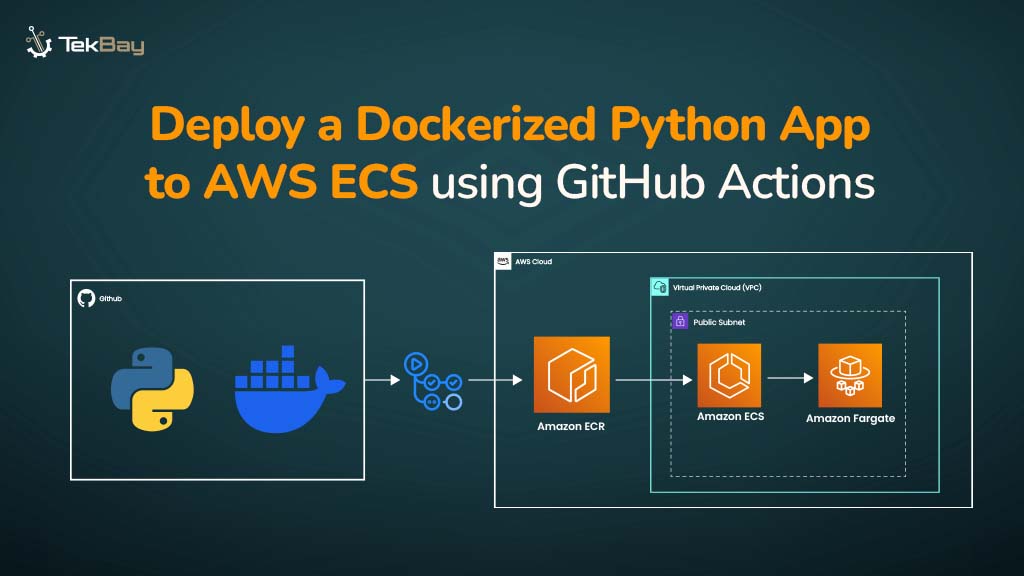
GenAI APIs enable real-time capabilities across various workloads, including intelligent assistants, content creation tools, and more. But when those APIs are hosted in a single AWS region, global users often face slow responses, timeouts, or failed requests—issues that adding compute or caching in one region cannot fully resolve.
As a result, even the best outputs lose value. To deliver fast and reliable responses globally, APIs must be deployed across multiple regions, with user requests routed to the nearest endpoint.
This guide shows how to build a resilient, multi-region GenAI API using AWS services like Amazon Bedrock, API Gateway, Lambda, and Global Accelerator.
Why Use a Multi-Region Architecture for GenAI APIs?
A multi-region architecture for GenAI APIs improves both reliability and performance. By distributing API endpoints across multiple AWS regions, users connect to the nearest location, reducing latency and improving responsiveness worldwide. This setup also increases availability, automatically rerouting traffic if a region experiences issues.
Additionally, it enhances resilience by supporting disaster recovery and maintaining continuous service during regional failures.
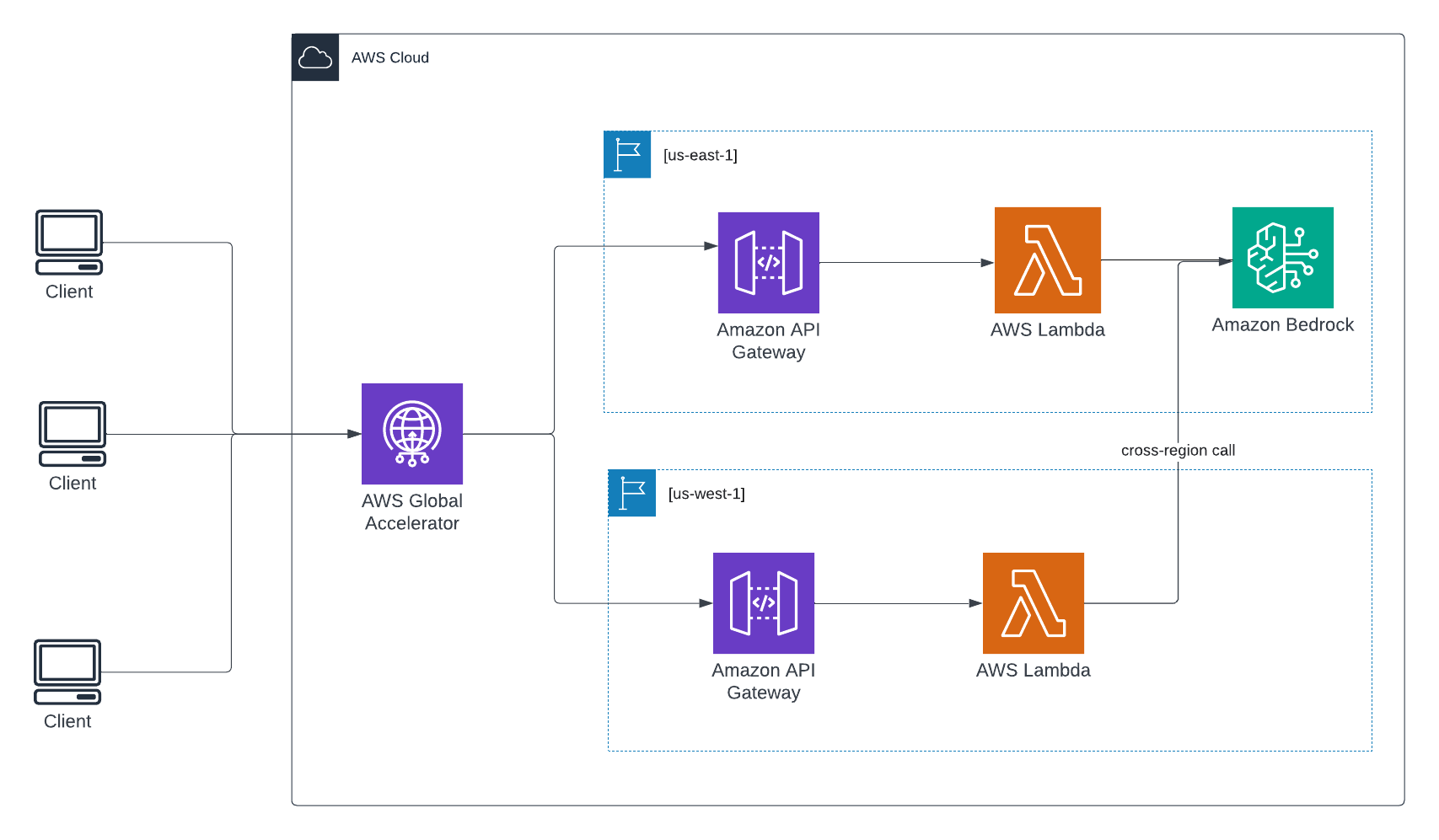
