Delivering real-time stock market data efficiently to millions of concurrent users is a significant challenge for modern applications. Traditional server-based architectures often struggle with unpredictable traffic spikes and high performance demands.
Serverless architectures offer a compelling alternative by enabling automated scaling, reducing operational complexity, and providing cost-effective handling of fluctuating workloads.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through building a serverless backend system that delivers stock market data reliably and at scale, leveraging AWS services such as Lambda and DynamoDB, along with API Gateway’s caching capabilities.
What Makes Building Stock Market Data Systems Challenging?
The modern stock trading market is a high-stakes environment where every millisecond in real-time data delivery can directly impact profit or loss. To build backend systems that handle stock market data at scale, you need to understand both the market’s unique demands and the technical challenges involved:
- Highly Volatile Data – Prices change rapidly, requiring real-time updates.
- Variable Demand – Market opens, earnings reports, and economic events create traffic spikes.
- Low Latency Requirements – Traders need immediate access to current prices.
- Historical Data Access – Analysis requires both current and historical pricing.
With these challenges in mind, let’s explore how a serverless approach can help overcome them.
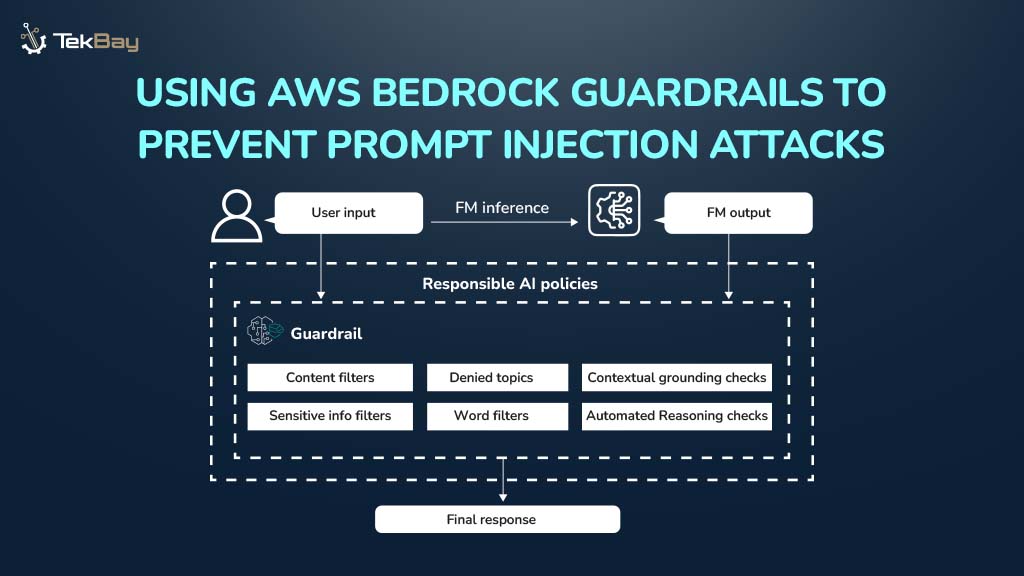
Architecture Solution: How It Addresses The Use Case
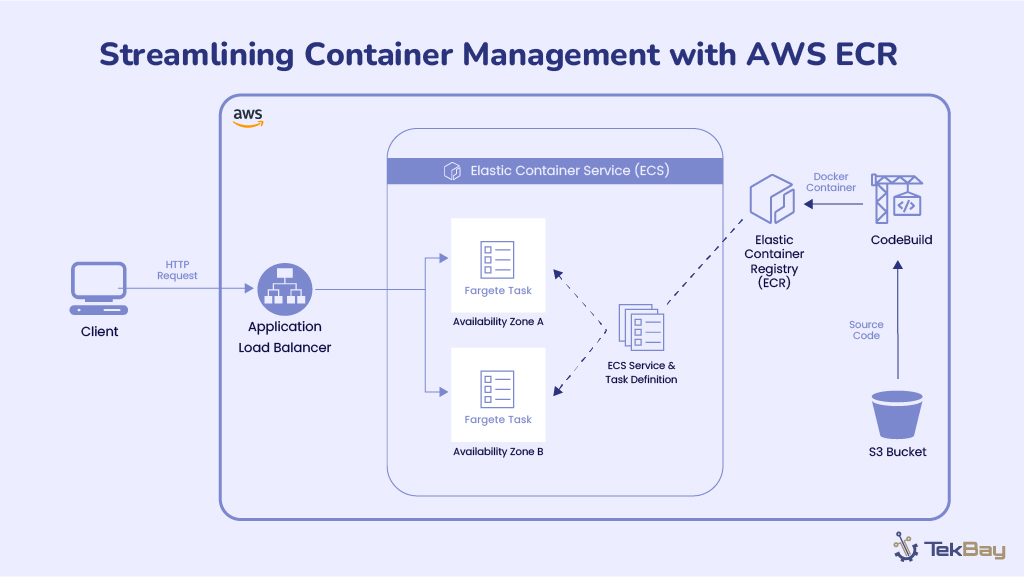
To address the challenges of delivering real-time stock market data, this solution utilizes a serverless architecture with AWS SAM and a carefully selected set of AWS services like DynamoDB, API Gateway, AWS Lambda, AWS X-Ray, and CloudWatch.
