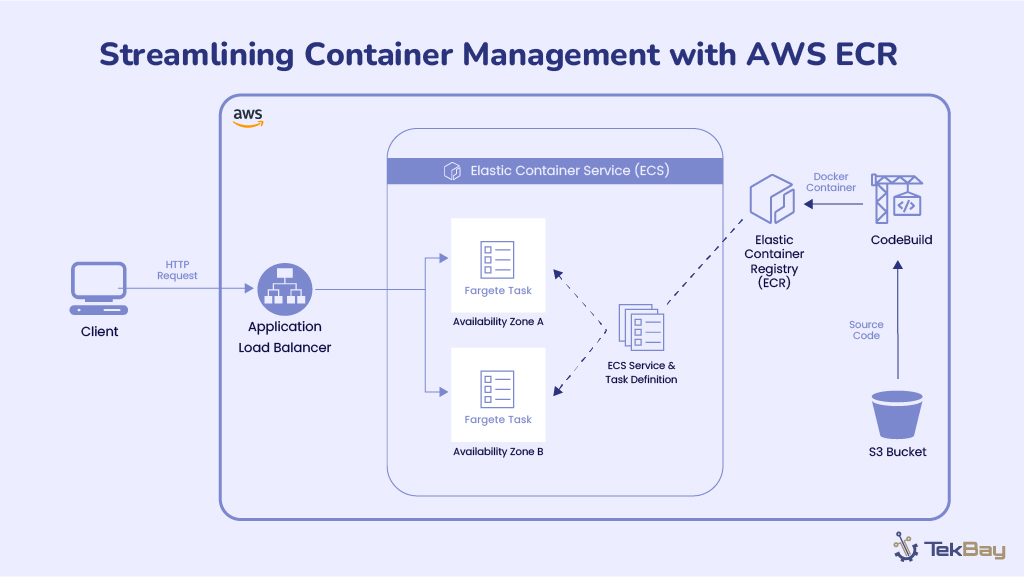
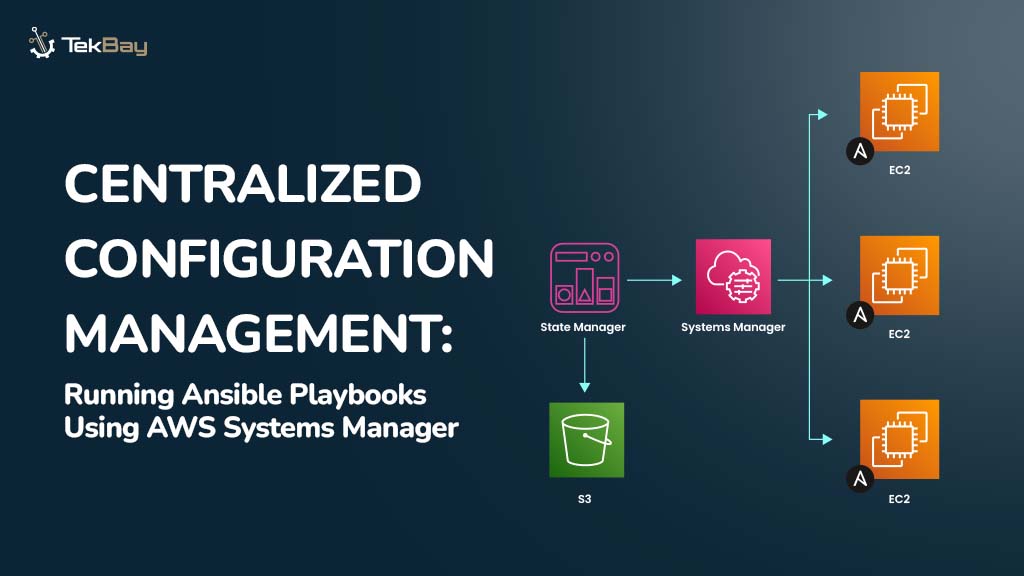
Managing containers in a cloud environment can be complex and time-consuming. The challenges are numerous, from ensuring security to handling scalability. Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a solution that simplifies container management: Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR).
Overview
As organizations increasingly use containerized applications, managing container images becomes important. AWS Elastic Container Registry (ECR) offers a seamless and scalable solution to store, manage, and deploy Docker container images. This blog explores why AWS ECR is an essential tool for container management and how to leverage its features effectively.
This blog post explores why AWS ECR is essential for modern cloud-based applications and how it can streamline container management processes.
Components of ECR
- Registry (hosts your container images in a highly available and scalable architecture.)
- Authorization Token (access to the registry that your IAM principal has access to.)
- Repository (stores container images)
- Repository Policy (manage access to the repositories and the images within them.)
- Image (file used to execute code within a Docker container.)
Features of ECR
- Lifecycle policies: You define rules that result in cleaning unused images.
- Image scanning (scan on push: each new image) helps identify software vulnerabilities in your container images.
- Cross-region and cross-account replication are configured as a registry setting on a per-region basis.
- Pull-through cache rules provide a way to cache repositories in an upstream registry in your private Amazon ECR registry.
