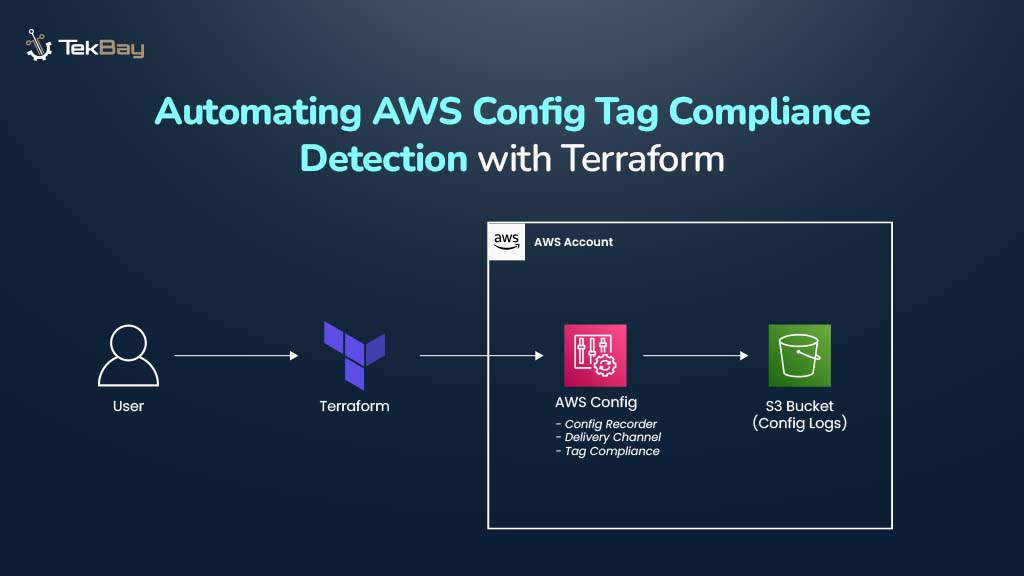
Consistent tagging of AWS resources is vital for governance, cost management, security audits, and operational efficiency. AWS Config provides built-in rules to check if resources have required tags, but manually tracking and enforcing tagging policies can be tedious and error-prone.
By using Terraform, organizations can automate the deployment and management of AWS Config, as well as its tagging compliance rules.
This blog walks through steps to automate AWS Config tag compliance checks using Terraform for consistent, scalable resource tagging.
Why Automate Tag Compliance with AWS Config and Terraform?
Manually setting up and managing AWS Config and its components becomes time-consuming and inconsistent as resources scale across multiple accounts and regions, often leading to unmonitored or non-compliant resources.
To address this issue, Terraform, an infrastructure-as-code (IaC) tool, automates the provisioning and configuration of AWS Config components (such as configuration recorders, delivery channels, and compliance rules) through declarative, version-controlled code.
With Terraform, managing AWS Config compliance becomes:
- Uniformly deployed across accounts and regions by applying Terraform configurations per environment or through centralized automation tooling.
- Effortlessly updated and version-controlled via Git, ensuring quick, scalable propagation of configuration changes.
- Integrated into CI/CD pipelines, enabling automated and consistent deployments with DevOps best practices.
- Fully auditable, with all configurations tracked in version control for complete traceability and governance.
- Reliably maintained with minimal manual intervention, reducing human error and accelerating compliance enforcement.
Guide Overview And Workflow
In this guide, AWS Config is being enabled from scratch and automating tag compliance enforcement using Terraform. The solution will ensure that AWS services like S3 buckets, DB instances, security groups, and VPCs within the account have the required tags to remain compliant.
The Terraform workflow will:
- Create an IAM role so AWS Config can record and evaluate resources.
- (Optional) Configure an SNS topic to send compliance alerts.
- Provision an S3 bucket to store AWS Config logs and snapshots.
- Enable the configuration recorder and delivery channel for tracking changes.
- Deploy a managed rule to check for required tags across targeted resources.
Notes:
- Region-specific: AWS Config must be enabled in each region.
- No retroactive tracking: Compliance checks apply only after enablement.
- Cost model: Pricing is based on the number of active rules and resource evaluations.
Steps to Automate AWS Resource Tag Compliance Detection with Terraform
Step 1: Create an IAM Role for AWS Config
AWS Config needs an IAM role with permissions to record resource configurations and evaluate compliance rules.
resource "aws_iam_role" "aws_config" {
name = "aws_config_role"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [{
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = {
Service = "config.amazonaws.com"
}
Action = "sts:AssumeRole"
}]
})
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "aws_config_attach" {
role = aws_iam_role.aws_config.name
policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSConfigRole"
}Step 2: S3 Bucket Setup for AWS Config Logs
Create an S3 bucket using a reusable Terraform module to store AWS Config snapshots and compliance logs.
module "config_logs_s3" {
source = "./modules/terraform-aws-s3-module"
bucket = "${module.naming.resources.s3.name}-config-logs-bucket"
force_destroy = false
versioning = {
enabled = true
}
attach_policy = true
policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.aws_config_s3_policy.json
tags = module.naming.default_tags
}Step 3: Attach IAM Policy to the S3 Bucket
Grant AWS Config permissions to check bucket permissions, verify bucket existence, and deliver configuration snapshots and logs.
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "aws_config_s3_policy" {
statement {
sid = "AWSConfigBucketPermissionsCheck"
effect = "Allow"
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["config.amazonaws.com"]
}
actions = [
"s3:GetBucketAcl",
"s3:GetBucketLocation"
]
resources = [module.config_logs_s3.s3_bucket_arn]
condition {
test = "StringEquals"
variable = "AWS:SourceAccount"
values = [data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id]
}
}
statement {