Note: Since Amazon Bedrock is currently available in only a few regions (such as us-east-1), Lambda functions deployed in other regions must invoke Bedrock endpoints in us-east-1 over the network.
Prerequisites
Before going with the deployment steps, ensure the following are in place:
- An AWS account with permissions to create and manage Lambda functions, API Gateway, and Global Accelerator.
- AWS CLI configured (optional: useful for automation or advanced configurations).
- Basic familiarity with the AWS Management Console.
Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1: Create Lambda Functions in Multiple Regions
To ensure low-latency access and regional fault tolerance, deploy identical Lambda functions in multiple AWS regions. Each function routes requests to Amazon Bedrock centrally (e.g., in us-east-1).
1.1. Create the Function
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and navigate to Services > Lambda.
- Click “Create function.”
- Choose Author from scratch, then set:
-Function name (for example, genai-inference-function)
– Runtime (for example, Python 3.11)
- Finalize the setup by clicking Create.
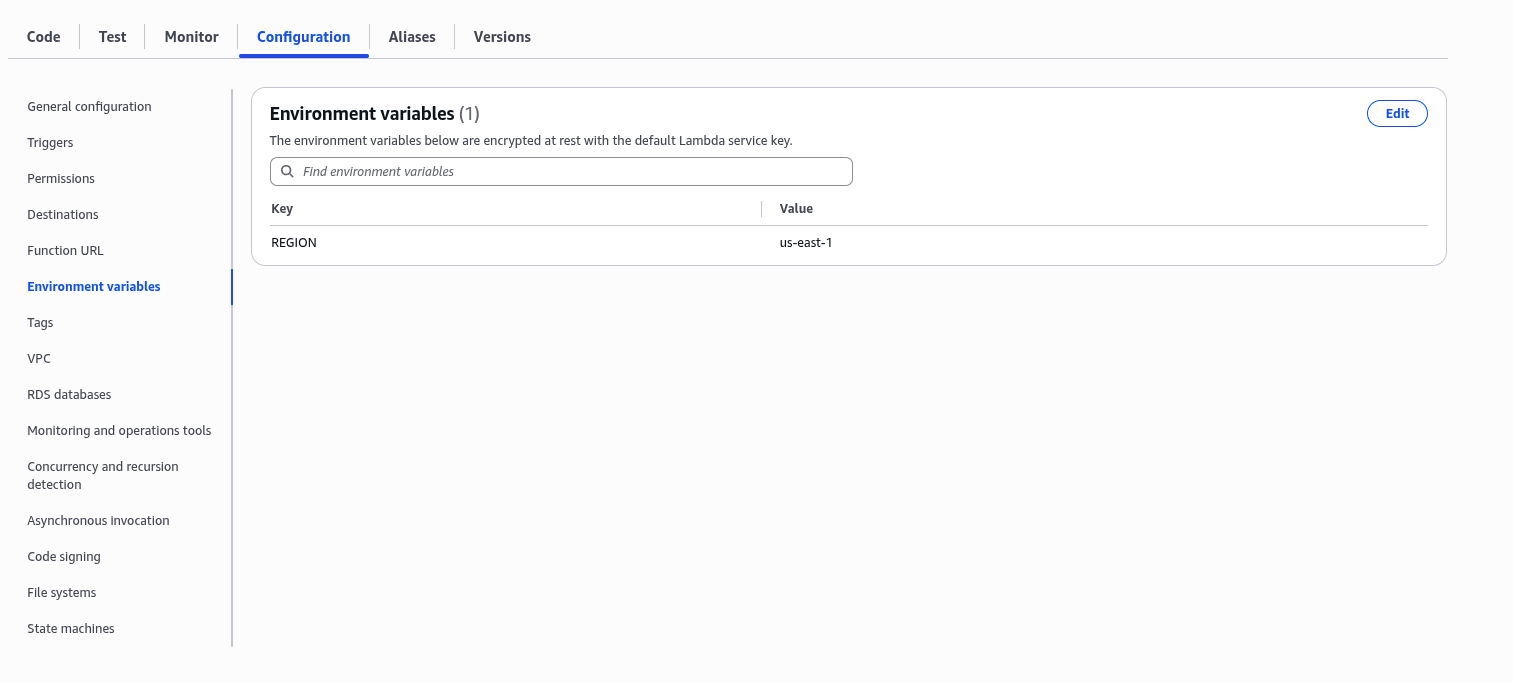
1.2 Add Environment Variable
In the function’s configuration, add an environment variable:
- Key:
REGION - Value:
us-east-1
1.3 Implement the Lambda Function Code
In the Code editor section of the Lambda function console, replace the default code with the following:
import boto3
import json
import os
def lambda_handler(event, context):
region = os.environ['REGION']
bedrock = boto3.client("bedrock-runtime", region_name=region)
body = json.dumps({"prompt": event["body"], "maxTokens": 100})
response = bedrock.invoke_model(
modelId="ai21.j2-mid-v1",
body=body,
contentType="application/json",
accept="application/json"
)
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": response["body"].read().decode()
}1.4 Deploy in Multiple Regions:
Repeat the previous steps to deploy identical Lambda functions in other AWS regions (e.g., eu-west-1). For all functions, keep the REGION environment variable set to us-east-1 to ensure they invoke Amazon Bedrock in the correct region.
Step 2: Create API Gateways in Each Region
API Gateway endpoints created in multiple regions enable reliable, low-latency access to Lambda functions. This setup allows clients worldwide to access the GenAI API with enhanced responsiveness and availability.
2.1 Create a New HTTP API
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and go to Services > API Gateway.
- Click “Create API” to start creating a new API.
- Select “HTTP API” as the API type, then click “Build.”
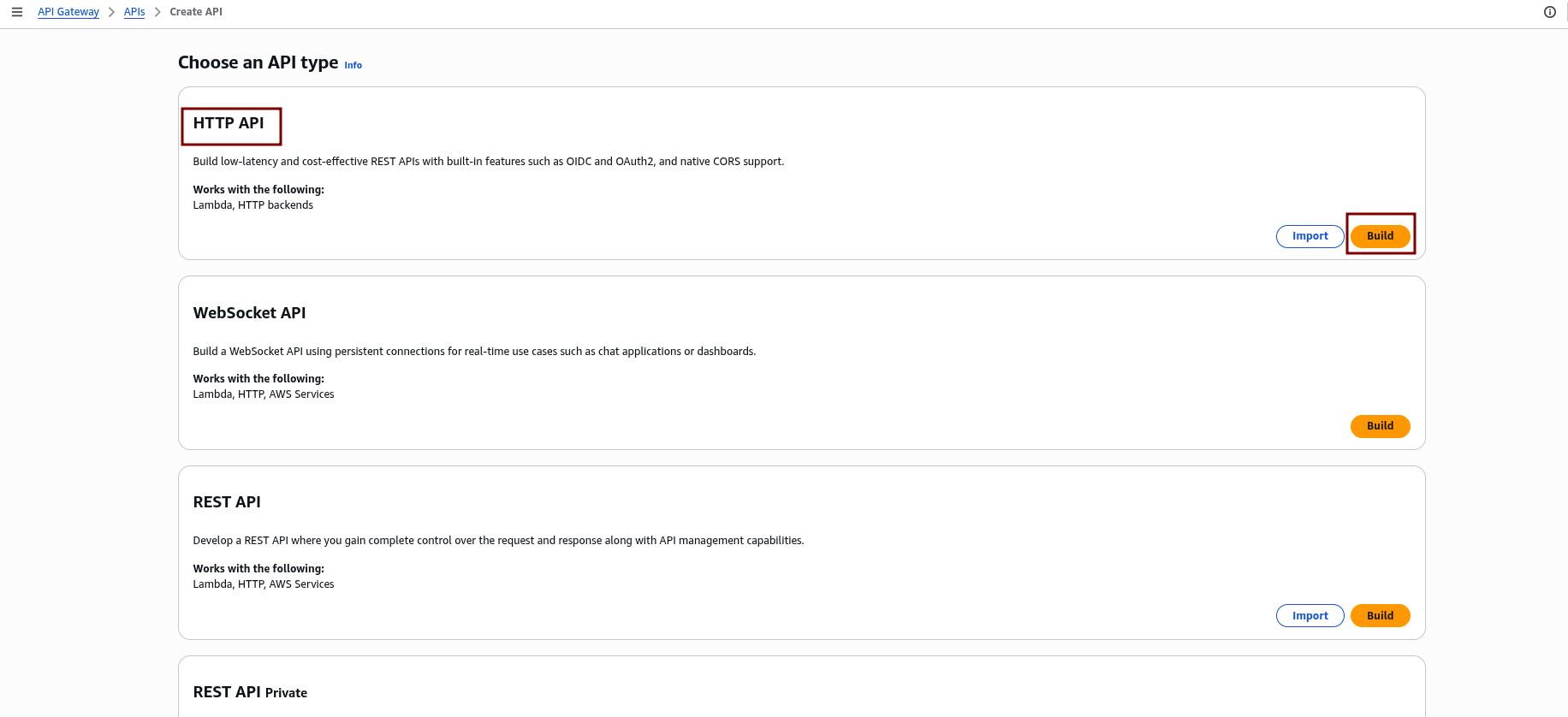
2.2 Configure Integrations
- Under Integrations, click “Add integration” and choose “Lambda.”
