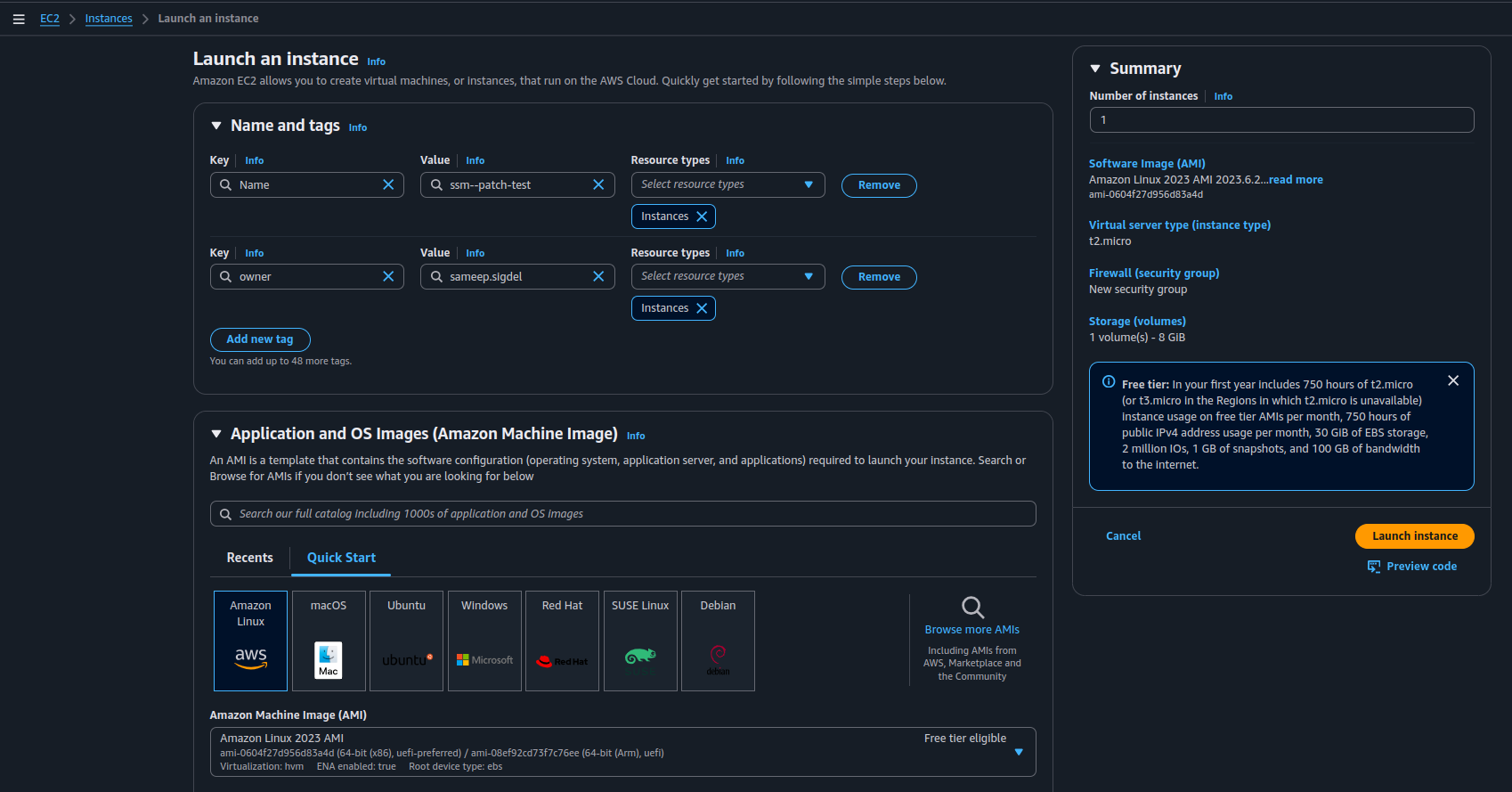
1.1. Create A New EC2 Instance
- Launch an EC2 instance (Amazon Linux 2023).