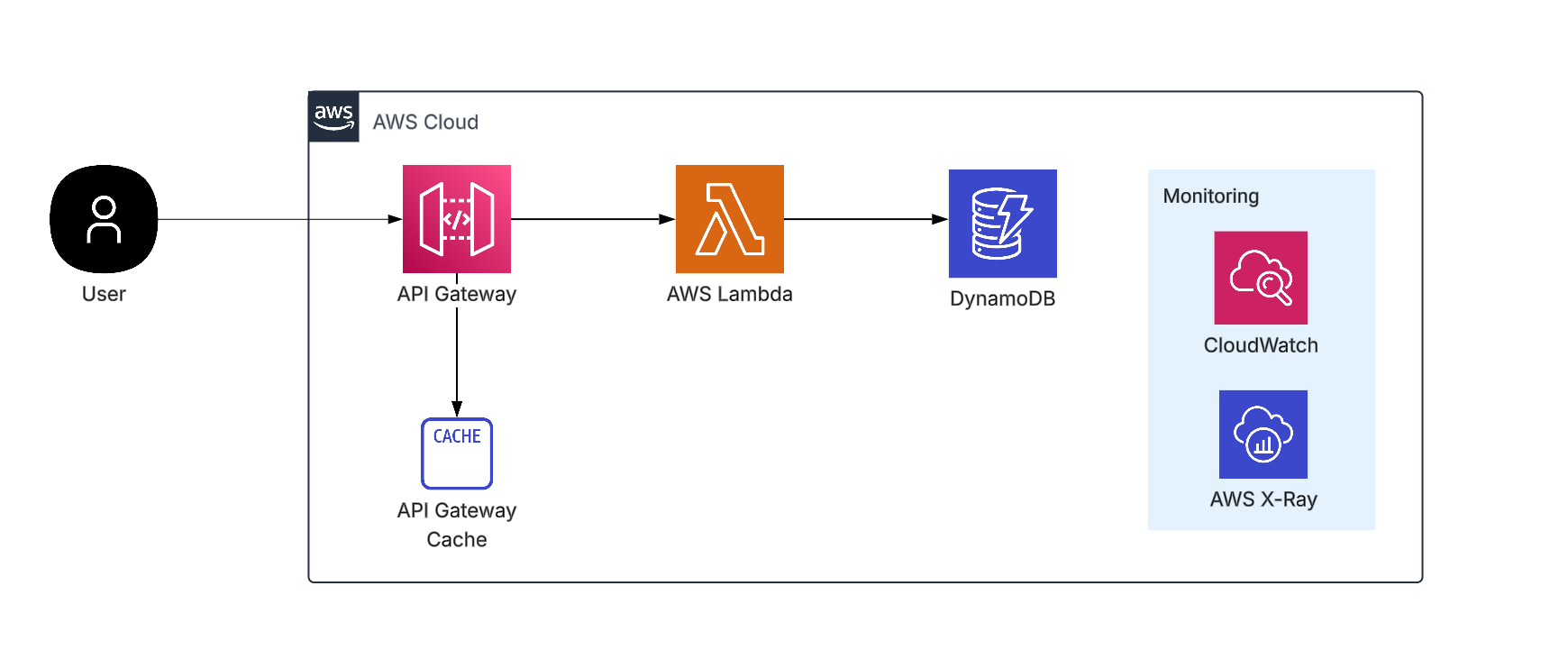
Core Services And Their Capabilities
1 . DynamoDB
- Stores stock data with composite keys (stockId + timestamp) for lightning-fast retrieval of current and historical prices.