- Select the Lambda function created earlier in the same region.
- Click “Next.”
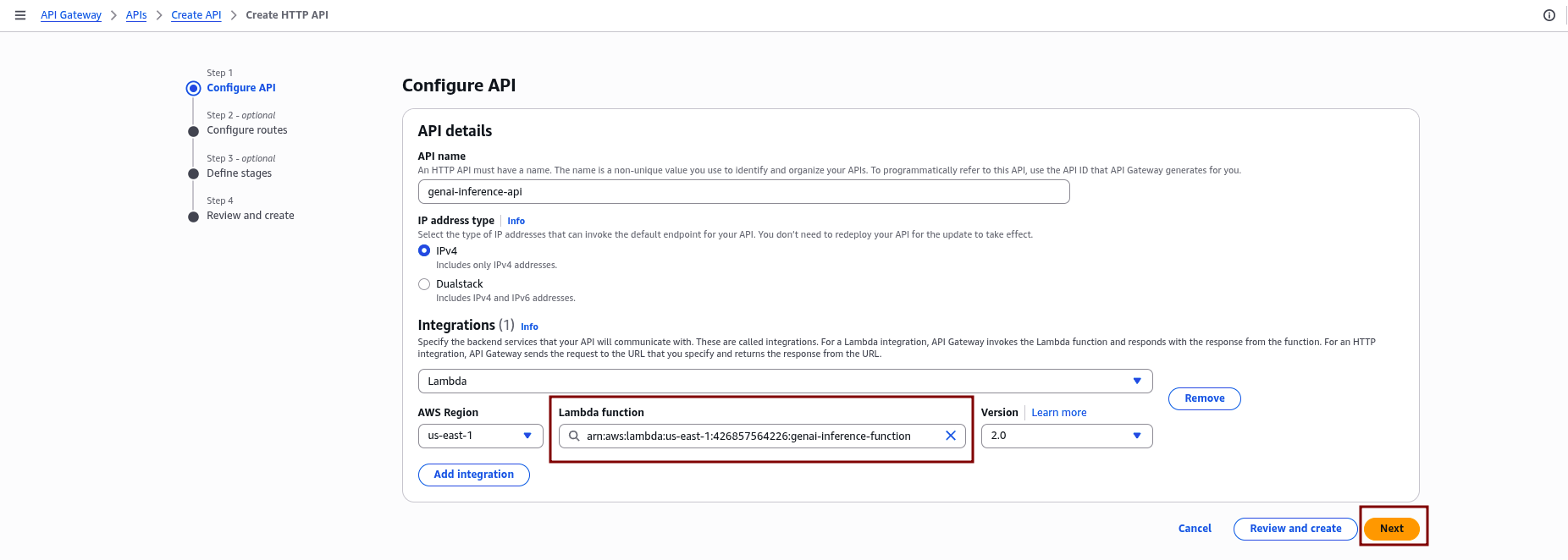
2.3 Define Routes
- In the Configure routes section, define the route for your API, for example:
POST /invoke. - Click “Next”.
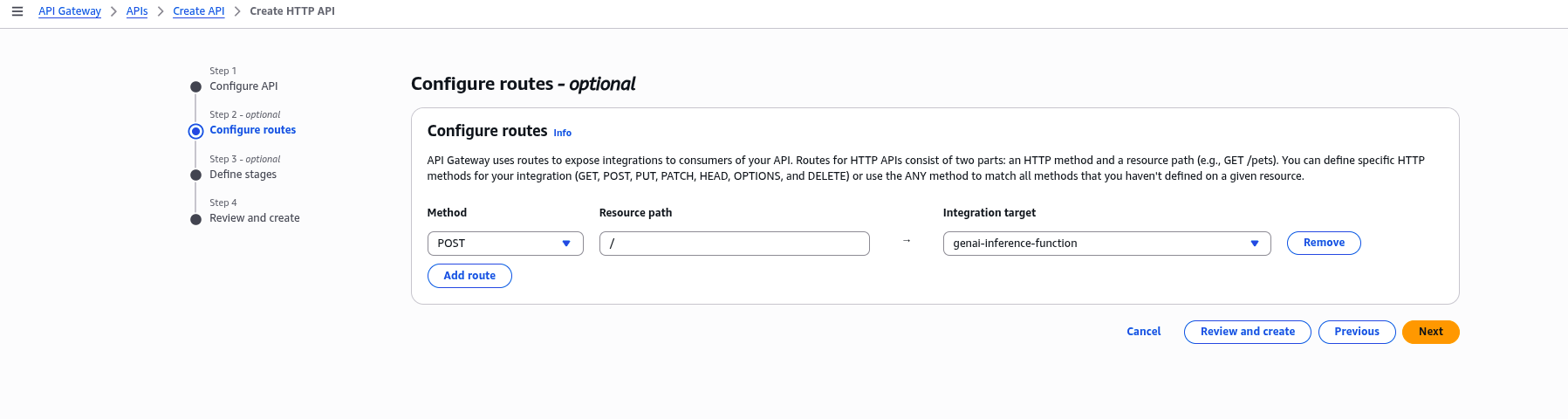
2.4 Configure Stage:
In the Configure stages section, name your deployment stage (for example, prod), and click “Next” to proceed.