sid = "AWSConfigBucketExistenceCheck"
effect = "Allow"
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["config.amazonaws.com"]
}
actions = ["s3:ListBucket"]
resources = [module.config_logs_s3.s3_bucket_arn]
condition {
test = "StringEquals"
variable = "AWS:SourceAccount"
values = [data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id]
}
}
statement {
sid = "AWSConfigBucketDelivery"
effect = "Allow"
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["config.amazonaws.com"]
}
actions = ["s3:PutObject"]
resources = [
"${module.config_logs_s3.s3_bucket_arn}/AWSLogs/${data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id}/Config/*"
]
condition {
test = "StringEquals"
variable = "s3:x-amz-acl"
values = ["bucket-owner-full-control"]
}
condition {
test = "StringEquals"
variable = "AWS:SourceAccount"
values = [data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id]
}
}
}Step 4: Enable AWS Config Core Components
a) Configuration Recorder
Records changes to all supported AWS resource types.
resource "aws_config_configuration_recorder" "main" {
name = "default"
role_arn = aws_iam_role.aws_config.arn
recording_group {
all_supported = true
include_global_resource_types = true
}
}b) Delivery Channel
Sends configuration snapshots and compliance data to the defined S3 bucket.
resource "aws_config_delivery_channel" "main" {
name = "default"
s3_bucket_name = module.config_logs_s3.s3_bucket_id
depends_on = [aws_config_configuration_recorder.main]
}c) Recorder Activation
Starts the configuration recorder to begin monitoring.
resource "aws_config_configuration_recorder_status" "main" {
name = aws_config_configuration_recorder.main.name
is_enabled = true
depends_on = [aws_config_delivery_channel.main]
}Step 5: Deploy AWS Config Rule to Enforce Required Tags
Since AWS Config is now enabled and actively recording, define an AWS-managed Config Rule that validates whether specified resource types have the required tags.
resource "aws_config_config_rule" "required_tags" {
name = "${module.naming.resources.prefix.name}-required-tags-compliance"
description = "Ensure AWS resources are tagged according to compliance requirements"
source {
owner = "AWS"
source_identifier = "REQUIRED_TAGS"
}
input_parameters = jsonencode({
tag1Key = "Environment",
tag2Key = "Project",
tag3Key = "CreatedBy",
tag4Key = "Application",
tag5Key = "Compliance",
tag6Key = "Terraform"
})
scope {
compliance_resource_types = [
"AWS::S3::Bucket",
"AWS::RDS::DBInstance",
"AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup",
"AWS::EC2::VPC"
]
}
depends_on = [aws_config_configuration_recorder_status.main]
}What Does This Rule Do?
This AWS-managed rule (REQUIRED_TAGS) checks whether the listed resource types have the required tags (Environment, Owner, and others that are defined).
Any missing tag causes AWS Config to mark the resource as NON_COMPLIANT, helping organizations enforce governance, cost management, and security policies effectively.
Verifying Tag Compliance Automation in AWS Config
After deploying AWS Config and the tag compliance rule via Terraform, confirm the setup is working by visiting the AWS Config dashboard.
- The configuration recorder should be running and delivering logs to an S3 bucket, supported by the appropriate IAM role.

- The compliance rule is active and evaluating resources, automatically enforcing required tags across key services like S3 buckets, RDS instances, EC2 security groups, and VPCs.

- Non-compliant resources are highlighted on the dashboard, displaying resource IDs and types to facilitate quick identification and remediation of missing tags.

Scaling Tag Compliance Across Accounts with Conformance Packs
For organizations that require broader compliance across multiple accounts or standards (e.g., CIS, HIPAA, NIST 800-53), Conformance Packs provide a scalable solution.
A Conformance Pack is a YAML-based collection of multiple Config Rules and optional remediation actions. While not required for the simple tagging scenario above, they are ideal for implementing full compliance frameworks across an enterprise environment.
Conclusion
Automating AWS resource tag compliance with AWS Config and Terraform transforms compliance from a manual, periodic task into a continuous, automated monitoring process. It provides centralized, auditable compliance results, integrates with CI/CD pipelines, and flags non-compliant resources, ensuring consistent tagging enforcement across accounts and regions with minimal manual effort.