- Automatically partitions data to maintain consistent performance at scale.
2. API Gateway
- Serves RESTful endpoints with selective caching to reduce latency.
- Critical price queries bypass the cache to ensure real-time accuracy.
3. AWS Lambda
- Handles data processing and updates.
- Manages event-driven cache invalidation to ensure fresh data is maintained.
4. Monitoring and Operations (X-Ray, CloudWatch)
- Provides end-to-end visibility and performance monitoring.
5. AWS SAM and CI/CD Pipelines
- Enables automated, consistent deployments for streamlined operations
Prerequisites
To follow the steps below, ensure you have the following:
AWS Account Setup:
- An active AWS account with appropriate permissions for Lambda, API Gateway, DynamoDB, and CloudFormation.
- IAM user configured with programmatic access and necessary service permissions.
Development Tools:
- AWS CLI: Installed and configured with your AWS credentials (aws configure).
- AWS SAM CLI: Required for building and deploying serverless applications.
- Docker: Needed for local building and packaging of Lambda functions.
- Git: To clone the project repository.
- Python 3.12: Runtime environment for Lambda functions (ensure it’s added to your system PATH).
- Postman or curl: For testing API endpoints and analyzing cache behavior.
Steps to Build a Serverless Stock Market Data API
1. Core Setup and Deployment
Step 1: Install SAM CLI
- Download and install the AWS SAM CLI to manage your serverless app:
curl -Lo aws-sam-cli-linux-x86_64.zip https://github.com/aws/aws-sam-cli/releases/latest/download/aws-sam-cli-linux-x86_64.zip
unzip aws-sam-cli-linux-x86_64.zip -d sam-installation
sudo ./sam-installation/install- Verify the installation:
sam --versionStep 2: Clone the Repository
- Clone the project repository to download all required resources, including Lambda functions, SAM templates, and configuration files.
git clone https://github.com/soocrates/SAM-App-API-GW-Cache-Lambda-DynamoDB
cd SAM-App-API-GW-Cache-Lambda-DynamoDBProject Structure Overview:
├── cache_invalidator/
│ └── app.py # Cache invalidation Lambda function
├── events/
│ └── event.json # Test event data
├── samconfig.toml # SAM configuration file
├── stock_api/
│ ├── app.py # Main stock API Lambda function
│ └── requirements.txt # Python dependencies
└── template.yaml # SAM infrastructure template
Step 3: Validate SAM Template
The following command checks the SAM template for syntax errors and validates the resource definitions.
sam validateStep 4: Build the Application
Run the following command to download dependencies and prepare the Lambda functions for deployment:
sam buildStep 5: Deploy the Stack
Run the following command to start a guided deployment:
sam deploy --guidedThe guided deployment prompts for configuration options on the first run and creates a samconfig.toml file to store these settings for future deployments.
2. Post-Deployment Verification and Testing
2.1 Verify AWS Resources
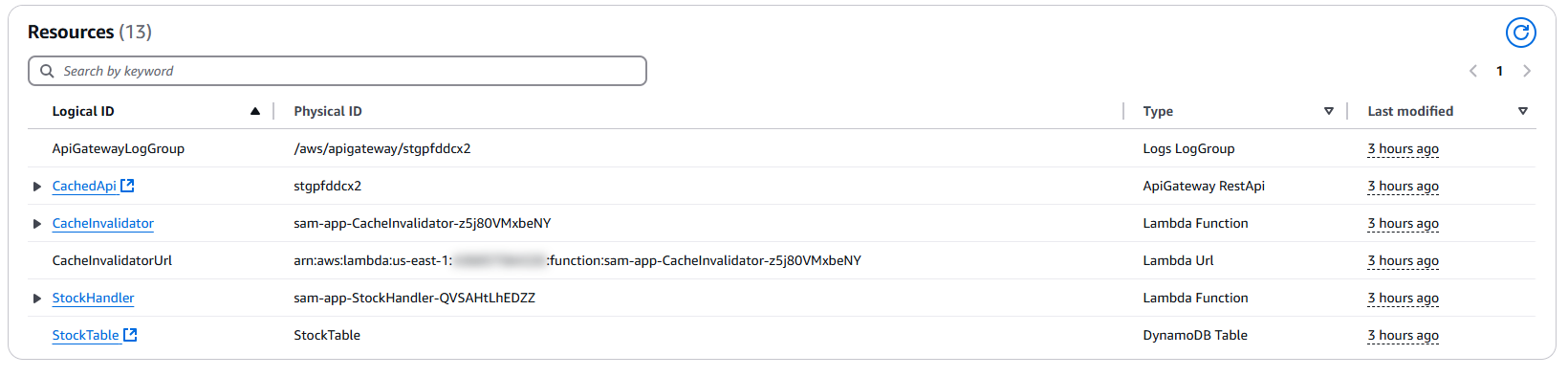
Ensure the following AWS resources were created successfully after deployment:
- DynamoDB Table: StockTable
Composite key structure withstockId(Partition Key) andtimestamp(Sort Key). - API Gateway: REST API with caching enabled to improve performance.