- Ensure it has outbound internet access or a connection to AWS Systems Manager (SSM) endpoints if it resides in a private subnet within your cloud services infrastructure.
1.2. Attach the Required SSM Policy
- Ensure the EC2 instance profile role includes the AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore policy, which grants necessary permissions for AWS Systems Manager.
- Navigate to IAM > Roles, select the role assigned to the instance, and attach the AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore policy.
Learn more about AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore here.
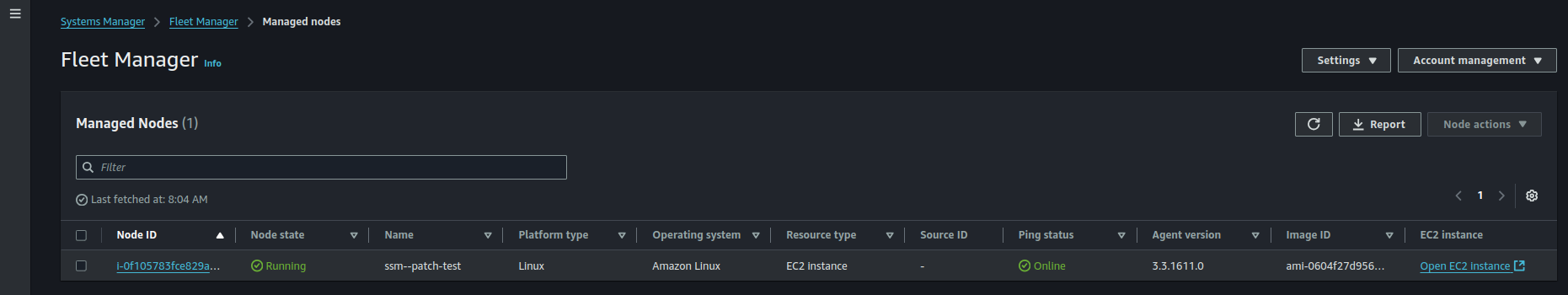
1.3. Verify EC2 Registration in Systems Manager
1. Go to AWS Systems Manager > Fleet Manager.
2. Verify that your instance appears under Managed Nodes. If it is not listed:
- Ensure the SSM Agent is installed and running:
sudo systemctl status amazon-ssm-agent- Verify IAM permissions for the instance.
Step 2: View and Test Patch Baselines
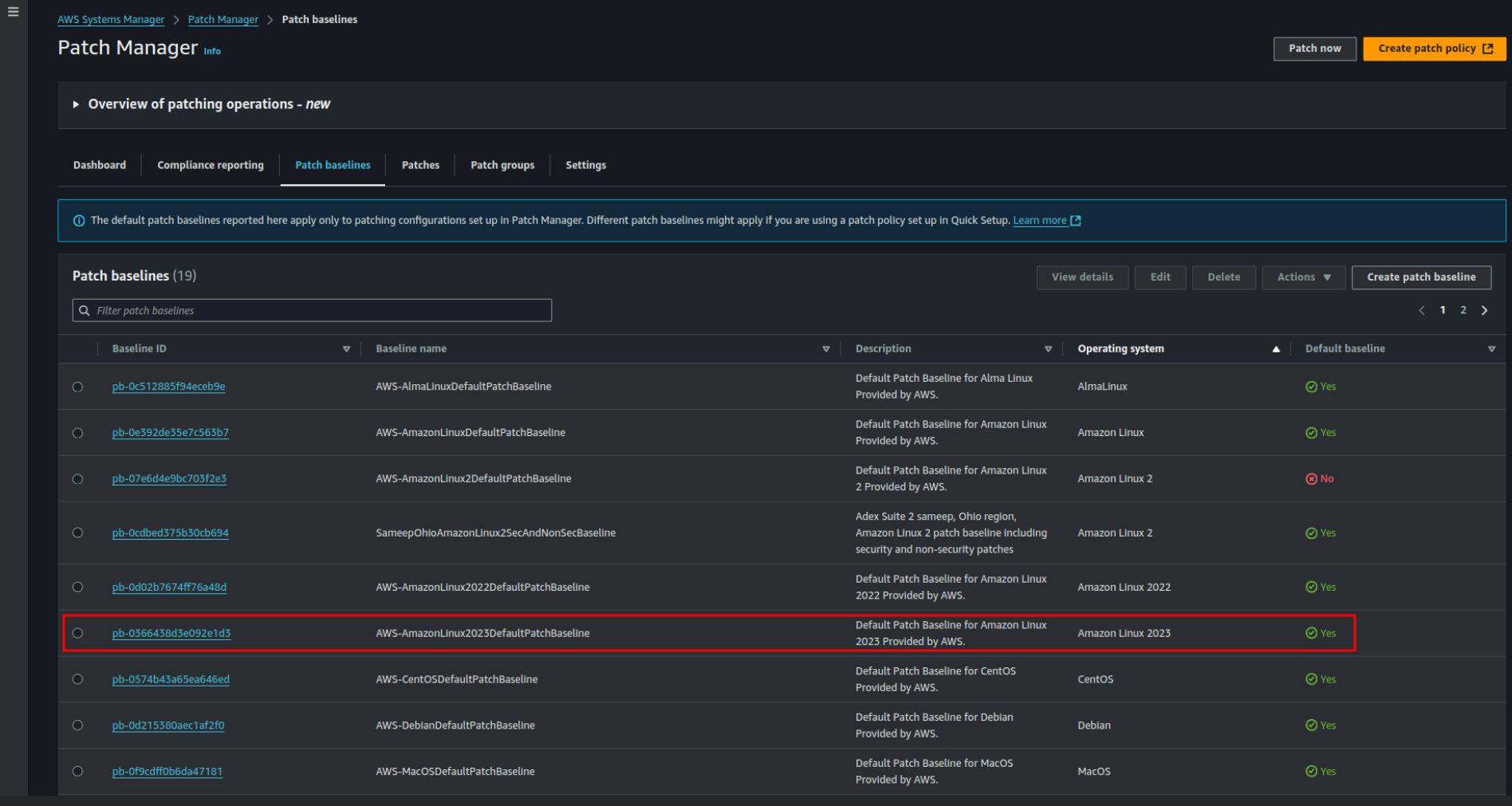
2.1 Check Default Patch Baselines
Go to AWS Systems Manager > Patch Manager. Click on Patch Baselines to view AWS’s predefined patch baselines available for Amazon Linux 2023.
2.2 Test the Default Patch Baseline
In Patch Manager, click Patch Now to initiate the default patching process. After completion, verify the Patch Baseline ID applied (e.g., pb-0366438d3e092e1d3).

Step 3: Create a Custom Patch Baseline
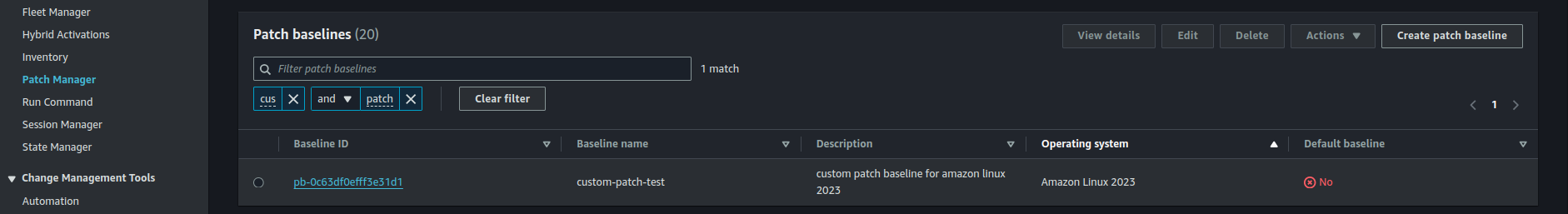
- Click Create Patch Baseline in Patch Manager and configure patch approval rules (e.g., security patches only, auto-approval after X days).