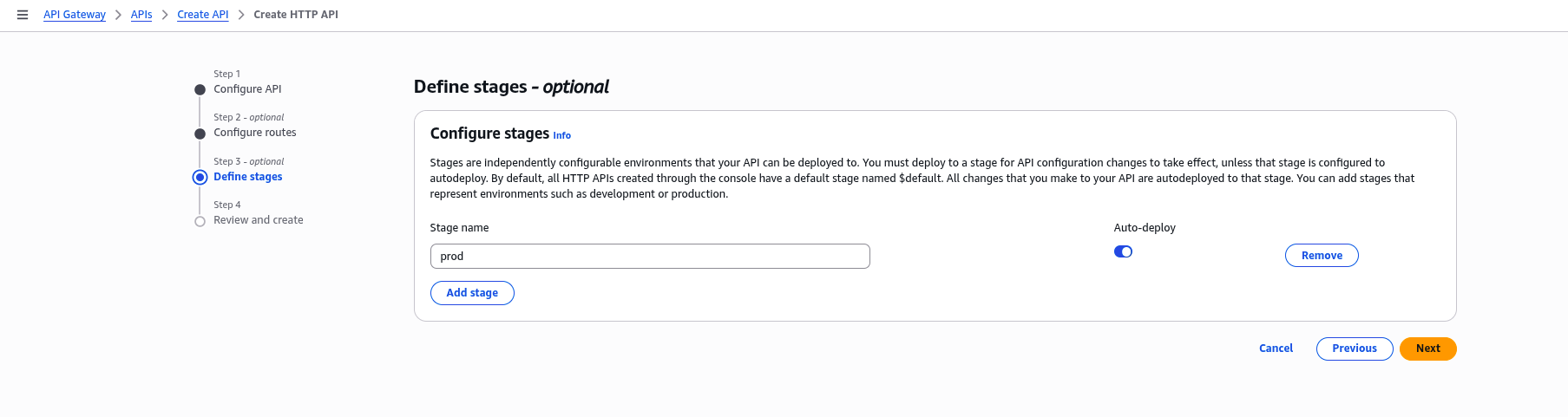
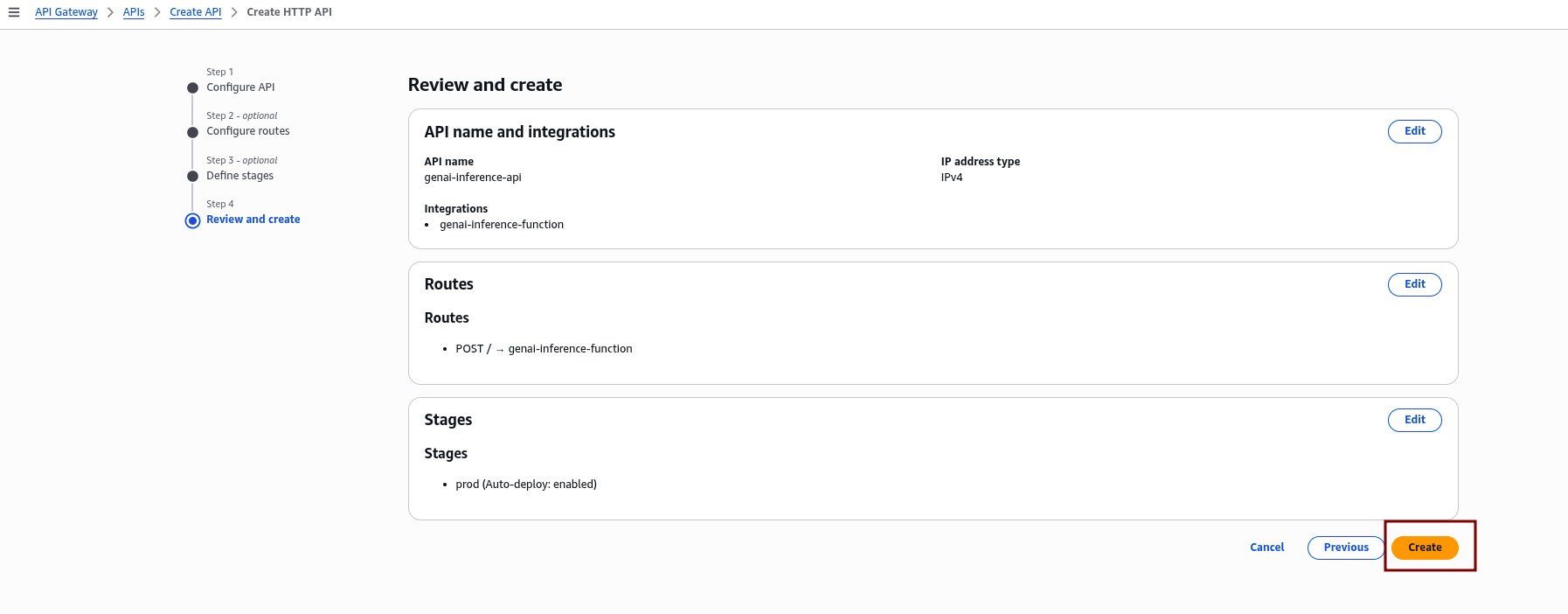
2.5 Review and Create:
Carefully review all the configured API settings, including routes, integrations, and stage details. Once confirmed, click “Create” to finalize and deploy your API.