- Lambda Functions:
– StockHandler: Main API processing function.
– CacheInvalidator: Manages cache invalidation. - IAM Roles: Proper permissions assigned for Lambda, API Gateway, and DynamoDB.
- CloudWatch Logs: Centralized logging setup for monitoring and debugging Lambda and API Gateway activities.
2.2 Trigger Cache Invalidation
Cache invalidation is important to ensure that stale data is cleared from the API Gateway cache when underlying data changes.
- Open the AWS Lambda Console and select the
CacheInvalidatorLambda function from the list. - Locate and copy the Function URL (which looks like,
https://<id>.lambda-url.<region>.on.aws/). - Open a new browser tab and paste the Function URL.

2.3 Verify DynamoDB Stock Data
Confirm that the DynamoDB table contains the expected test data and that its structure is correct.
a) Navigate to the AWS Console → DynamoDB → Tables → StockTable.
b) Click Explore table items to view data entries.
c) Observe the data schema:
- Partition Key:
stockId(String) - Sort Key:
timestamp(Number) - Sample attributes: price, volume, lastUpdated
Alternatively, run this AWS CLI command to retrieve a sample item:
aws dynamodb scan table-name StockTable \
--limit 5 \
--query "Items[0]" \
--output json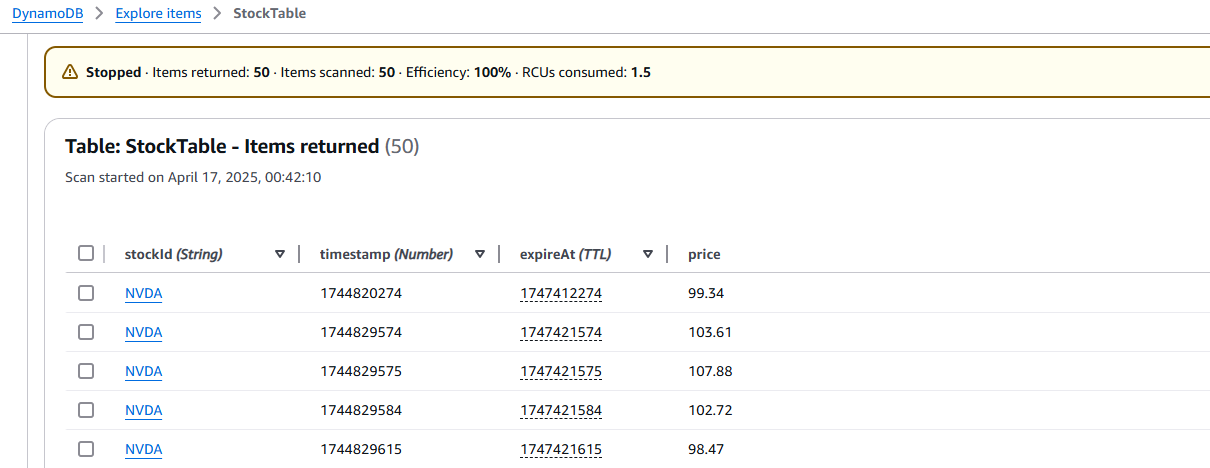
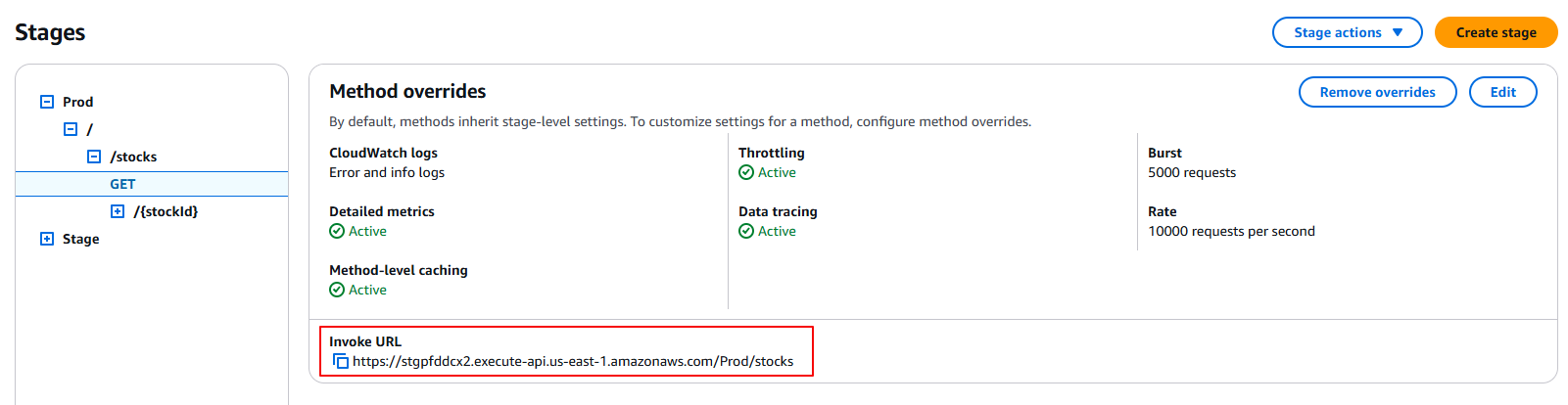
2.4 Retrieve API Gateway Invoke URL
Get the URL to call your deployed API using these steps:
- Navigate to the API Gateway Console → APIs → Select your API (e.g., CachedApi).
- In the left sidebar, click “Stages” and select your deployed stage name (usually
Prod). - Copy the Invoke URL displayed in the stage details, for example:
https://{api-id}.execute-api.{region}.amazonaws.com/Prod).
3. Monitoring Cache Performance
To validate the caching behavior, controlled tests using Postman with precision timing enabled were conducted. The API Gateway was deployed in us-east-1, and all tests were executed from the same place to minimize network latency.
Two endpoints were compared:
- Cached Route:
GET /stocks(configured with 1-minute TTL) - Non-Cached Route:
GET /stocks/{stockId}(caching explicitly disabled)
3.1 Testing the Cached Route
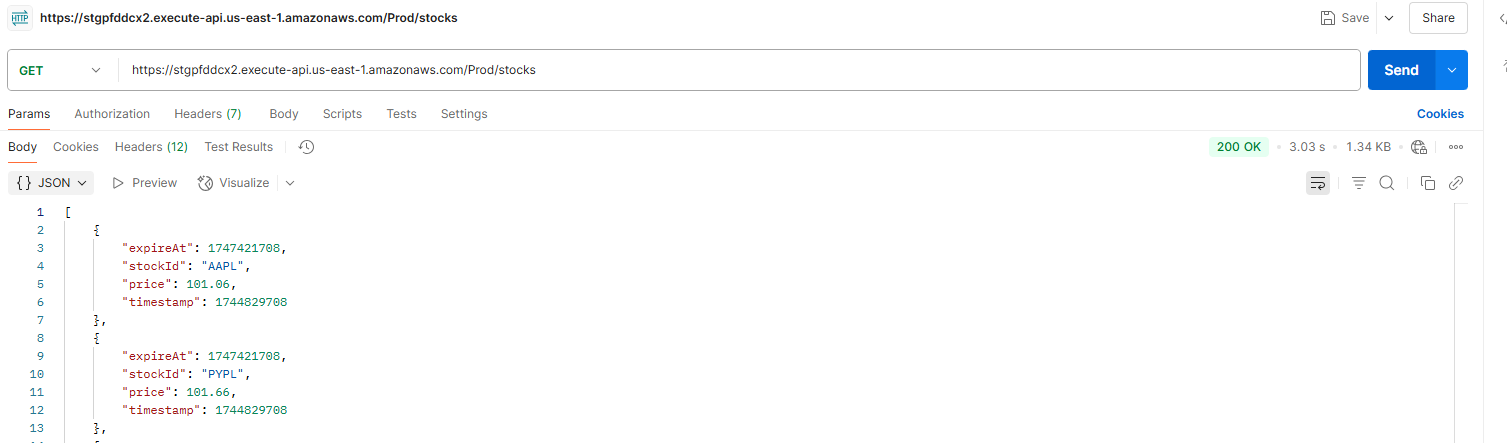
3.1.1 First Request (Cache Miss)
- Action: Send a
GETrequest to the/stocksendpoint. - Expected Behavior: Higher latency (~3.03 seconds) as API Gateway routes the request to Lambda, which queries DynamoDB; the response is then cached.