- Save the baseline and note the Custom Patch Baseline ID.

- To confirm its creation, view the custom patch baseline created in the Patch Baseline list under AWS Systems Manager > Patch Manager.
Step 4: Assign the Custom Patch Baseline
AWS automatically applies default patch baselines to instances. So, to ensure that your custom patch baseline is applied instead, use Patch Groups.
Here are the tagging conventions for Patch Groups:
- If Instance Metadata Tags are enabled, use:
PatchGroup. - If Instance Metadata Tags are disabled, use:
Patch Group[By default, it is disabled]
Process To Assign a Patch Group and Tag Instances
1. Assign the Custom Patch Baseline
- Navigate to AWS Systems Manager > Patch Manager.
- Select your custom patch baseline, add a patch group name (e.g., DEV_PATCH_TEST), and save.
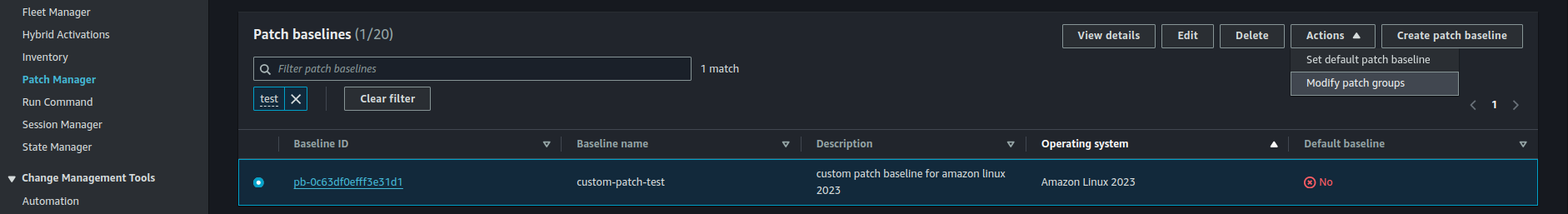
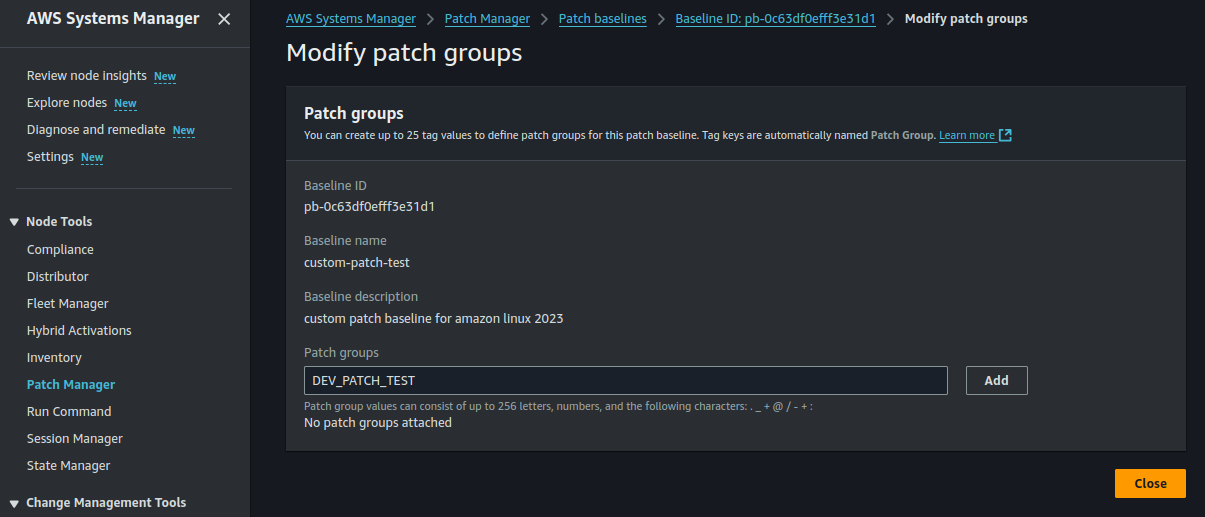
2. Tag EC2 Instances for the Patch Group
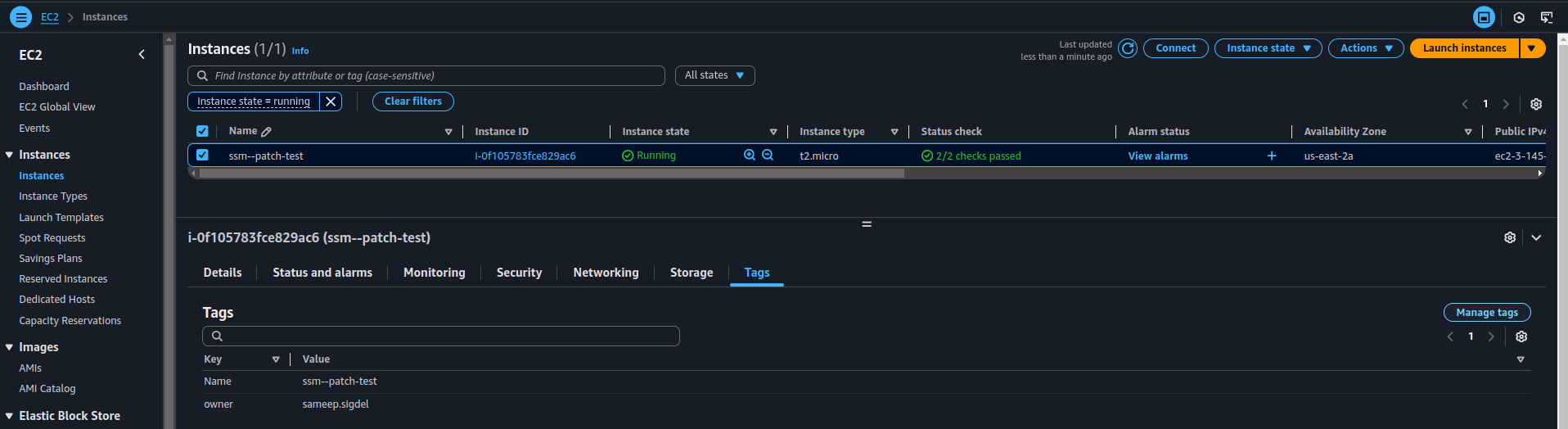
- Navigate to AWS Systems Manager > Patch Manager and select your custom patch baseline.
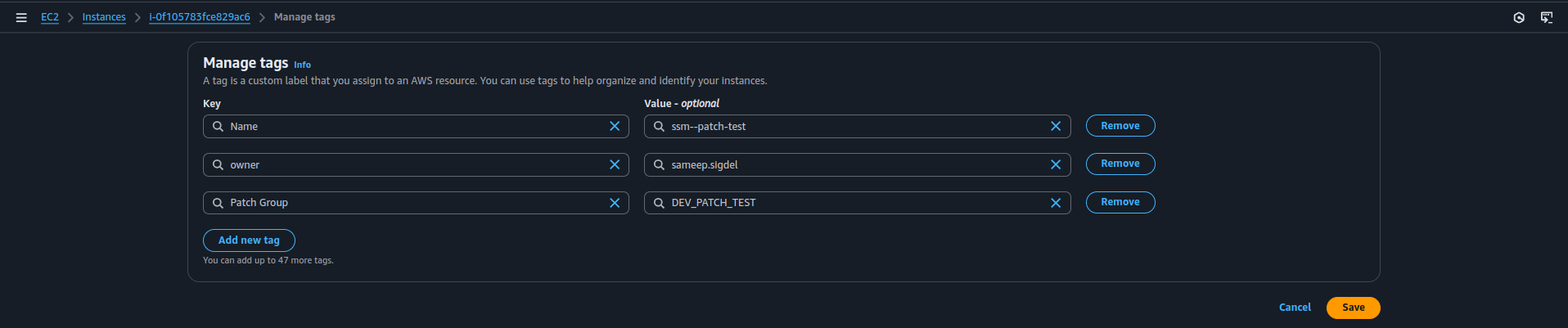
- Click Tags > Manage Tags > Add Tag.