2.6 Repeat for Other Regions:
Repeat the steps above to create API Gateways in additional regions, making sure to integrate each with its corresponding Lambda function.
Step 3: Set Up AWS Global Accelerator
AWS Global Accelerator improves global availability and performance by routing user traffic to the nearest healthy regional API Gateway endpoint.
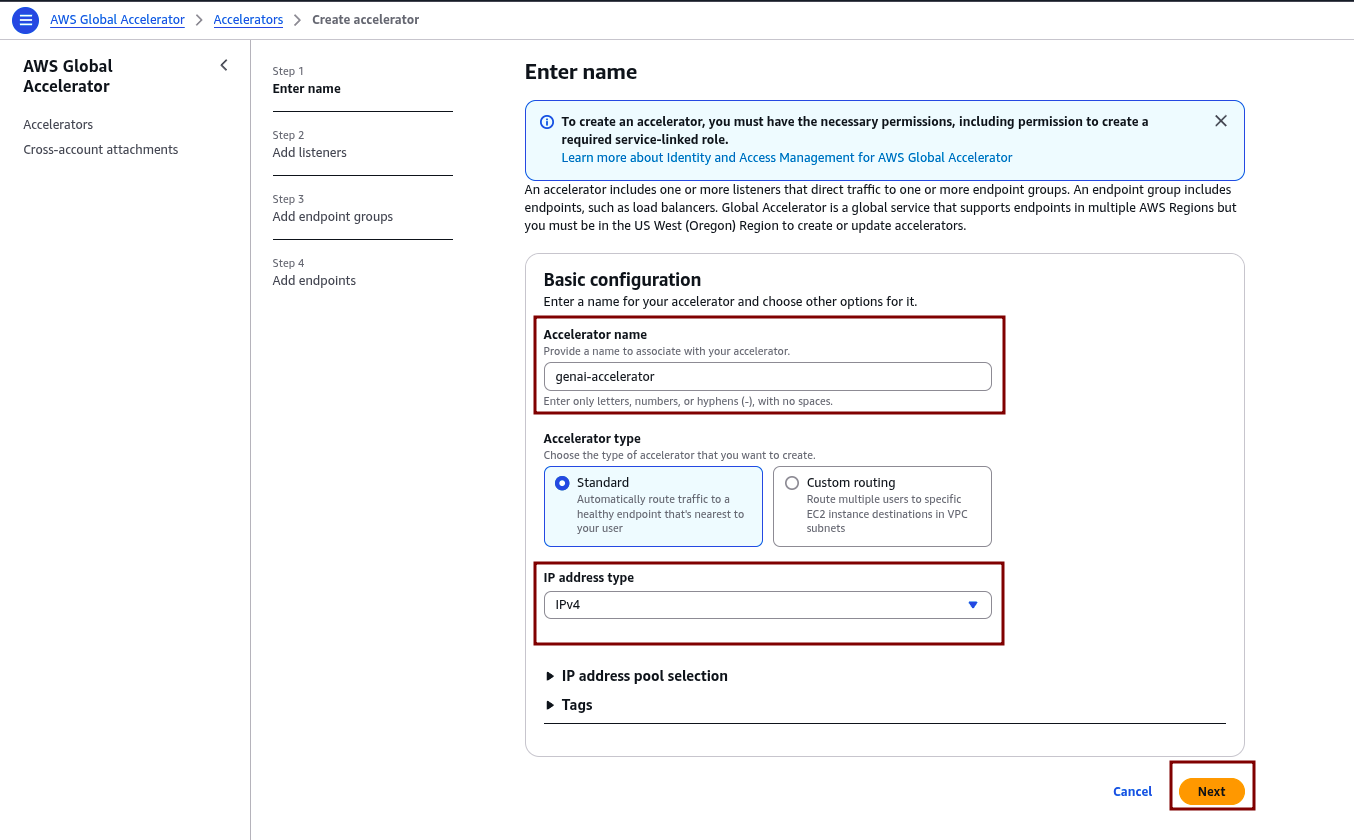
3.1 Create a New Global Accelerator
- In the AWS Management Console, navigate to Services > Global Accelerator.
- Click on “Create accelerator.”