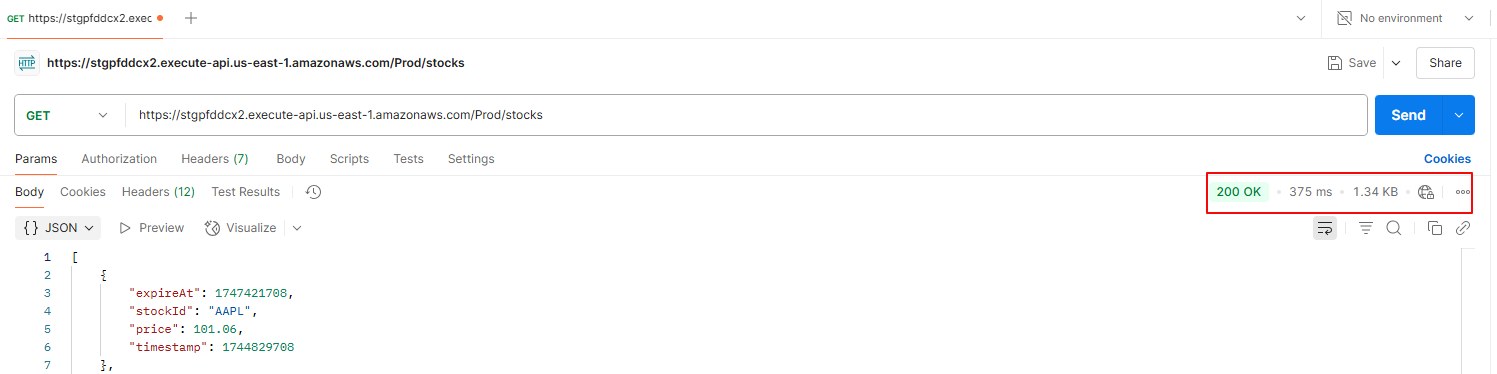
3.1.2 Subsequent Requests (Cache Hit)
- Action: Send the same
GETrequest to the/stocksagain within the 1-minute TTL period. - Expected Behavior: Much lower latency (~375 ms) as API Gateway serves the response from cache, bypassing Lambda and DynamoDB.
3.2 Testing the Non-Cached Route
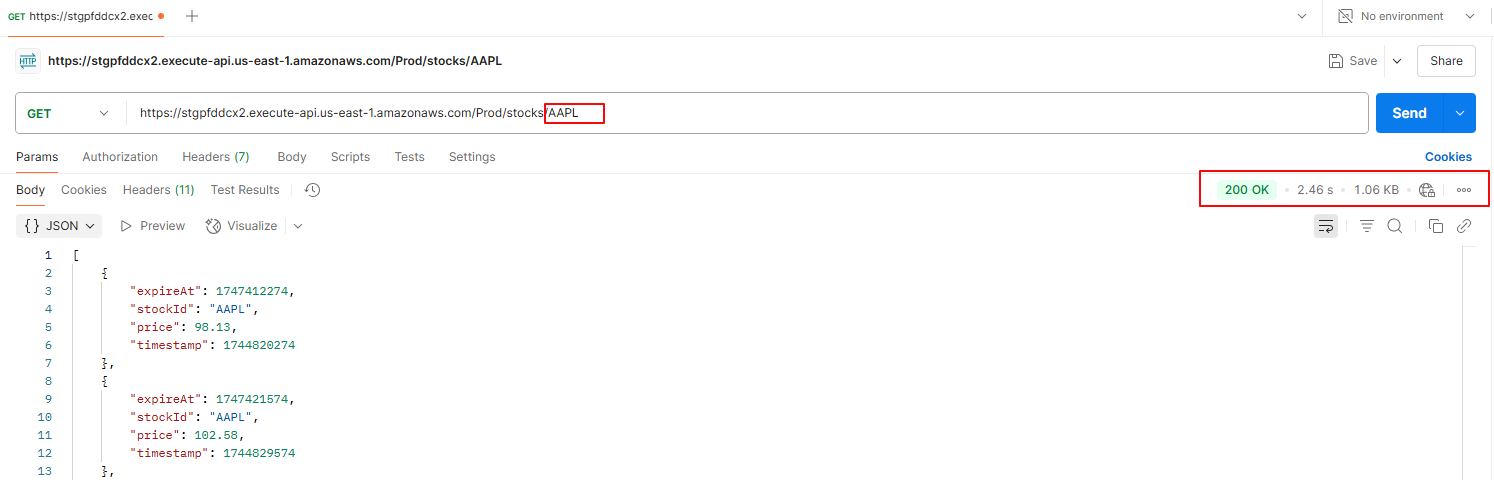
The non-cached route (GET /stocks/{stockId}) consistently exhibits higher latency (~2.46 seconds) because every request triggers full processing, without any caching:
- API Gateway forwards the request to Lambda.