How AWS ECR Works
Image Management:
- ECR acts as a private Docker container registry where developers can push, pull, and manage Docker images.
- Each repository in ECR can store multiple versions of an image, enabling version control and rollback capabilities.
Integration with CI/CD Pipelines:
- Developers can seamlessly integrate ECR into their CI/CD pipelines for automated building, testing, and deployment of containerized applications.
- Tools like AWS CodePipeline can automate the entire workflow from source code to production deployment.
Security and Compliance Features:
- IAM Policies: Control access to ECR repositories using IAM policies, specifying which users and roles can push, pull, or manage Docker images.
- Image Scanning: ECR integrates with Amazon ECR Public and Amazon ECR Public Gallery for scanning container images for vulnerabilities. It provides actionable insights to improve the security posture of applications.
Why choose ECR?
1. Managed Service
AWS ECR is a fully managed container registry that takes the burden off managing your infrastructure. It handles the complexities of operating a container registry, allowing you to focus on developing and deploying applications.
2. Seamless Integration with AWS Services
AWS ECR effortlessly integrates with other AWS services like Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service), Amazon EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service), and AWS Fargate. This integration ensures a smooth workflow from development to deployment, reducing operational overhead and simplifying the container management process.
3. Enhanced Security
Security is paramount when dealing with container images. AWS ECR provides built-in security features such as:
- Image Scanning: Automatically scan images for vulnerabilities to ensure they are secure before deployment.
- Encryption at Rest: Use AWS Key Management Service (KMS) to encrypt images stored in the registry.
- IAM Roles: Leverage Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles and policies to control access to your repositories, ensuring only authorized users can push or pull images.
4. Scalability and High Availability
AWS ECR automatically scales to handle many images and requests, providing high availability and reliability. This scalability ensures that your container operations run smoothly regardless of the workload size.
5. Cost-Effective
AWS ECR operates on a pay-as-you-go model, meaning you only pay for the storage and data transfer you use. There are no upfront costs or long-term commitments, making it a cost-effective choice for businesses of all sizes.
Prerequisites Before Provisioning
1. Required AWS Account and Permissions
Before provisioning an AWS ECR repository, you need an active AWS account with the necessary permissions. Ensure that your IAM user or role has the permissions to create and manage ECR repositories.
2. Setting Up the AWS Management Console
To begin provisioning ECR, log in to the AWS Management Console. Familiarize yourself with the layout and navigation, as you will be using the console extensively throughout this guide.
3. Understanding IAM Roles and Policies
IAM (Identity and Access Management) roles and policies are essential for controlling access to your ECR repositories. Ensure you have set up appropriate IAM roles with policies granting the necessary permissions for managing ECR.
Provisioning AWS ECR via console
This guide provides a step-by-step walkthrough of provisioning AWS ECR via the AWS Management Console. Whether you are new to AWS or an experienced user, this guide will help you understand the key features of ECR and how to use it effectively in your cloud environments.
Step 1:Navigate to the Elastic Container Registry service in the console
Start by logging into your AWS Management Console. Enter your credentials, and you will be directed to the AWS dashboard, where you can access all AWS services.
From the AWS dashboard, type “ECR” in the search bar and select “Elastic Container Registry” from the dropdown. This will take you to the ECR dashboard, where you can manage your container repositories.