- Enter a name for the accelerator (e.g., genai-accelerator).
- Select Standard as the accelerator type, and choose IPv4 for the IP address type.
- Click “Next.”
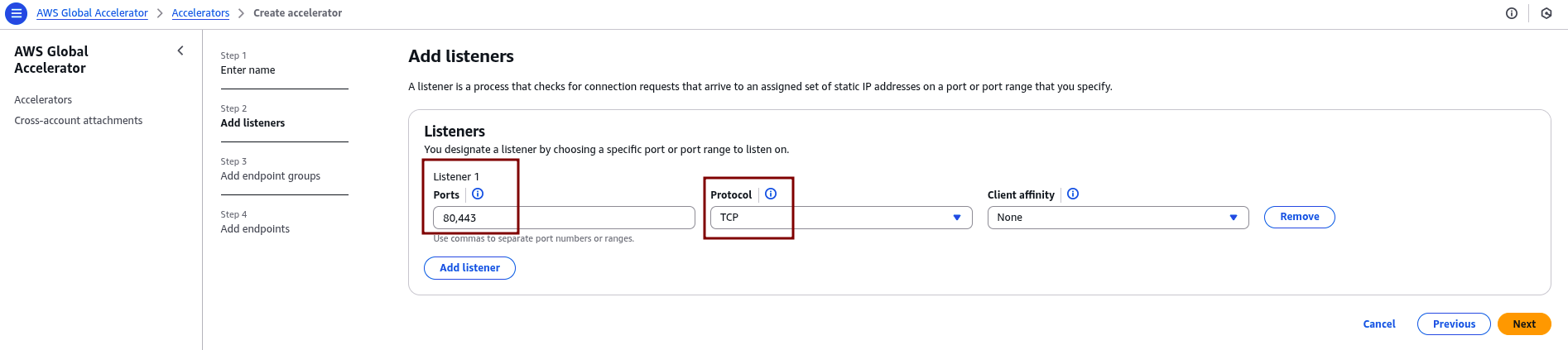
3.2 Configure Listener
After completing the accelerator creation, proceed to configure the listener settings:
- Protocol: TCP
- Ports: 80, 443 (or as per your API’s requirements)
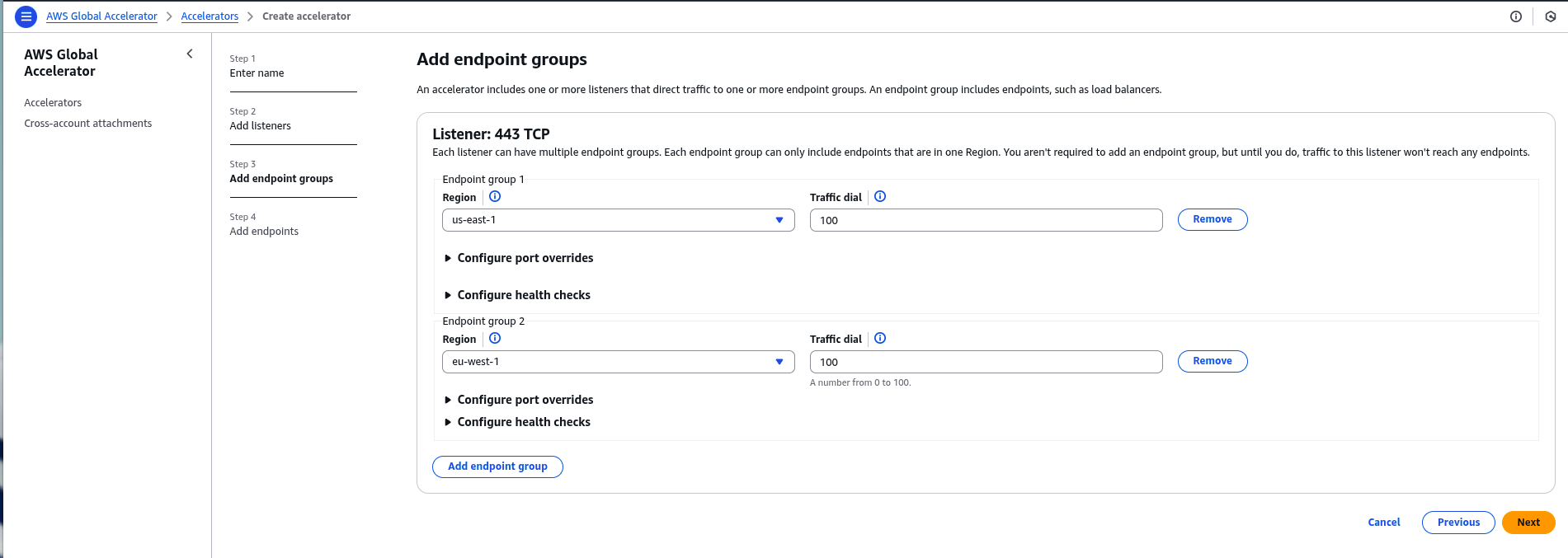
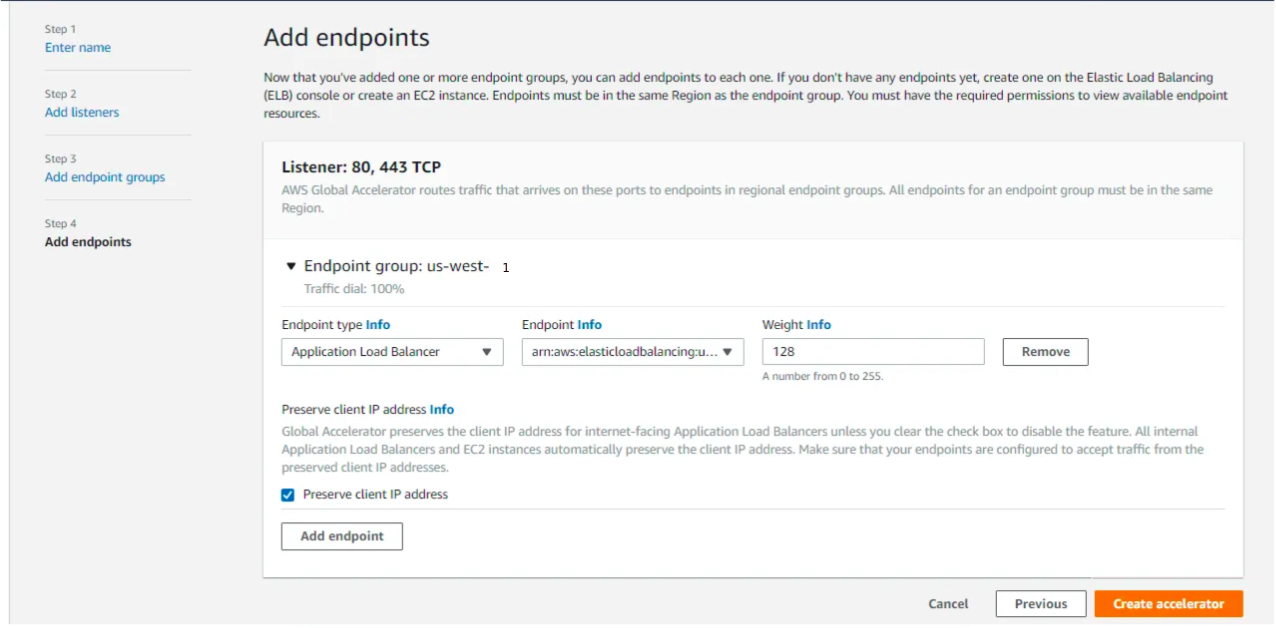
3.3 Add Endpoint Groups
For each region where the API Gateway is deployed (e.g., us-east-1, eu-west-1):
- Click “Add endpoint group.”
- Select the region.
- Under endpoint settings, choose the Application Load Balancer (ALB) or Network Load Balancer (NLB) that fronts the API Gateway or Lambda function in that region.
- Configure health checks and traffic dial percentage as needed.
3.4 Review and Create
Review all settings and click “Create accelerator.“
Step 4: Test and Validate
4.1 Obtain the Global Accelerator DNS Name
In the AWS Global Accelerator console, locate and copy the DNS name assigned to your accelerator.
4.2 Send Test Requests
Use curl or any HTTP client to send a POST request to the accelerator endpoint, for example:
curl -X POST https://<global-accelerator-dns>/invoke -d '{"prompt": "Explain AI"}'A successful response indicates the API is reachable through the Global Accelerator.
4.3 Verify Regional Routing
Use network diagnostic tools such as traceroute or online latency testers to confirm traffic routes to the nearest healthy endpoint.
For example, running traceroute to the DNS name from different geographic locations should show traffic reaching the regional load balancer closest to that location. This confirms Global Accelerator is correctly directing users to the nearest endpoint, ensuring low latency and high availability.