- Lambda executes and queries DynamoDB (20–50 ms).
- Occasional Lambda cold starts add a 100–300 ms delay.
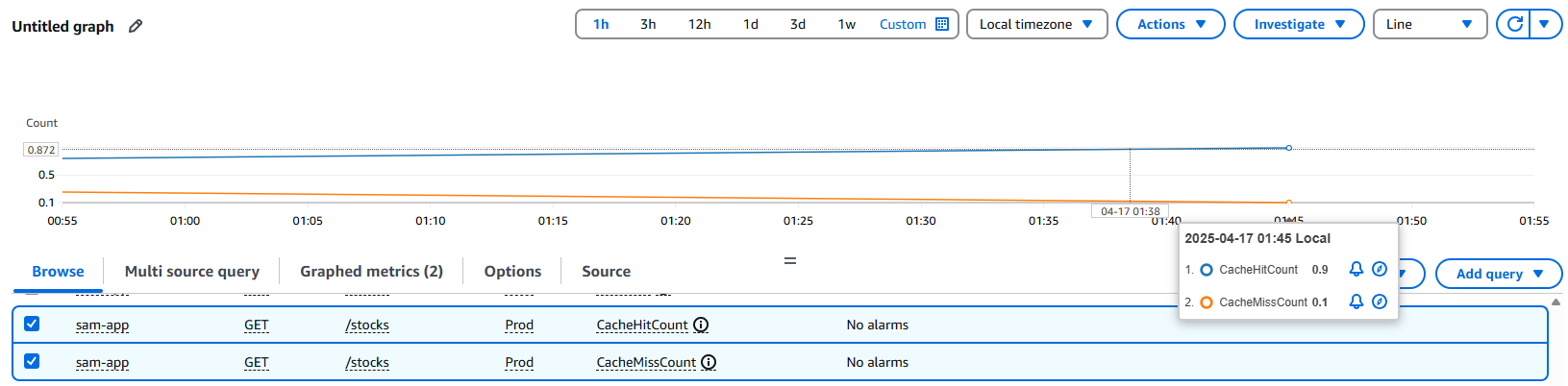
3.3 CloudWatch Cache Performance Analysis
In addition to Postman tests, CloudWatch metrics confirm real-world cache performance, showing optimal utilization with a 9:1 hit-to-miss ratio.
3.3.1 CacheHitCount (ⓐ)
- Value: 0.9 requests/second (87% of traffic)
- Implication: Most requests are served directly from the cache, reducing backend load and latency.
3.3.2 CacheMissCount (ⓑ)
- Value: 0.1 requests/second (13% of traffic)
- Implication: Occasional cache misses require full backend processing, which may slightly impact performance.
Conclusion
This guide demonstrated how to build a serverless stock market data API using AWS Lambda, DynamoDB, and API Gateway caching. Leveraging intelligent caching reduced response times from over 3 seconds to just 375 ms, while maintaining real-time data accuracy and handling millions of requests efficiently.
The serverless approach simplifies scaling, cuts costs by around 70%, and eliminates infrastructure overhead, making it a practical solution for modern stock market applications.