- Set the following key-value pair: Key =
Patch Group, Value =DEV_PATCH_TEST.
Step 5: Confirm Custom Patch Baseline Usage (Before Patching)
Go to Patch Manager > Patch Now. You will see that the instance is already associated with the custom patch baseline instead of the default one.
Notice: You don’t need to manually select the instance for patching because the patch group tag is already assigned, and the instance is associated with the correct patch baseline. This ensures that AWS automatically applies the intended patch baseline.
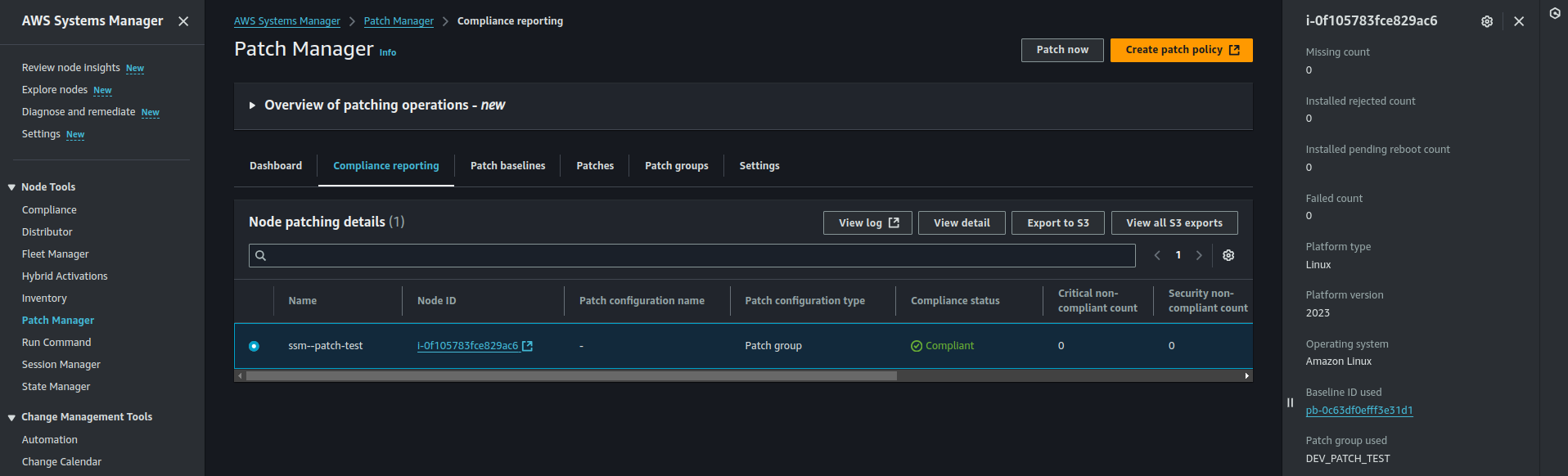
Step 6: Verify the Applied Patch Baseline (After Patching)
After the patching process is complete, check the Patch Baseline ID used. It should match your custom patch baseline ID, confirming that the correct patches were applied.
Conclusion
With default patch baselines, AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager provides a structured approach to managing patches across EC2 instances. However, these built-in baselines may not accommodate an organization’s unique operational policies or security requirements.
Organizations gain complete control over patching strategy by creating custom patch baselines and assigning them through Patch Groups. It ensures precise patching, compliance adherence, and minimal disruptions while aligning with business needs.
Whether managed in-house or through IT outsourcing, AWS Patch Manager offers a scalable solution for enterprise patch management with minimal disruptions.