The ECR dashboard provides an overview of your existing repositories, including the number of images stored and the total size of your repositories. Here, you can also create new repositories and manage existing ones.
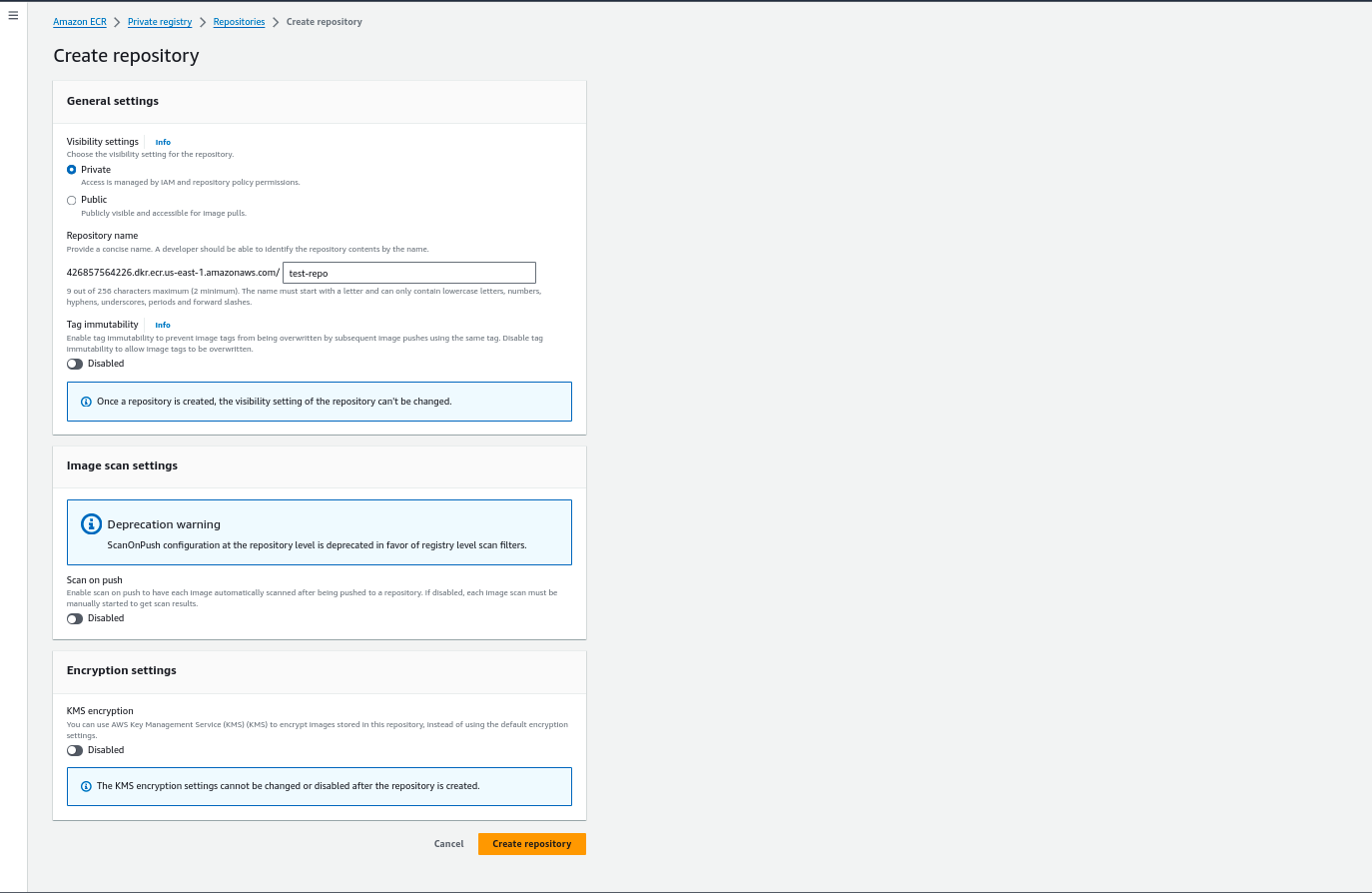
Step 2: Click on Create Repository and fill in the repository name.
Step-by-Step Guide to Repository Creation
- In the ECR dashboard, click on the “Create Repository” button.
- Enter a name for your repository.
- Choose whether the repository will be private or public.
- Optionally, configure settings, such as image tag mutability or scan on push.
Configuring Repository Settings
You can configure settings such as:
- Image Tag Mutability: Controls whether image tags can be overwritten.
- Scan on Push: Automatically scan images for vulnerabilities when pushed to the repository.
Setting Up Permissions for the Repository
Set up permissions for your repository by creating or attaching an IAM policy that defines who can push or pull images. This ensures that only authorized users can access your repository.
Step 3: Result
How to Use AWS ECR
1. Setting up an ECR Repository
Create a Repository
Creating a new repository in AWS ECR is straightforward. You can use the AWS Management Console, CLI, or SDKs. For instance, using the AWS CLI:
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name my-repo --region us-east-1Configure Repository Policies
Define repository policies to control access using IAM roles and policies. Here’s an example policy that allows a specific IAM role to push and pull images:
{
"Version": "2008-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowPushPull",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::account-id:role/role-name"
},
"Action": [
"ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer",
"ecr:BatchGetImage",
"ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability",
"ecr:PutImage",
"ecr:InitiateLayerUpload",
"ecr:UploadLayerPart",
"ecr:CompleteLayerUpload"
]
}
]
}
Pushing Images to ECR
Authenticate Docker to ECR
Authenticate your Docker client to your ECR registry using the AWS CLI:
aws ecr get-login-password --region us-east-1 | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.comTag and Push Image
Tag your Docker image and push it to your ECR repository:
docker tag my-image:latest aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my-repo:latest docker push aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my-repo:latestPulling Images from ECR
Authenticate and Pull Image
Authenticate Docker to ECR and pull the image to your local machine or deployment environment:
aws ecr get-login-password --region us-east-1 | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com docker pull aws_account_id.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/my-repo:latestIntegration with other services
- Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service): ECR stores Docker images for ECS tasks, with IAM integration for secure access control directly from task definitions.
- Amazon EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service): This service acts as a private registry for Kubernetes clusters, supporting IAM Roles for Service Accounts (IRSA) for secure image access.
- AWS CodePipeline: Automates Docker image build and deployment to ECS or EKS from ECR, enabling CI/CD workflows with versioning and tagging.
- AWS Lambda: Supports container images stored in ECR as packaging for AWS Lambda functions, facilitating event-driven execution with secure IAM roles.
- AWS IAM: Provides granular access control to ECR repositories, supporting cross-account access for secure image sharing between environments.
Conclusion
AWS ECR is a robust, secure, and scalable solution for managing container images. Its seamless integration with other AWS services and built-in security features make it ideal for modern containerized application deployments. By leveraging AWS ECR, you can focus on building and deploying your applications without worrying about the underlying registry infrastructure.