Security Best Practices
Deploying GenAI APIs across multiple regions increases their exposure to the internet, making it critical to secure every layer of the architecture.
- IAM Roles: Assign least privilege permissions to Lambda functions, allowing only necessary actions (e.g.,
bedrock:InvokeModel). - Authentication: Implement API keys or integrate with Amazon Cognito for API authentication.
- Monitoring: Enable CloudWatch Logs for Lambda and API Gateway to monitor and debug issues.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Consider integrating AWS WAF to protect against common web exploits.
Cost Considerations
Each component that powers a GenAI API’s speed, reliability, and global reach comes with its cost profile. Understanding where expenses scale helps maintain performance without letting costs spiral out of control.
- AWS Global Accelerator: Charges include a fixed hourly rate and data transfer fees.
- Amazon Bedrock: Costs are based on model usage and token consumption.
- Lambda & API Gateway: Pay-per-use pricing based on the number of requests and compute time.
- Monitoring: Use AWS Cost Explorer to monitor and manage expenses.
Conclusion
This guide demonstrates how to build a globally available, multi-region GenAI API using Amazon Bedrock, API Gateway, Lambda, and AWS Global Accelerator. It addresses the limitations of single-region deployments by distributing workloads across multiple regions to improve latency, availability, and resilience.
The solution leverages serverless services that scale automatically and ensure fault tolerance through cross-region failover. This architecture is ideal for GenAI applications requiring high performance and global reach.